100 змінених файлів з 17896 додано та 0 видалено
BIN
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/ADC_ENOB.PNG
Переглянути файл
BIN
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/ADCdocs/ATmegaADCAccuracy.pdf
Переглянути файл
BIN
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/ADCdocs/ExcelFFT.pdf
Переглянути файл
+ 98
- 0
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/AdcErrorStudy.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,98 @@ | |||
| Static Tests of the Arduino Internal ADC. | |||
| Several people have asked about the DC accuracy of the Arduino ADC when used in my data logging applications at slow sample rates. | |||
| Here are my results of some "hobby level" measurements of the Arduino ADC. | |||
| One question is how important is the ADC clock rate. I did measurents for an ADC clock rate of 125 kHz to 2MHz. | |||
| Another question is how much does Noise Reduction Mode help. I did a series of measurements using this mode. | |||
| Noise Reduction Mode only reduced the mean absolute error slightly. | |||
| I do calibration to remove Offset Error and Gain Error. Calibration is very important for good accuracy. | |||
| These tests depend on the Arduino voltage regulator providing a stable voltage during the tests. The Arduino ADC reference voltage is Vcc for these tests. This may not be realistic for practical applications | |||
| Integral Non-linearity (INL) is the main remaining source of error. | |||
| Here are my results for static (DC) tests of the internal ADC for three UNOs. | |||
| The Arduinos are powered by a high quality nine volt power supply. | |||
| These tests measure a DC level so do not include problems due to time jitter, S/H time, and other dynamic errors. | |||
| There are several studies of the dynamic behavior of the Arduino ADC that determine ENOB (Effective Number Of Bits). | |||
| I used a shield with a 12-bit MCP4921 DAC to generate voltage levels. This ADC has an output buffer so it provides a very low impedance source. | |||
| I measured the voltage of the DAC with a calibrated 18-bit MCP3422 ADC on the shield. | |||
| I used DAC levels from 20 to 4075 to avoid zero offset errors at low voltages and DAC buffer problems at high voltages. | |||
| Each series of measurements has 4056 data points. | |||
| This is a voltage range of about 0.023 to 4.972 volts. | |||
| I calibrated the Arduino ADC for each series of measurements with a linear fit of the form. | |||
| v = a + b*adcValue | |||
| Errors are the difference between the value measured with the 18-bit ADC and the calibrated value measured with the AVR ADC. | |||
| I also show the results for no calibration, the NoCal column, using the datasheet formula. | |||
| Vin = Vref*adcValue/1024 | |||
| The rows in the tables tables are. | |||
| Min - minimum error in millivolts | |||
| Max - maximum error in millivolts | |||
| MAE - mean absolute error in millivolts | |||
| The columns in the tables are: | |||
| Ideal - results for a perfect 10-bit ADC for comparison. | |||
| NoCal - datasheet formula (5/1024)*adcValue with Noise Reduction Mode. | |||
| NR128 - Noise Reduction mode with Prescaler of 128 (ADC clock of 125 kHz). | |||
| PS128 - analogRead with Prescaler of 128 (ADC clock of 125 kHz). | |||
| PS64 - analogRead with Prescaler of 64 (ADC clock of 250 kHz). | |||
| PS32 - analogRead with Prescaler of 32 (ADC clock of 500 kHz). | |||
| PS16 - analogRead with Prescaler of 16 (ADC clock of 1 MHz). | |||
| PS8 - analogRead with Prescaler of 8 (ADC clock of 2 MHz). | |||
| Results for three UNO Arduinos | |||
| First Arduino - Error Millivolts | |||
| Ideal NoCal NR128 PS128 PS64 PS32 PS16 PS8 | |||
| Min -2.44 -2.43 -3.72 -4.01 -3.88 -4.53 -6.57 -27.18 | |||
| Max 2.44 11.69 3.74 4.24 4.15 5.17 8.69 23.21 | |||
| MAE 1.22 5.02 1.33 1.38 1.37 1.44 1.96 4.11 | |||
| Second Arduino - Error Millivolts | |||
| Ideal NoCal NR128 PS128 PS64 PS32 PS16 PS8 | |||
| Min -2.44 -9.24 -4.87 -4.86 -5.05 -5.34 -6.52 -24.04 | |||
| Max 2.44 11.62 3.95 4.64 4.69 5.71 8.41 21.29 | |||
| MAE 1.22 5.33 1.41 1.43 1.44 1.53 2.02 4.05 | |||
| Third Arduino - Error Millivolts | |||
| Ideal NoCal NR128 PS128 PS64 PS32 PS16 PS8 | |||
| Min -2.44 -7.88 -4.12 -4.40 -4.32 -4.41 -6.97 -26.93 | |||
| Max 2.44 12.53 3.80 4.04 4.18 5.27 8.84 24.59 | |||
| MAE 1.22 4.85 1.29 1.33 1.34 1.42 1.91 4.10 | |||
BIN
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/DATA.png
Переглянути файл
BIN
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/FFT.png
Переглянути файл
+ 21
- 0
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/RateTable.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,21 @@ | |||
| Maximum Sample Rate Table | |||
| ADC clock kHz | |||
| 125 250 500 1000 | |||
| pins | |||
| 1 7692 14286 25000 40000 | |||
| 2 3810 6667 11111 16667 | |||
| 3 2572 4790 8421 13559 | |||
| 4 1942 3636 6452 10526 | |||
| 5 1559 2930 5229 8602 | |||
| 6 1303 2454 4396 7273 | |||
| 7 1119 2111 3791 6299 | |||
| 8 980 1852 3333 5556 | |||
| 9 872 1649 2974 4969 | |||
| 10 786 1487 2685 4494 | |||
| 11 715 1354 2446 4103 | |||
| 12 656 1242 2247 3774 | |||
| 13 606 1148 2078 3493 | |||
| 14 563 1067 1932 3252 | |||
| 15 525 996 1806 3042 | |||
| 16 493 935 1695 2857 | |||
+ 39
- 0
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/bintocsv/AnalogBinLogger.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,39 @@ | |||
| #ifndef AnalogBinLogger_h | |||
| #define AnalogBinLogger_h | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // First block of file. | |||
| struct metadata_t { | |||
| unsigned long adcFrequency; // ADC clock frequency | |||
| unsigned long cpuFrequency; // CPU clock frequency | |||
| unsigned long sampleInterval; // Sample interval in CPU cycles. | |||
| unsigned long recordEightBits; // Size of ADC values, nonzero for 8-bits. | |||
| unsigned long pinCount; // Number of analog pins in a sample. | |||
| unsigned long pinNumber[123]; // List of pin numbers in a sample. | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Data block for 8-bit ADC mode. | |||
| const size_t DATA_DIM8 = 508; | |||
| struct block8_t { | |||
| unsigned short count; // count of data bytes | |||
| unsigned short overrun; // count of overruns since last block | |||
| unsigned char data[DATA_DIM8]; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Data block for 10-bit ADC mode. | |||
| const size_t DATA_DIM16 = 254; | |||
| struct block16_t { | |||
| unsigned short count; // count of data bytes | |||
| unsigned short overrun; // count of overruns since last block | |||
| unsigned short data[DATA_DIM16]; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Data block for PC use | |||
| struct adcdata_t { | |||
| unsigned short count; // count of data bytes | |||
| unsigned short overrun; // count of overruns since last block | |||
| union { | |||
| unsigned char u8[DATA_DIM8]; | |||
| unsigned short u16[DATA_DIM16]; | |||
| } data; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // AnalogBinLogger_h | |||
+ 82
- 0
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/bintocsv/bintocsv.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,82 @@ | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #include "AnalogBinLogger.h" | |||
| FILE *source; | |||
| FILE *destination; | |||
| int count = 0; | |||
| int main(int argc, char** argv) { | |||
| metadata_t meta; | |||
| adcdata_t adc; | |||
| // Make sure no padding/size problems. | |||
| if (sizeof(meta) != 512 || sizeof(adc) != 512) { | |||
| printf("block size error\n"); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| if (argc != 3) { | |||
| printf("missing arguments:\n"); | |||
| printf("%s binFile csvFile\n", argv[0]); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| source = fopen(argv[1], "rb"); | |||
| if (!source) { | |||
| printf("open failed for %s\n", argv[1]); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| if (fread(&meta, sizeof(meta), 1, source) != 1) { | |||
| printf("read meta data failed\n"); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| if ( meta.pinCount == 0 | |||
| || meta.pinCount > (sizeof(meta.pinNumber)/sizeof(meta.pinNumber[0])) | |||
| || meta.adcFrequency < 50000 || meta.adcFrequency > 4000000) { | |||
| printf("Invalid meta data\n"); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| destination = fopen(argv[2], "w"); | |||
| if (!destination) { | |||
| printf("open failed for %s\n", argv[2]); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| int pinCount = meta.pinCount; | |||
| printf("pinCount: %d\n", pinCount); | |||
| printf("Sample pins:"); | |||
| for (unsigned i = 0; i < meta.pinCount; i++) { | |||
| printf(" %d", meta.pinNumber[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| printf("\n"); | |||
| printf("ADC clock rate: %g kHz\n", 0.001*meta.adcFrequency); | |||
| float sampleInterval = (float)meta.sampleInterval/(float)meta.cpuFrequency; | |||
| printf("Sample rate: %g per sec\n", 1.0/sampleInterval); | |||
| printf("Sample interval: %.4f usec\n", 1.0e6*sampleInterval); | |||
| fprintf(destination, "Interval,%.4f,usec\n", 1.0e6*sampleInterval); | |||
| // Write header with pin numbers | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < ((int)meta.pinCount - 1); i++) { | |||
| fprintf(destination, "pin%d,", meta.pinNumber[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| fprintf(destination, "pin%d\n", meta.pinNumber[meta.pinCount - 1]); | |||
| unsigned maxCount = meta.recordEightBits ? DATA_DIM8 : DATA_DIM16; | |||
| while (!feof(source)) { | |||
| if (fread(&adc, sizeof(adc), 1, source) != 1) break; | |||
| if (adc.count > maxCount) { | |||
| printf("****Invalid data block****\n"); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| if (adc.overrun) { | |||
| fprintf(destination, "Overruns,%d\n", adc.overrun); | |||
| } | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < adc.count; i++) { | |||
| unsigned value = meta.recordEightBits ? adc.data.u8[i] : adc.data.u16[i]; | |||
| if ((i + 1)%pinCount) { | |||
| fprintf(destination, "%d,", value); | |||
| } else { | |||
| fprintf(destination, "%d\n", value); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| count += adc.count; | |||
| } | |||
| printf("%d ADC values read\n", count); | |||
| fclose(source); | |||
| fclose(destination); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
BIN
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/bintocsv/bintocsv.exe
Переглянути файл
+ 96
- 0
AnalogBinLoggerExtras/readme.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,96 @@ | |||
| AnalogBinLogger.ino logs analog data to a binary SD file at high rates. | |||
| Samples are logged at regular intervals by using timer1. Timer/Counter1 | |||
| Compare Match B is used to trigger the ADC for the first pin in a sample. | |||
| The ADC is triggered for remaining sample pins in the ADC conversion complete | |||
| interrupt routine. | |||
| Data is captured in the ADC interrupt routine and saved in 512 byte buffers. | |||
| Buffered data is written to the SD in a function called from loop(). The | |||
| entire data set is written to a large contiguous file as a single multi-block | |||
| write. This reduces write latency problems. | |||
| Many inexpensive SD cards work well at lower rates. I used a $6.00 | |||
| SanDisk 4 GB class 4 card for testing. | |||
| SanDisk class 4 cards work well at fairly high rates. I used the 4 GB SanDisk | |||
| card to log a single pin at 40,000 samples per second. | |||
| You may need to increase the time between samples if your card has higher | |||
| latency. Using a Mega Arduino can help since it has more buffering. | |||
| The bintocsv folder contains a PC program for converting binary files to | |||
| CSV files. I have included a executable for Windows. Linux and Mac users | |||
| can build from the included source files. bintocvs is a command line program. | |||
| bintocsv binFile csvFile | |||
| AnalogBinLogger requires a recent version of the SdFat library. The SdFat | |||
| folder contains a beta version I used for development. | |||
| The latest stable version is here: | |||
| http://code.google.com/p/sdfatlib/downloads/list | |||
| You also need to install the included BufferedWriter library. It provides | |||
| fast text formatting. | |||
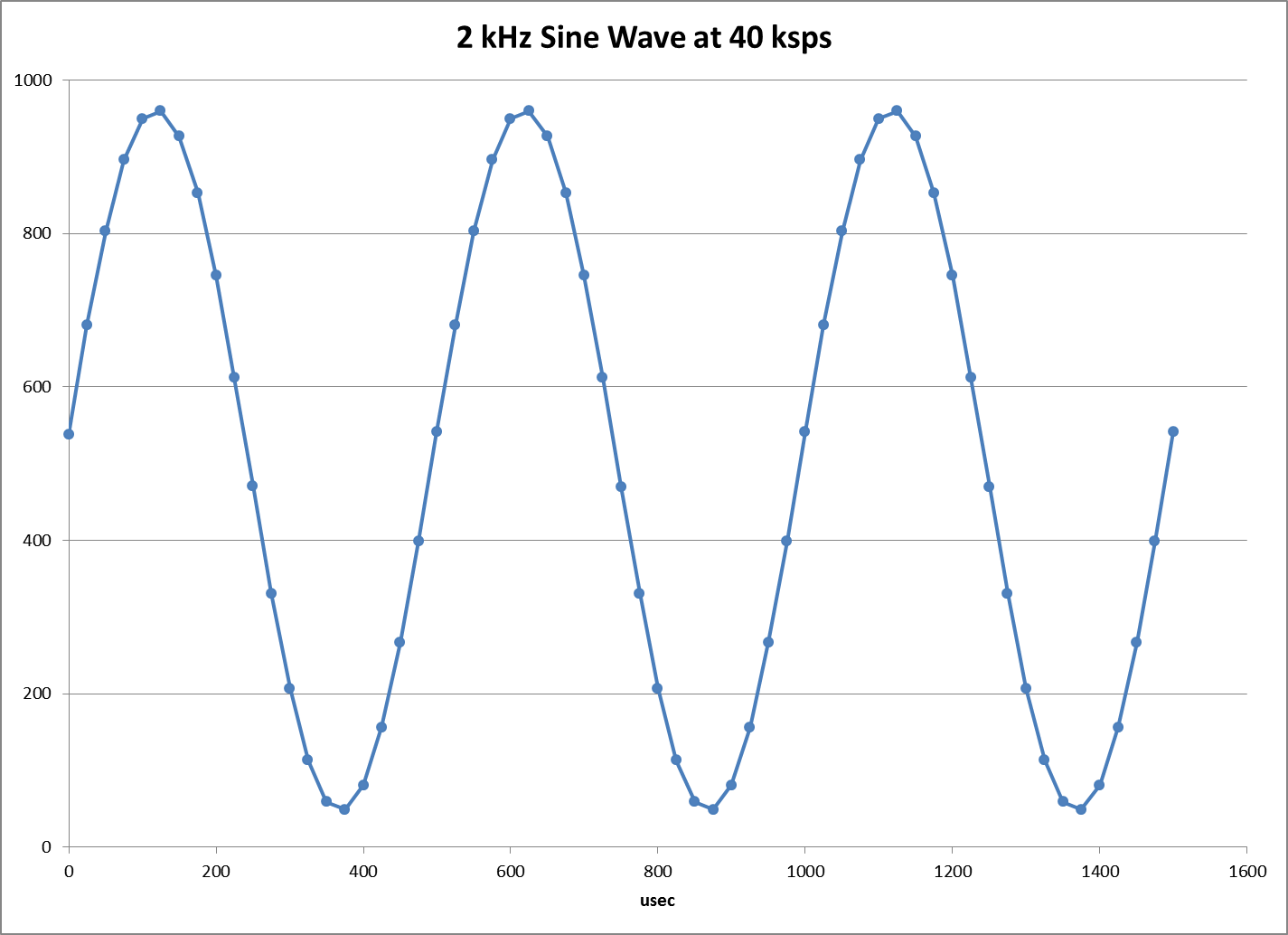
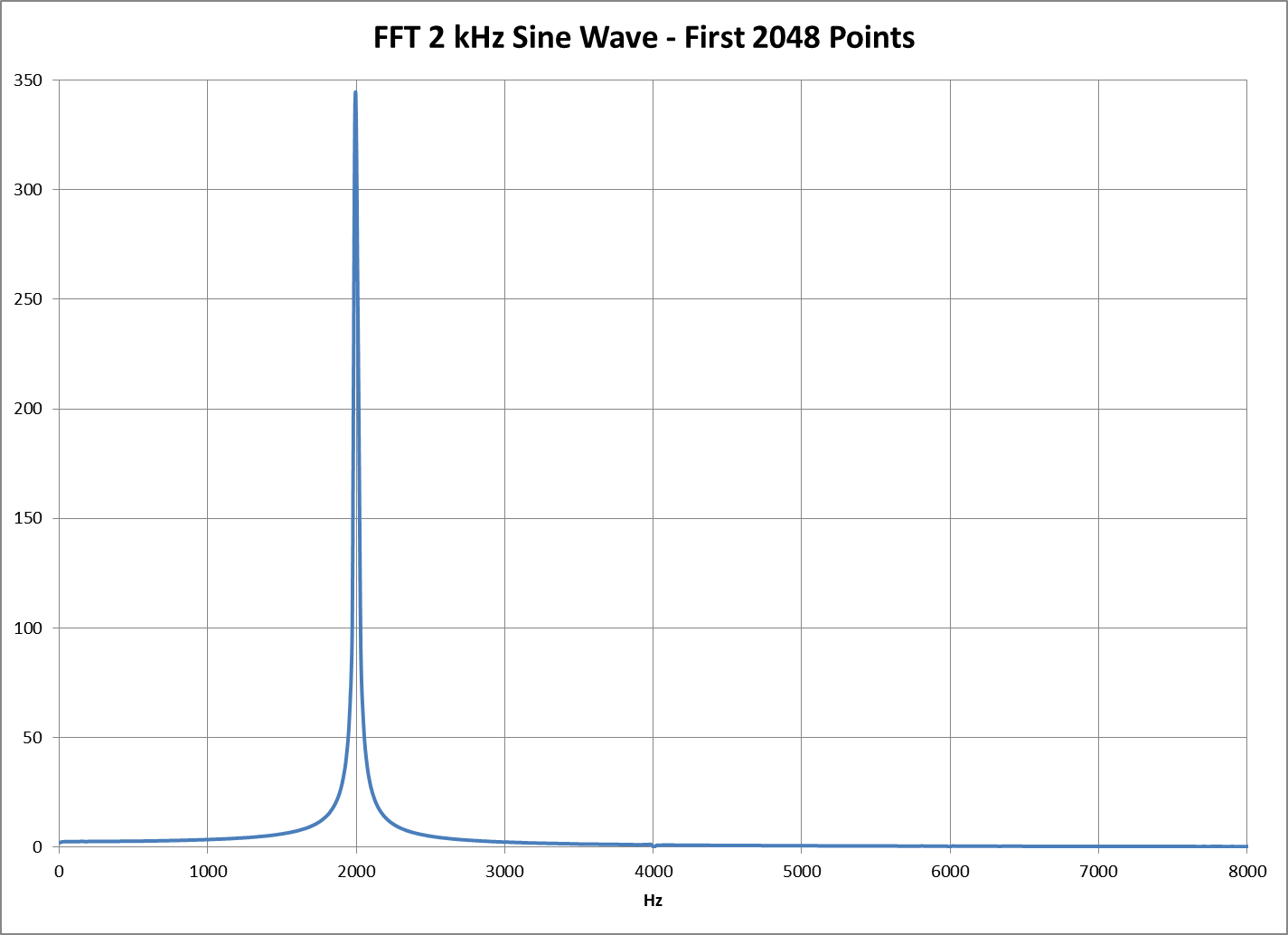
| Example data for a 2 kHz sine wave logged at 40,000 samples per second is | |||
| shown in DATA.PNG and FFT.PNG shows a FFT of the data. See ExcelFFT.pdf | |||
| in the ADCdocs folder for details on calculating a FFT. | |||
| The accuracy of the ADC samples depends on the ADC clock rate. See the | |||
| ADC_ENOB.PNG file for a plot of accuracy vs ADC clock frequency. | |||
| See files in the ADCdocs folder for more information on ADC accuracy. | |||
| To modify this program you will need a good knowledge of the Arduino | |||
| ADC, timer1 and C++ programming. This is not for the newbie. | |||
| I have an LED and resistor connected to pin 3 to signal fatal errors and | |||
| data overruns. Fatal errors are indicated by a blinking led. Overrun errors | |||
| are indicated by a solid lit led. The count of samples dropped is written | |||
| to the SD and data logging continues. | |||
| You can disable the error led feature by setting the error pin number negative: | |||
| To use AnalogBinLogger, install these items. | |||
| Place the BufferWriter and SdFat folders in your sketchbook libraries folder. | |||
| Place the AnalogIsrLogger folder in your sketchbook folder. | |||
| You must edit the configuration constants at the beginning of the program | |||
| to set the sample pins, sample rate, and other configuration values. | |||
| Initially the program is setup to log the first five analog pins at 5000 | |||
| samples per second. Change these values to suit your needs. | |||
| See RateTable.txt for maximum allowed sample rates vs pin count and ADC clock | |||
| frequency. | |||
| The program has four commands: | |||
| c - convert file to CSV | |||
| d - dump data to Serial | |||
| e - overrun error details | |||
| r - record ADC data | |||
| All commands can be terminated by entering a character from the serial monitor. | |||
| The c command converts the current binary file to a text file. Entering a | |||
| character on the serial monitor terminates the command. | |||
| The d command converts the binary file to text and displays it on the serial | |||
| monitor. Entering a character on the serial monitor terminates the command. | |||
| The e command displays details about overruns in the current binary file. | |||
| Data overruns happen when data samples are lost due to long write latency | |||
| of the SD. | |||
| The r command will record ADC data to a binary file. It will terminate | |||
| when a character is entered on the serial monitor or the the maximum file | |||
| block count has been reached. | |||
| A number of program options can be set by changing constants at the beginning | |||
| of the program. | |||
+ 62
- 0
ArduinoDue.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,62 @@ | |||
| Support has been added for the Arduino Due. | |||
| You must connect your SD socket to the 6-pin "ISP connector". You must have short | |||
| wires or a custom shield to run at full speed, 42 MHz. | |||
| If you have problems use a lower SPI speed. You can also check for SPI | |||
| errors by editing SdFatCobfig.h to enable CRC checking. | |||
| You should be be able to use any digital pin for SD chip select. The default | |||
| pin is SS which is pin 10 for Due. | |||
| The default SPI rate is 42 MHz. You can set SD chip select and the SPI rate | |||
| by calling: | |||
| bool SdFat::begin(uint8_t chipSelectPin, uint8_t spiRateID); | |||
| The second argument, spiRateID, sets the SCK rate and can be these symbols: | |||
| SPI_FULL_SPEED - 42 MHz | |||
| SPI_DIV3_SPEED - 28 MHz | |||
| SPI_HALF_SPEED - 21 MHz | |||
| SPI_DIV6_SPEED - 14 MHz | |||
| SPI_QUARTER_SPEED 10.5 MHz | |||
| SPI_EIGHTH_SPEED 5.25 MHz | |||
| Large reads and writes use fast multi-block SD read/write commands. For optimal | |||
| speed, use records that are a multiple of 512 bytes. | |||
| Run the bench.ino example to explore large read/write speed. | |||
| Replace this line: | |||
| #define BUF_SIZE 100 | |||
| With a large size like this: | |||
| #define BUF_SIZE 8192 | |||
| For best results the record size should be a power of two (512, 1024, 2048, | |||
| 4096, 8192). In this case records will be aligned with FAT cluster boundaries. | |||
| Since Due is fast, increase the test file size by editing this line: | |||
| #define FILE_SIZE_MB 5 | |||
| Run the PrintBenchmark.ino example to compare text formatting speed of Due | |||
| with AVR boards. | |||
| A number of options are available to configure SPI for the Due board. | |||
| You can use the standard SPI.h library by editing SdFatConfig.h and set | |||
| USE_ARDUINO_SPI_LIBRARY nonzero. You must include SPI.h in your sketch. | |||
| Several options can be set in Sd2Card.cpp in the USE_NATIVE_SAM3X_SPI | |||
| section. These include USE_SAM3X_DMAC to control use of DMA and | |||
| USE_SAM3X_BUS_MATRIX_FIX to change Bus Matrix operation. Most people | |||
| will not need to change these. | |||
+ 13
- 0
MultipleCards.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ | |||
| SdFat has support for multiple SD cards. This requires multiple instances | |||
| of SdFat objects. | |||
| You must edit SdFatConfig.h to enable multiple instances of SdFat. Set | |||
| USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS nonzero like this: | |||
| #define USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS 1 | |||
| Look at TwoCards.pde in the SdFat/examples folder. This example demonstrates | |||
| use of two SD cards. | |||
| Read WorkingDirectory.txt for more information on volume working | |||
| directories and the current working directory. | |||
+ 21
- 0
QuickStart.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,21 @@ | |||
| For those who don't like too much documentation. | |||
| To use this library place the SdFat folder into the libraries | |||
| subfolder in your main sketches folder. You may need to | |||
| create the libraries folder. Restart the Arduino IDE if | |||
| it was open. | |||
| Run the QuickStart.ino sketch from the | |||
| libraries/SdFat/examples/QuickStart folder. Click the | |||
| IDE up-arrow icon then -> libraries -> SdFat -> QuickStart. | |||
| You can also click File -> Examples -> SdFat -> QuickStart. | |||
| If problems occur try reading more documentation and use these | |||
| forums for help: | |||
| http://forums.adafruit.com/ | |||
| http://arduino.cc/forum/ | |||
| If QuickStart.ino runs successfully try more examples. | |||
+ 23
- 0
SPI_Transactions.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,23 @@ | |||
| To enable support for SPI transactions, edit SfFatCinfig.h and modify these | |||
| defines. | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION nonzero to enable the SPI transaction feature | |||
| * of the standard Arduino SPI library. You must include SPI.h in your | |||
| * sketches when ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION is nonzero. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set ENABLE_SPI_YIELD nonzero to enable release of the SPI bus during | |||
| * SD card busy waits. | |||
| * | |||
| * This will allow interrupt routines to access the SPI bus if | |||
| * ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION is nonzero. | |||
| * | |||
| * Setting ENABLE_SPI_YIELD will introduce some extra overhead and will | |||
| * slightly slow transfer rates. A few older SD cards may fail when | |||
| * ENABLE_SPI_YIELD is nonzero. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define ENABLE_SPI_YIELD 0 | |||
+ 10
- 0
SdFat.html
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,10 @@ | |||
| <html> | |||
| <head> | |||
| <title>A web page that points a browser to a different page</title> | |||
| <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0; URL=html/index.html"> | |||
| <meta name="keywords" content="automatic redirection"> | |||
| </head> | |||
| <body> | |||
| Your browser didn't automatically redirect. Open html/index.html manually. | |||
| </body> | |||
| </html> | |||
+ 119
- 0
SdFat/ArduinoStream.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,119 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef ArduinoStream_h | |||
| #define ArduinoStream_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief ArduinoInStream and ArduinoOutStream classes | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <bufstream.h> | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ArduinoInStream | |||
| * \brief Input stream for Arduino Stream objects | |||
| */ | |||
| class ArduinoInStream : public ibufstream { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** | |||
| * Constructor | |||
| * \param[in] hws hardware stream | |||
| * \param[in] buf buffer for input line | |||
| * \param[in] size size of input buffer | |||
| */ | |||
| ArduinoInStream(Stream &hws, char* buf, size_t size) { | |||
| m_hw = &hws; | |||
| m_line = buf; | |||
| m_size = size; | |||
| } | |||
| /** read a line. */ | |||
| void readline() { | |||
| size_t i = 0; | |||
| uint32_t t; | |||
| m_line[0] = '\0'; | |||
| while (!m_hw->available()) {} | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| t = millis(); | |||
| while (!m_hw->available()) { | |||
| if ((millis() - t) > 10) goto done; | |||
| } | |||
| if (i >= (m_size - 1)) { | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| m_line[i++] = m_hw->read(); | |||
| m_line[i] = '\0'; | |||
| } | |||
| done: | |||
| init(m_line); | |||
| } | |||
| protected: | |||
| /** Internal - do not use. | |||
| * \param[in] off | |||
| * \param[in] way | |||
| * \return true/false. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) {return false;} | |||
| /** Internal - do not use. | |||
| * \param[in] pos | |||
| * \return true/false. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos) {return false;} | |||
| private: | |||
| char *m_line; | |||
| size_t m_size; | |||
| Stream* m_hw; | |||
| }; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ArduinoOutStream | |||
| * \brief Output stream for Arduino Print objects | |||
| */ | |||
| class ArduinoOutStream : public ostream { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** constructor | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print object for this ArduinoOutStream. | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit ArduinoOutStream(Print& pr) : m_pr(&pr) {} | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| /** | |||
| * Internal do not use | |||
| * \param[in] c | |||
| */ | |||
| void putch(char c) { | |||
| if (c == '\n') m_pr->write('\r'); | |||
| m_pr->write(c); | |||
| } | |||
| void putstr(const char* str) {m_pr->write(str);} | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) {return false;} | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos) {return false;} | |||
| bool sync() {return true;} | |||
| pos_type tellpos() {return 0;} | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| private: | |||
| ArduinoOutStream() {} | |||
| Print* m_pr; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // ArduinoStream_h | |||
+ 71
- 0
SdFat/MinimumSerial.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,71 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| #if defined(UDR0) || defined(DOXYGEN) | |||
| #include <MinimumSerial.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set baud rate for serial port zero and enable in non interrupt mode. | |||
| * Do not call this function if you use another serial library. | |||
| * \param[in] baud rate | |||
| */ | |||
| void MinimumSerial::begin(uint32_t baud) { | |||
| uint16_t baud_setting; | |||
| // don't worry, the compiler will squeeze out F_CPU != 16000000UL | |||
| if (F_CPU != 16000000UL || baud != 57600) { | |||
| // Double the USART Transmission Speed | |||
| UCSR0A = 1 << U2X0; | |||
| baud_setting = (F_CPU / 4 / baud - 1) / 2; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // hardcoded exception for compatibility with the bootloader shipped | |||
| // with the Duemilanove and previous boards and the firmware on the 8U2 | |||
| // on the Uno and Mega 2560. | |||
| UCSR0A = 0; | |||
| baud_setting = (F_CPU / 8 / baud - 1) / 2; | |||
| } | |||
| // assign the baud_setting | |||
| UBRR0H = baud_setting >> 8; | |||
| UBRR0L = baud_setting; | |||
| // enable transmit and receive | |||
| UCSR0B |= (1 << TXEN0) | (1 << RXEN0); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Unbuffered read | |||
| * \return -1 if no character is available or an available character. | |||
| */ | |||
| int MinimumSerial::read() { | |||
| if (UCSR0A & (1 << RXC0)) return UDR0; | |||
| return -1; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Unbuffered write | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] b byte to write. | |||
| * \return 1 | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t MinimumSerial::write(uint8_t b) { | |||
| while (((1 << UDRIE0) & UCSR0B) || !(UCSR0A & (1 << UDRE0))) {} | |||
| UDR0 = b; | |||
| return 1; | |||
| } | |||
| MinimumSerial MiniSerial; | |||
| #endif // defined(UDR0) || defined(DOXYGEN) | |||
+ 36
- 0
SdFat/MinimumSerial.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,36 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef MinimumSerial_h | |||
| #define MinimumSerial_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class MinimumSerial | |||
| * \brief mini serial class for the %SdFat library. | |||
| */ | |||
| class MinimumSerial : public Print { | |||
| public: | |||
| void begin(uint32_t baud); | |||
| int read(); | |||
| size_t write(uint8_t b); | |||
| using Print::write; | |||
| }; | |||
| #ifdef UDR0 | |||
| extern MinimumSerial MiniSerial; | |||
| #endif // UDR0 | |||
| #endif // MinimumSerial_h | |||
+ 649
- 0
SdFat/Sd2Card.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,649 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino Sd2Card Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino Sd2Card Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino Sd2Card Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <Sd2Card.h> | |||
| #include <SdSpi.h> | |||
| #if !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION | |||
| #include <SPI.h> | |||
| #endif // !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && defined(SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION) | |||
| // debug trace macro | |||
| #define SD_TRACE(m, b) | |||
| // #define SD_TRACE(m, b) Serial.print(m);Serial.println(b); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| SdSpi Sd2Card::m_spi; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| #if USE_SD_CRC | |||
| // CRC functions | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| static uint8_t CRC7(const uint8_t* data, uint8_t n) { | |||
| uint8_t crc = 0; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| uint8_t d = data[i]; | |||
| for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; j++) { | |||
| crc <<= 1; | |||
| if ((d & 0x80) ^ (crc & 0x80)) crc ^= 0x09; | |||
| d <<= 1; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return (crc << 1) | 1; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #if USE_SD_CRC == 1 | |||
| // slower CRC-CCITT | |||
| // uses the x^16,x^12,x^5,x^1 polynomial. | |||
| static uint16_t CRC_CCITT(const uint8_t *data, size_t n) { | |||
| uint16_t crc = 0; | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| crc = (uint8_t)(crc >> 8) | (crc << 8); | |||
| crc ^= data[i]; | |||
| crc ^= (uint8_t)(crc & 0xff) >> 4; | |||
| crc ^= crc << 12; | |||
| crc ^= (crc & 0xff) << 5; | |||
| } | |||
| return crc; | |||
| } | |||
| #elif USE_SD_CRC > 1 // CRC_CCITT | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // faster CRC-CCITT | |||
| // uses the x^16,x^12,x^5,x^1 polynomial. | |||
| #ifdef __AVR__ | |||
| static const uint16_t crctab[] PROGMEM = { | |||
| #else // __AVR__ | |||
| static const uint16_t crctab[] = { | |||
| #endif // __AVR__ | |||
| 0x0000, 0x1021, 0x2042, 0x3063, 0x4084, 0x50A5, 0x60C6, 0x70E7, | |||
| 0x8108, 0x9129, 0xA14A, 0xB16B, 0xC18C, 0xD1AD, 0xE1CE, 0xF1EF, | |||
| 0x1231, 0x0210, 0x3273, 0x2252, 0x52B5, 0x4294, 0x72F7, 0x62D6, | |||
| 0x9339, 0x8318, 0xB37B, 0xA35A, 0xD3BD, 0xC39C, 0xF3FF, 0xE3DE, | |||
| 0x2462, 0x3443, 0x0420, 0x1401, 0x64E6, 0x74C7, 0x44A4, 0x5485, | |||
| 0xA56A, 0xB54B, 0x8528, 0x9509, 0xE5EE, 0xF5CF, 0xC5AC, 0xD58D, | |||
| 0x3653, 0x2672, 0x1611, 0x0630, 0x76D7, 0x66F6, 0x5695, 0x46B4, | |||
| 0xB75B, 0xA77A, 0x9719, 0x8738, 0xF7DF, 0xE7FE, 0xD79D, 0xC7BC, | |||
| 0x48C4, 0x58E5, 0x6886, 0x78A7, 0x0840, 0x1861, 0x2802, 0x3823, | |||
| 0xC9CC, 0xD9ED, 0xE98E, 0xF9AF, 0x8948, 0x9969, 0xA90A, 0xB92B, | |||
| 0x5AF5, 0x4AD4, 0x7AB7, 0x6A96, 0x1A71, 0x0A50, 0x3A33, 0x2A12, | |||
| 0xDBFD, 0xCBDC, 0xFBBF, 0xEB9E, 0x9B79, 0x8B58, 0xBB3B, 0xAB1A, | |||
| 0x6CA6, 0x7C87, 0x4CE4, 0x5CC5, 0x2C22, 0x3C03, 0x0C60, 0x1C41, | |||
| 0xEDAE, 0xFD8F, 0xCDEC, 0xDDCD, 0xAD2A, 0xBD0B, 0x8D68, 0x9D49, | |||
| 0x7E97, 0x6EB6, 0x5ED5, 0x4EF4, 0x3E13, 0x2E32, 0x1E51, 0x0E70, | |||
| 0xFF9F, 0xEFBE, 0xDFDD, 0xCFFC, 0xBF1B, 0xAF3A, 0x9F59, 0x8F78, | |||
| 0x9188, 0x81A9, 0xB1CA, 0xA1EB, 0xD10C, 0xC12D, 0xF14E, 0xE16F, | |||
| 0x1080, 0x00A1, 0x30C2, 0x20E3, 0x5004, 0x4025, 0x7046, 0x6067, | |||
| 0x83B9, 0x9398, 0xA3FB, 0xB3DA, 0xC33D, 0xD31C, 0xE37F, 0xF35E, | |||
| 0x02B1, 0x1290, 0x22F3, 0x32D2, 0x4235, 0x5214, 0x6277, 0x7256, | |||
| 0xB5EA, 0xA5CB, 0x95A8, 0x8589, 0xF56E, 0xE54F, 0xD52C, 0xC50D, | |||
| 0x34E2, 0x24C3, 0x14A0, 0x0481, 0x7466, 0x6447, 0x5424, 0x4405, | |||
| 0xA7DB, 0xB7FA, 0x8799, 0x97B8, 0xE75F, 0xF77E, 0xC71D, 0xD73C, | |||
| 0x26D3, 0x36F2, 0x0691, 0x16B0, 0x6657, 0x7676, 0x4615, 0x5634, | |||
| 0xD94C, 0xC96D, 0xF90E, 0xE92F, 0x99C8, 0x89E9, 0xB98A, 0xA9AB, | |||
| 0x5844, 0x4865, 0x7806, 0x6827, 0x18C0, 0x08E1, 0x3882, 0x28A3, | |||
| 0xCB7D, 0xDB5C, 0xEB3F, 0xFB1E, 0x8BF9, 0x9BD8, 0xABBB, 0xBB9A, | |||
| 0x4A75, 0x5A54, 0x6A37, 0x7A16, 0x0AF1, 0x1AD0, 0x2AB3, 0x3A92, | |||
| 0xFD2E, 0xED0F, 0xDD6C, 0xCD4D, 0xBDAA, 0xAD8B, 0x9DE8, 0x8DC9, | |||
| 0x7C26, 0x6C07, 0x5C64, 0x4C45, 0x3CA2, 0x2C83, 0x1CE0, 0x0CC1, | |||
| 0xEF1F, 0xFF3E, 0xCF5D, 0xDF7C, 0xAF9B, 0xBFBA, 0x8FD9, 0x9FF8, | |||
| 0x6E17, 0x7E36, 0x4E55, 0x5E74, 0x2E93, 0x3EB2, 0x0ED1, 0x1EF0 | |||
| }; | |||
| static uint16_t CRC_CCITT(const uint8_t* data, size_t n) { | |||
| uint16_t crc = 0; | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| #ifdef __AVR__ | |||
| crc = pgm_read_word(&crctab[(crc >> 8 ^ data[i]) & 0XFF]) ^ (crc << 8); | |||
| #else // __AVR__ | |||
| crc = crctab[(crc >> 8 ^ data[i]) & 0XFF] ^ (crc << 8); | |||
| #endif // __AVR__ | |||
| } | |||
| return crc; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // CRC_CCITT | |||
| #endif // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Sd2Card member functions | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Initialize an SD flash memory card. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] chipSelectPin SD chip select pin number. | |||
| * \param[in] sckDivisor SPI SCK clock rate divisor. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. The reason for failure | |||
| * can be determined by calling errorCode() and errorData(). | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::begin(uint8_t chipSelectPin, uint8_t sckDivisor) { | |||
| m_errorCode = m_type = 0; | |||
| m_chipSelectPin = chipSelectPin; | |||
| // 16-bit init start time allows over a minute | |||
| uint16_t t0 = (uint16_t)millis(); | |||
| uint32_t arg; | |||
| pinMode(m_chipSelectPin, OUTPUT); | |||
| digitalWrite(m_chipSelectPin, HIGH); | |||
| m_spi.begin(); | |||
| // set SCK rate for initialization commands | |||
| m_sckDivisor = SPI_SCK_INIT_DIVISOR; | |||
| m_spi.init(m_sckDivisor); | |||
| // must supply min of 74 clock cycles with CS high. | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 10; i++) m_spi.send(0XFF); | |||
| // command to go idle in SPI mode | |||
| while (cardCommand(CMD0, 0) != R1_IDLE_STATE) { | |||
| if (((uint16_t)millis() - t0) > SD_INIT_TIMEOUT) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD0); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| #if USE_SD_CRC | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD59, 1) != R1_IDLE_STATE) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD59); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| // check SD version | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD8, 0x1AA) == (R1_ILLEGAL_COMMAND | R1_IDLE_STATE)) { | |||
| type(SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) m_status = m_spi.receive(); | |||
| if (m_status == 0XAA) { | |||
| type(SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (((uint16_t)millis() - t0) > SD_INIT_TIMEOUT) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD8); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // initialize card and send host supports SDHC if SD2 | |||
| arg = type() == SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2 ? 0X40000000 : 0; | |||
| while (cardAcmd(ACMD41, arg) != R1_READY_STATE) { | |||
| // check for timeout | |||
| if (((uint16_t)millis() - t0) > SD_INIT_TIMEOUT) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_ACMD41); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // if SD2 read OCR register to check for SDHC card | |||
| if (type() == SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2) { | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD58, 0)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD58); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if ((m_spi.receive() & 0XC0) == 0XC0) type(SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC); | |||
| // Discard rest of ocr - contains allowed voltage range. | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 3; i++) m_spi.receive(); | |||
| } | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| m_sckDivisor = sckDivisor; | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // send command and return error code. Return zero for OK | |||
| uint8_t Sd2Card::cardCommand(uint8_t cmd, uint32_t arg) { | |||
| // select card | |||
| chipSelectLow(); | |||
| // wait if busy | |||
| waitNotBusy(SD_WRITE_TIMEOUT); | |||
| uint8_t *pa = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t *>(&arg); | |||
| #if USE_SD_CRC | |||
| // form message | |||
| uint8_t d[6] = {cmd | 0X40, pa[3], pa[2], pa[1], pa[0]}; | |||
| // add crc | |||
| d[5] = CRC7(d, 5); | |||
| // send message | |||
| for (uint8_t k = 0; k < 6; k++) m_spi.send(d[k]); | |||
| #else // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| // send command | |||
| m_spi.send(cmd | 0x40); | |||
| // send argument | |||
| for (int8_t i = 3; i >= 0; i--) m_spi.send(pa[i]); | |||
| // send CRC - correct for CMD0 with arg zero or CMD8 with arg 0X1AA | |||
| m_spi.send(cmd == CMD0 ? 0X95 : 0X87); | |||
| #endif // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| // skip stuff byte for stop read | |||
| if (cmd == CMD12) m_spi.receive(); | |||
| // wait for response | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; ((m_status = m_spi.receive()) & 0X80) && i != 0XFF; i++) { | |||
| } | |||
| return m_status; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Determine the size of an SD flash memory card. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The number of 512 byte data blocks in the card | |||
| * or zero if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t Sd2Card::cardSize() { | |||
| csd_t csd; | |||
| if (!readCSD(&csd)) return 0; | |||
| if (csd.v1.csd_ver == 0) { | |||
| uint8_t read_bl_len = csd.v1.read_bl_len; | |||
| uint16_t c_size = (csd.v1.c_size_high << 10) | |||
| | (csd.v1.c_size_mid << 2) | csd.v1.c_size_low; | |||
| uint8_t c_size_mult = (csd.v1.c_size_mult_high << 1) | |||
| | csd.v1.c_size_mult_low; | |||
| return (uint32_t)(c_size + 1) << (c_size_mult + read_bl_len - 7); | |||
| } else if (csd.v2.csd_ver == 1) { | |||
| uint32_t c_size = 0X10000L * csd.v2.c_size_high + 0X100L | |||
| * (uint32_t)csd.v2.c_size_mid + csd.v2.c_size_low; | |||
| return (c_size + 1) << 10; | |||
| } else { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_BAD_CSD); | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void Sd2Card::spiYield() { | |||
| #if ENABLE_SPI_YIELD && !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && defined(SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION) | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| chipSelectLow(); | |||
| #endif // ENABLE_SPI_YIELD && !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && defined(SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION) | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void Sd2Card::chipSelectHigh() { | |||
| digitalWrite(m_chipSelectPin, HIGH); | |||
| // insure MISO goes high impedance | |||
| m_spi.send(0XFF); | |||
| #if !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && defined(SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION) | |||
| SPI.endTransaction(); | |||
| #endif // !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && defined(SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION) | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void Sd2Card::chipSelectLow() { | |||
| #if !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && defined(SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION) | |||
| SPI.beginTransaction(SPISettings()); | |||
| #endif // !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI && defined(SPI_HAS_TRANSACTION) | |||
| m_spi.init(m_sckDivisor); | |||
| digitalWrite(m_chipSelectPin, LOW); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Erase a range of blocks. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] firstBlock The address of the first block in the range. | |||
| * \param[in] lastBlock The address of the last block in the range. | |||
| * | |||
| * \note This function requests the SD card to do a flash erase for a | |||
| * range of blocks. The data on the card after an erase operation is | |||
| * either 0 or 1, depends on the card vendor. The card must support | |||
| * single block erase. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::erase(uint32_t firstBlock, uint32_t lastBlock) { | |||
| csd_t csd; | |||
| if (!readCSD(&csd)) goto fail; | |||
| // check for single block erase | |||
| if (!csd.v1.erase_blk_en) { | |||
| // erase size mask | |||
| uint8_t m = (csd.v1.sector_size_high << 1) | csd.v1.sector_size_low; | |||
| if ((firstBlock & m) != 0 || ((lastBlock + 1) & m) != 0) { | |||
| // error card can't erase specified area | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_ERASE_SINGLE_BLOCK); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_type != SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC) { | |||
| firstBlock <<= 9; | |||
| lastBlock <<= 9; | |||
| } | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD32, firstBlock) | |||
| || cardCommand(CMD33, lastBlock) | |||
| || cardCommand(CMD38, 0)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_ERASE); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!waitNotBusy(SD_ERASE_TIMEOUT)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_ERASE_TIMEOUT); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Determine if card supports single block erase. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned if single block erase is supported. | |||
| * The value zero, false, is returned if single block erase is not supported. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::eraseSingleBlockEnable() { | |||
| csd_t csd; | |||
| return readCSD(&csd) ? csd.v1.erase_blk_en : false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Check for busy. MISO low indicates the card is busy. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true if busy else false. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::isBusy() { | |||
| bool rtn; | |||
| chipSelectLow(); | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 8; i++) { | |||
| rtn = m_spi.receive() != 0XFF; | |||
| if (!rtn) break; | |||
| } | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return rtn; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Read a 512 byte block from an SD card. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] blockNumber Logical block to be read. | |||
| * \param[out] dst Pointer to the location that will receive the data. | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::readBlock(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t* dst) { | |||
| SD_TRACE("RB", blockNumber); | |||
| // use address if not SDHC card | |||
| if (type()!= SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC) blockNumber <<= 9; | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD17, blockNumber)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD17); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| return readData(dst, 512); | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Read one data block in a multiple block read sequence | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] dst Pointer to the location for the data to be read. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::readData(uint8_t *dst) { | |||
| chipSelectLow(); | |||
| return readData(dst, 512); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::readData(uint8_t* dst, size_t count) { | |||
| #if USE_SD_CRC | |||
| uint16_t crc; | |||
| #endif // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| // wait for start block token | |||
| uint16_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| while ((m_status = m_spi.receive()) == 0XFF) { | |||
| if (((uint16_t)millis() - t0) > SD_READ_TIMEOUT) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_READ_TIMEOUT); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| spiYield(); | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_status != DATA_START_BLOCK) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_READ); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // transfer data | |||
| if ((m_status = m_spi.receive(dst, count))) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_SPI_DMA); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| #if USE_SD_CRC | |||
| // get crc | |||
| crc = (m_spi.receive() << 8) | m_spi.receive(); | |||
| if (crc != CRC_CCITT(dst, count)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_READ_CRC); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| #else | |||
| // discard crc | |||
| m_spi.receive(); | |||
| m_spi.receive(); | |||
| #endif // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** read CID or CSR register */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::readRegister(uint8_t cmd, void* buf) { | |||
| uint8_t* dst = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(buf); | |||
| if (cardCommand(cmd, 0)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_READ_REG); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| return readData(dst, 16); | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Start a read multiple blocks sequence. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] blockNumber Address of first block in sequence. | |||
| * | |||
| * \note This function is used with readData() and readStop() for optimized | |||
| * multiple block reads. SPI chipSelect must be low for the entire sequence. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::readStart(uint32_t blockNumber) { | |||
| SD_TRACE("RS", blockNumber); | |||
| if (type()!= SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC) blockNumber <<= 9; | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD18, blockNumber)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD18); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** End a read multiple blocks sequence. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::readStop() { | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD12, 0)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD12); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // wait for card to go not busy | |||
| bool Sd2Card::waitNotBusy(uint16_t timeoutMillis) { | |||
| uint16_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| while (m_spi.receive() != 0XFF) { | |||
| if (((uint16_t)millis() - t0) >= timeoutMillis) goto fail; | |||
| spiYield(); | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Writes a 512 byte block to an SD card. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] blockNumber Logical block to be written. | |||
| * \param[in] src Pointer to the location of the data to be written. | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::writeBlock(uint32_t blockNumber, const uint8_t* src) { | |||
| SD_TRACE("WB", blockNumber); | |||
| // use address if not SDHC card | |||
| if (type() != SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC) blockNumber <<= 9; | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD24, blockNumber)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD24); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!writeData(DATA_START_BLOCK, src)) goto fail; | |||
| #define CHECK_PROGRAMMING 0 | |||
| #if CHECK_PROGRAMMING | |||
| // wait for flash programming to complete | |||
| if (!waitNotBusy(SD_WRITE_TIMEOUT)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE_TIMEOUT); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // response is r2 so get and check two bytes for nonzero | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD13, 0) || m_spi.receive()) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE_PROGRAMMING); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // CHECK_PROGRAMMING | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Write one data block in a multiple block write sequence | |||
| * \param[in] src Pointer to the location of the data to be written. | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::writeData(const uint8_t* src) { | |||
| chipSelectLow(); | |||
| // wait for previous write to finish | |||
| if (!waitNotBusy(SD_WRITE_TIMEOUT)) goto fail; | |||
| if (!writeData(WRITE_MULTIPLE_TOKEN, src)) goto fail; | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE_MULTIPLE); | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // send one block of data for write block or write multiple blocks | |||
| bool Sd2Card::writeData(uint8_t token, const uint8_t* src) { | |||
| #if USE_SD_CRC | |||
| uint16_t crc = CRC_CCITT(src, 512); | |||
| #else // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| uint16_t crc = 0XFFFF; | |||
| #endif // USE_SD_CRC | |||
| m_spi.send(token); | |||
| m_spi.send(src, 512); | |||
| m_spi.send(crc >> 8); | |||
| m_spi.send(crc & 0XFF); | |||
| m_status = m_spi.receive(); | |||
| if ((m_status & DATA_RES_MASK) != DATA_RES_ACCEPTED) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Start a write multiple blocks sequence. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] blockNumber Address of first block in sequence. | |||
| * \param[in] eraseCount The number of blocks to be pre-erased. | |||
| * | |||
| * \note This function is used with writeData() and writeStop() | |||
| * for optimized multiple block writes. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::writeStart(uint32_t blockNumber, uint32_t eraseCount) { | |||
| SD_TRACE("WS", blockNumber); | |||
| // send pre-erase count | |||
| if (cardAcmd(ACMD23, eraseCount)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_ACMD23); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // use address if not SDHC card | |||
| if (type() != SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC) blockNumber <<= 9; | |||
| if (cardCommand(CMD25, blockNumber)) { | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD25); | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** End a write multiple blocks sequence. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool Sd2Card::writeStop() { | |||
| chipSelectLow(); | |||
| if (!waitNotBusy(SD_WRITE_TIMEOUT)) goto fail; | |||
| m_spi.send(STOP_TRAN_TOKEN); | |||
| if (!waitNotBusy(SD_WRITE_TIMEOUT)) goto fail; | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| error(SD_CARD_ERROR_STOP_TRAN); | |||
| chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
+ 201
- 0
SdFat/Sd2Card.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,201 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino Sd2Card Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino Sd2Card Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino Sd2Card Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SpiCard_h | |||
| #define SpiCard_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief Sd2Card class for V2 SD/SDHC cards | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatConfig.h> | |||
| #include <SdInfo.h> | |||
| #include <SdSpi.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // SD card errors | |||
| /** timeout error for command CMD0 (initialize card in SPI mode) */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD0 = 0X1; | |||
| /** CMD8 was not accepted - not a valid SD card*/ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD8 = 0X2; | |||
| /** card returned an error response for CMD12 (stop multiblock read) */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD12 = 0X3; | |||
| /** card returned an error response for CMD17 (read block) */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD17 = 0X4; | |||
| /** card returned an error response for CMD18 (read multiple block) */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD18 = 0X5; | |||
| /** card returned an error response for CMD24 (write block) */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD24 = 0X6; | |||
| /** WRITE_MULTIPLE_BLOCKS command failed */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD25 = 0X7; | |||
| /** card returned an error response for CMD58 (read OCR) */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD58 = 0X8; | |||
| /** SET_WR_BLK_ERASE_COUNT failed */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_ACMD23 = 0X9; | |||
| /** ACMD41 initialization process timeout */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_ACMD41 = 0XA; | |||
| /** card returned a bad CSR version field */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_BAD_CSD = 0XB; | |||
| /** erase block group command failed */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_ERASE = 0XC; | |||
| /** card not capable of single block erase */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_ERASE_SINGLE_BLOCK = 0XD; | |||
| /** Erase sequence timed out */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_ERASE_TIMEOUT = 0XE; | |||
| /** card returned an error token instead of read data */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_READ = 0XF; | |||
| /** read CID or CSD failed */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_READ_REG = 0X10; | |||
| /** timeout while waiting for start of read data */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_READ_TIMEOUT = 0X11; | |||
| /** card did not accept STOP_TRAN_TOKEN */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_STOP_TRAN = 0X12; | |||
| /** card returned an error token as a response to a write operation */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE = 0X13; | |||
| /** attempt to write protected block zero */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE_BLOCK_ZERO = 0X14; // REMOVE - not used | |||
| /** card did not go ready for a multiple block write */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE_MULTIPLE = 0X15; | |||
| /** card returned an error to a CMD13 status check after a write */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE_PROGRAMMING = 0X16; | |||
| /** timeout occurred during write programming */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_WRITE_TIMEOUT = 0X17; | |||
| /** incorrect rate selected */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_SCK_RATE = 0X18; | |||
| /** init() not called */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_INIT_NOT_CALLED = 0X19; | |||
| /** card returned an error for CMD59 (CRC_ON_OFF) */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD59 = 0X1A; | |||
| /** invalid read CRC */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_READ_CRC = 0X1B; | |||
| /** SPI DMA error */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_ERROR_SPI_DMA = 0X1C; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // card types | |||
| /** Standard capacity V1 SD card */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1 = 1; | |||
| /** Standard capacity V2 SD card */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2 = 2; | |||
| /** High Capacity SD card */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC = 3; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class Sd2Card | |||
| * \brief Raw access to SD and SDHC flash memory cards. | |||
| */ | |||
| class Sd2Card { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** Construct an instance of Sd2Card. */ | |||
| Sd2Card() : m_errorCode(SD_CARD_ERROR_INIT_NOT_CALLED), m_type(0) {} | |||
| bool begin(uint8_t chipSelectPin = SD_CHIP_SELECT_PIN, | |||
| uint8_t sckDivisor = SPI_FULL_SPEED); | |||
| uint32_t cardSize(); | |||
| bool erase(uint32_t firstBlock, uint32_t lastBlock); | |||
| bool eraseSingleBlockEnable(); | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set SD error code. | |||
| * \param[in] code value for error code. | |||
| */ | |||
| void error(uint8_t code) {m_errorCode = code;} | |||
| /** | |||
| * \return error code for last error. See Sd2Card.h for a list of error codes. | |||
| */ | |||
| int errorCode() const {return m_errorCode;} | |||
| /** \return error data for last error. */ | |||
| int errorData() const {return m_status;} | |||
| /** | |||
| * Initialize an SD flash memory card. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] chipSelectPin SD chip select pin number. | |||
| * \param[in] sckDivisor SPI SCK clock rate divisor. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. The reason for failure | |||
| * can be determined by calling errorCode() and errorData(). | |||
| */ | |||
| bool init(uint8_t sckDivisor = SPI_FULL_SPEED, | |||
| uint8_t chipSelectPin = SD_CHIP_SELECT_PIN) { | |||
| return begin(chipSelectPin, sckDivisor); | |||
| } | |||
| bool isBusy(); | |||
| bool readBlock(uint32_t block, uint8_t* dst); | |||
| /** | |||
| * Read a card's CID register. The CID contains card identification | |||
| * information such as Manufacturer ID, Product name, Product serial | |||
| * number and Manufacturing date. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] cid pointer to area for returned data. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true for success or false for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool readCID(cid_t* cid) { | |||
| return readRegister(CMD10, cid); | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Read a card's CSD register. The CSD contains Card-Specific Data that | |||
| * provides information regarding access to the card's contents. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] csd pointer to area for returned data. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true for success or false for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool readCSD(csd_t* csd) { | |||
| return readRegister(CMD9, csd); | |||
| } | |||
| bool readData(uint8_t *dst); | |||
| bool readStart(uint32_t blockNumber); | |||
| bool readStop(); | |||
| /** Return SCK divisor. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Requested SCK divisor. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t sckDivisor() {return m_sckDivisor;} | |||
| /** Return the card type: SD V1, SD V2 or SDHC | |||
| * \return 0 - SD V1, 1 - SD V2, or 3 - SDHC. | |||
| */ | |||
| int type() const {return m_type;} | |||
| bool writeBlock(uint32_t blockNumber, const uint8_t* src); | |||
| bool writeData(const uint8_t* src); | |||
| bool writeStart(uint32_t blockNumber, uint32_t eraseCount); | |||
| bool writeStop(); | |||
| private: | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // private functions | |||
| uint8_t cardAcmd(uint8_t cmd, uint32_t arg) { | |||
| cardCommand(CMD55, 0); | |||
| return cardCommand(cmd, arg); | |||
| } | |||
| uint8_t cardCommand(uint8_t cmd, uint32_t arg); | |||
| bool readData(uint8_t* dst, size_t count); | |||
| bool readRegister(uint8_t cmd, void* buf); | |||
| void chipSelectHigh(); | |||
| void chipSelectLow(); | |||
| void spiYield(); | |||
| void type(uint8_t value) {m_type = value;} | |||
| bool waitNotBusy(uint16_t timeoutMillis); | |||
| bool writeData(uint8_t token, const uint8_t* src); | |||
| // private data | |||
| static SdSpi m_spi; | |||
| uint8_t m_chipSelectPin; | |||
| uint8_t m_errorCode; | |||
| uint8_t m_sckDivisor; | |||
| uint8_t m_status; | |||
| uint8_t m_type; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // SpiCard_h | |||
+ 2024
- 0
SdFat/SdBaseFile.cpp
Різницю між файлами не показано, бо вона завелика
Переглянути файл
+ 288
- 0
SdFat/SdBaseFile.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,288 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdBaseFile_h | |||
| #define SdBaseFile_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief SdBaseFile class | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifdef __AVR__ | |||
| #include <avr/pgmspace.h> | |||
| #else // __AVR__ | |||
| #ifndef PGM_P | |||
| /** pointer to flash for ARM */ | |||
| #define PGM_P const char* | |||
| #endif // PGM_P | |||
| #ifndef PSTR | |||
| /** store literal string in flash for ARM */ | |||
| #define PSTR(x) (x) | |||
| #endif // PSTR | |||
| #ifndef pgm_read_byte | |||
| /** read 8-bits from flash for ARM */ | |||
| #define pgm_read_byte(addr) (*(const unsigned char*)(addr)) | |||
| #endif // pgm_read_byte | |||
| #ifndef pgm_read_word | |||
| /** read 16-bits from flash for ARM */ | |||
| #define pgm_read_word(addr) (*(const uint16_t*)(addr)) | |||
| #endif // pgm_read_word | |||
| #ifndef PROGMEM | |||
| /** store in flash for ARM */ | |||
| #define PROGMEM const | |||
| #endif // PROGMEM | |||
| #endif // __AVR__ | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatConfig.h> | |||
| #include <SdVolume.h> | |||
| #include <utility/FatApiConstants.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct FatPos_t | |||
| * \brief internal type for istream | |||
| * do not use in user apps | |||
| */ | |||
| struct FatPos_t { | |||
| /** stream position */ | |||
| uint32_t position; | |||
| /** cluster for position */ | |||
| uint32_t cluster; | |||
| FatPos_t() : position(0), cluster(0) {} | |||
| }; | |||
| // values for m_type | |||
| /** This file has not been opened. */ | |||
| uint8_t const FAT_FILE_TYPE_CLOSED = 0; | |||
| /** A normal file */ | |||
| uint8_t const FAT_FILE_TYPE_NORMAL = 1; | |||
| /** A FAT12 or FAT16 root directory */ | |||
| uint8_t const FAT_FILE_TYPE_ROOT_FIXED = 2; | |||
| /** A FAT32 root directory */ | |||
| uint8_t const FAT_FILE_TYPE_ROOT32 = 3; | |||
| /** A subdirectory file*/ | |||
| uint8_t const FAT_FILE_TYPE_SUBDIR = 4; | |||
| /** Test value for directory type */ | |||
| uint8_t const FAT_FILE_TYPE_MIN_DIR = FAT_FILE_TYPE_ROOT_FIXED; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class SdBaseFile | |||
| * \brief Base class for SdFile with Print and C++ streams. | |||
| */ | |||
| class SdBaseFile { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** Create an instance. */ | |||
| SdBaseFile() : writeError(false), m_type(FAT_FILE_TYPE_CLOSED) {} | |||
| SdBaseFile(const char* path, uint8_t oflag); | |||
| #if DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| ~SdBaseFile() {if(isOpen()) close();} | |||
| #endif // DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| /** | |||
| * writeError is set to true if an error occurs during a write(). | |||
| * Set writeError to false before calling print() and/or write() and check | |||
| * for true after calls to print() and/or write(). | |||
| */ | |||
| bool writeError; | |||
| /** \return value of writeError */ | |||
| bool getWriteError() {return writeError;} | |||
| /** Set writeError to zero */ | |||
| void clearWriteError() {writeError = 0;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // helpers for stream classes | |||
| /** get position for streams | |||
| * \param[out] pos struct to receive position | |||
| */ | |||
| void getpos(FatPos_t* pos); | |||
| /** set position for streams | |||
| * \param[out] pos struct with value for new position | |||
| */ | |||
| void setpos(FatPos_t* pos); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** \return number of bytes available from yhe current position to EOF */ | |||
| uint32_t available() {return fileSize() - curPosition();} | |||
| bool close(); | |||
| bool contiguousRange(uint32_t* bgnBlock, uint32_t* endBlock); | |||
| bool createContiguous(SdBaseFile* dirFile, | |||
| const char* path, uint32_t size); | |||
| /** \return The current cluster number for a file or directory. */ | |||
| uint32_t curCluster() const {return m_curCluster;} | |||
| /** \return The current position for a file or directory. */ | |||
| uint32_t curPosition() const {return m_curPosition;} | |||
| /** \return Current working directory */ | |||
| static SdBaseFile* cwd() {return m_cwd;} | |||
| /** Set the date/time callback function | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] dateTime The user's call back function. The callback | |||
| * function is of the form: | |||
| * | |||
| * \code | |||
| * void dateTime(uint16_t* date, uint16_t* time) { | |||
| * uint16_t year; | |||
| * uint8_t month, day, hour, minute, second; | |||
| * | |||
| * // User gets date and time from GPS or real-time clock here | |||
| * | |||
| * // return date using FAT_DATE macro to format fields | |||
| * *date = FAT_DATE(year, month, day); | |||
| * | |||
| * // return time using FAT_TIME macro to format fields | |||
| * *time = FAT_TIME(hour, minute, second); | |||
| * } | |||
| * \endcode | |||
| * | |||
| * Sets the function that is called when a file is created or when | |||
| * a file's directory entry is modified by sync(). All timestamps, | |||
| * access, creation, and modify, are set when a file is created. | |||
| * sync() maintains the last access date and last modify date/time. | |||
| * | |||
| * See the timestamp() function. | |||
| */ | |||
| static void dateTimeCallback( | |||
| void (*dateTime)(uint16_t* date, uint16_t* time)) { | |||
| m_dateTime = dateTime; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Cancel the date/time callback function. */ | |||
| static void dateTimeCallbackCancel() {m_dateTime = 0;} | |||
| bool dirEntry(dir_t* dir); | |||
| static void dirName(const dir_t& dir, char* name); | |||
| bool exists(const char* name); | |||
| int16_t fgets(char* str, int16_t num, char* delim = 0); | |||
| /** \return The total number of bytes in a file or directory. */ | |||
| uint32_t fileSize() const {return m_fileSize;} | |||
| /** \return The first cluster number for a file or directory. */ | |||
| uint32_t firstCluster() const {return m_firstCluster;} | |||
| bool getFilename(char* name); | |||
| /** \return True if this is a directory else false. */ | |||
| bool isDir() const {return m_type >= FAT_FILE_TYPE_MIN_DIR;} | |||
| /** \return True if this is a normal file else false. */ | |||
| bool isFile() const {return m_type == FAT_FILE_TYPE_NORMAL;} | |||
| /** \return True if this is an open file/directory else false. */ | |||
| bool isOpen() const {return m_type != FAT_FILE_TYPE_CLOSED;} | |||
| /** \return True if this is a subdirectory else false. */ | |||
| bool isSubDir() const {return m_type == FAT_FILE_TYPE_SUBDIR;} | |||
| /** \return True if this is the root directory. */ | |||
| bool isRoot() const { | |||
| return m_type == FAT_FILE_TYPE_ROOT_FIXED || m_type == FAT_FILE_TYPE_ROOT32; | |||
| } | |||
| void ls(Print* pr, uint8_t flags = 0, uint8_t indent = 0); | |||
| void ls(uint8_t flags = 0); | |||
| bool mkdir(SdBaseFile* dir, const char* path, bool pFlag = true); | |||
| // alias for backward compactability | |||
| bool makeDir(SdBaseFile* dir, const char* path) { | |||
| return mkdir(dir, path, false); | |||
| } | |||
| bool open(SdBaseFile* dirFile, uint16_t index, uint8_t oflag); | |||
| bool open(SdBaseFile* dirFile, const char* path, uint8_t oflag); | |||
| bool open(const char* path, uint8_t oflag = O_READ); | |||
| bool openNext(SdBaseFile* dirFile, uint8_t oflag); | |||
| bool openRoot(SdVolume* vol); | |||
| int peek(); | |||
| bool printCreateDateTime(Print* pr); | |||
| static void printFatDate(uint16_t fatDate); | |||
| static void printFatDate(Print* pr, uint16_t fatDate); | |||
| static void printFatTime(uint16_t fatTime); | |||
| static void printFatTime(Print* pr, uint16_t fatTime); | |||
| int printField(int16_t value, char term); | |||
| int printField(uint16_t value, char term); | |||
| int printField(int32_t value, char term); | |||
| int printField(uint32_t value, char term); | |||
| bool printModifyDateTime(Print* pr); | |||
| size_t printName(); | |||
| size_t printName(Print* pr); | |||
| size_t printFileSize(Print* pr); | |||
| int16_t read(); | |||
| int read(void* buf, size_t nbyte); | |||
| int8_t readDir(dir_t* dir); | |||
| static bool remove(SdBaseFile* dirFile, const char* path); | |||
| bool remove(); | |||
| /** Set the file's current position to zero. */ | |||
| void rewind() {seekSet(0);} | |||
| bool rename(SdBaseFile* dirFile, const char* newPath); | |||
| bool rmdir(); | |||
| // for backward compatibility | |||
| bool rmDir() {return rmdir();} | |||
| bool rmRfStar(); | |||
| /** Set the files position to current position + \a pos. See seekSet(). | |||
| * \param[in] offset The new position in bytes from the current position. | |||
| * \return true for success or false for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool seekCur(int32_t offset) { | |||
| return seekSet(m_curPosition + offset); | |||
| } | |||
| /** Set the files position to end-of-file + \a offset. See seekSet(). | |||
| * \param[in] offset The new position in bytes from end-of-file. | |||
| * \return true for success or false for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool seekEnd(int32_t offset = 0) {return seekSet(m_fileSize + offset);} | |||
| bool seekSet(uint32_t pos); | |||
| bool sync(); | |||
| bool timestamp(SdBaseFile* file); | |||
| bool timestamp(uint8_t flag, uint16_t year, uint8_t month, uint8_t day, | |||
| uint8_t hour, uint8_t minute, uint8_t second); | |||
| /** Type of file. You should use isFile() or isDir() instead of type() | |||
| * if possible. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The file or directory type. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t type() const {return m_type;} | |||
| bool truncate(uint32_t size); | |||
| /** \return SdVolume that contains this file. */ | |||
| SdVolume* volume() const {return m_vol;} | |||
| int write(const void* buf, size_t nbyte); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| private: | |||
| // allow SdFat to set m_cwd | |||
| friend class SdFat; | |||
| /** experimental don't use */ | |||
| bool openParent(SdBaseFile* dir); | |||
| // private functions | |||
| bool addCluster(); | |||
| cache_t* addDirCluster(); | |||
| dir_t* cacheDirEntry(uint8_t action); | |||
| int8_t lsPrintNext(Print *pr, uint8_t flags, uint8_t indent); | |||
| static bool make83Name(const char* str, uint8_t* name, const char** ptr); | |||
| bool mkdir(SdBaseFile* parent, const uint8_t dname[11]); | |||
| bool open(SdBaseFile* dirFile, const uint8_t dname[11], uint8_t oflag); | |||
| bool openCachedEntry(uint8_t cacheIndex, uint8_t oflags); | |||
| dir_t* readDirCache(); | |||
| static void setCwd(SdBaseFile* cwd) {m_cwd = cwd;} | |||
| bool setDirSize(); | |||
| // bits defined in m_flags | |||
| // should be 0X0F | |||
| static uint8_t const F_OFLAG = (O_ACCMODE | O_APPEND | O_SYNC); | |||
| // sync of directory entry required | |||
| static uint8_t const F_FILE_DIR_DIRTY = 0X80; | |||
| // global pointer to cwd dir | |||
| static SdBaseFile* m_cwd; | |||
| // data time callback function | |||
| static void (*m_dateTime)(uint16_t* date, uint16_t* time); | |||
| // private data | |||
| uint8_t m_flags; // See above for definition of m_flags bits | |||
| uint8_t m_type; // type of file see above for values | |||
| uint8_t m_dirIndex; // index of directory entry in dirBlock | |||
| SdVolume* m_vol; // volume where file is located | |||
| uint32_t m_curCluster; // cluster for current file position | |||
| uint32_t m_curPosition; // current file position in bytes from beginning | |||
| uint32_t m_dirBlock; // block for this files directory entry | |||
| uint32_t m_fileSize; // file size in bytes | |||
| uint32_t m_firstCluster; // first cluster of file | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // SdBaseFile_h | |||
+ 322
- 0
SdFat/SdBaseFilePrint.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,322 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <utility/FmtNumber.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** List directory contents to stdOut. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] flags The inclusive OR of | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_DATE - %Print file modification date | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_SIZE - %Print file size. | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_R - Recursive list of subdirectories. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdBaseFile::ls(uint8_t flags) { | |||
| ls(SdFat::stdOut(), flags, 0); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** List directory contents. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print stream for list. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] flags The inclusive OR of | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_DATE - %Print file modification date | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_SIZE - %Print file size. | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_R - Recursive list of subdirectories. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] indent Amount of space before file name. Used for recursive | |||
| * list to indicate subdirectory level. | |||
| */ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdBaseFile::ls(Print* pr, uint8_t flags, uint8_t indent) { | |||
| if (!isDir()) { | |||
| pr->println(F("bad dir")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| rewind(); | |||
| int8_t status; | |||
| while ((status = lsPrintNext(pr, flags, indent))) { | |||
| if (status > 1 && (flags & LS_R)) { | |||
| uint16_t index = curPosition()/32 - 1; | |||
| SdBaseFile s; | |||
| if (s.open(this, index, O_READ)) s.ls(pr, flags, indent + 2); | |||
| seekSet(32 * (index + 1)); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // saves 32 bytes on stack for ls recursion | |||
| // return 0 - EOF, 1 - normal file, or 2 - directory | |||
| int8_t SdBaseFile::lsPrintNext(Print *pr, uint8_t flags, uint8_t indent) { | |||
| dir_t dir; | |||
| uint8_t w = 0; | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| if (read(&dir, sizeof(dir)) != sizeof(dir)) return 0; | |||
| if (dir.name[0] == DIR_NAME_FREE) return 0; | |||
| // skip deleted entry and entries for . and .. | |||
| if (dir.name[0] != DIR_NAME_DELETED && dir.name[0] != '.' | |||
| && DIR_IS_FILE_OR_SUBDIR(&dir)) break; | |||
| } | |||
| // indent for dir level | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < indent; i++) pr->write(' '); | |||
| // print name | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 11; i++) { | |||
| if (dir.name[i] == ' ')continue; | |||
| if (i == 8) { | |||
| pr->write('.'); | |||
| w++; | |||
| } | |||
| pr->write(dir.name[i]); | |||
| w++; | |||
| } | |||
| if (DIR_IS_SUBDIR(&dir)) { | |||
| pr->write('/'); | |||
| w++; | |||
| } | |||
| if (flags & (LS_DATE | LS_SIZE)) { | |||
| while (w++ < 14) pr->write(' '); | |||
| } | |||
| // print modify date/time if requested | |||
| if (flags & LS_DATE) { | |||
| pr->write(' '); | |||
| printFatDate(pr, dir.lastWriteDate); | |||
| pr->write(' '); | |||
| printFatTime(pr, dir.lastWriteTime); | |||
| } | |||
| // print size if requested | |||
| if (!DIR_IS_SUBDIR(&dir) && (flags & LS_SIZE)) { | |||
| pr->write(' '); | |||
| pr->print(dir.fileSize); | |||
| } | |||
| pr->println(); | |||
| return DIR_IS_FILE(&dir) ? 1 : 2; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // print uint8_t with width 2 | |||
| static void print2u(Print* pr, uint8_t v) { | |||
| if (v < 10) pr->write('0'); | |||
| pr->print(v, DEC); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a file's creation date and time | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print stream for output. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdBaseFile::printCreateDateTime(Print* pr) { | |||
| dir_t dir; | |||
| if (!dirEntry(&dir)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| printFatDate(pr, dir.creationDate); | |||
| pr->write(' '); | |||
| printFatTime(pr, dir.creationTime); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a directory date field to stdOut. | |||
| * | |||
| * Format is yyyy-mm-dd. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] fatDate The date field from a directory entry. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdBaseFile::printFatDate(uint16_t fatDate) { | |||
| printFatDate(SdFat::stdOut(), fatDate); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a directory date field. | |||
| * | |||
| * Format is yyyy-mm-dd. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print stream for output. | |||
| * \param[in] fatDate The date field from a directory entry. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdBaseFile::printFatDate(Print* pr, uint16_t fatDate) { | |||
| pr->print(FAT_YEAR(fatDate)); | |||
| pr->write('-'); | |||
| print2u(pr, FAT_MONTH(fatDate)); | |||
| pr->write('-'); | |||
| print2u(pr, FAT_DAY(fatDate)); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a directory time field to stdOut. | |||
| * | |||
| * Format is hh:mm:ss. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] fatTime The time field from a directory entry. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdBaseFile::printFatTime(uint16_t fatTime) { | |||
| printFatTime(SdFat::stdOut(), fatTime); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a directory time field. | |||
| * | |||
| * Format is hh:mm:ss. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print stream for output. | |||
| * \param[in] fatTime The time field from a directory entry. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdBaseFile::printFatTime(Print* pr, uint16_t fatTime) { | |||
| print2u(pr, FAT_HOUR(fatTime)); | |||
| pr->write(':'); | |||
| print2u(pr, FAT_MINUTE(fatTime)); | |||
| pr->write(':'); | |||
| print2u(pr, FAT_SECOND(fatTime)); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Template for SdBaseFile::printField() */ | |||
| template <typename Type> | |||
| static int printFieldT(SdBaseFile* file, char sign, Type value, char term) { | |||
| char buf[3*sizeof(Type) + 3]; | |||
| char* str = &buf[sizeof(buf)]; | |||
| if (term) { | |||
| *--str = term; | |||
| if (term == '\n') { | |||
| *--str = '\r'; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| do { | |||
| Type m = value; | |||
| value /= 10; | |||
| *--str = '0' + m - 10*value; | |||
| } while (value); | |||
| if (sign) { | |||
| *--str = sign; | |||
| } | |||
| return file->write(str, &buf[sizeof(buf)] - str); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] term The field terminator. Use '\\n' for CR LF. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int SdBaseFile::printField(uint16_t value, char term) { | |||
| return printFieldT(this, 0, value, term); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] term The field terminator. Use '\\n' for CR LF. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int SdBaseFile::printField(int16_t value, char term) { | |||
| char sign = 0; | |||
| if (value < 0) { | |||
| sign = '-'; | |||
| value = -value; | |||
| } | |||
| return printFieldT(this, sign, (uint16_t)value, term); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] term The field terminator. Use '\\n' for CR LF. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int SdBaseFile::printField(uint32_t value, char term) { | |||
| return printFieldT(this, 0, value, term); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] term The field terminator. Use '\\n' for CR LF. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int SdBaseFile::printField(int32_t value, char term) { | |||
| char sign = 0; | |||
| if (value < 0) { | |||
| sign = '-'; | |||
| value = -value; | |||
| } | |||
| return printFieldT(this, sign, (uint32_t)value, term); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a file's modify date and time | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print stream for output. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdBaseFile::printModifyDateTime(Print* pr) { | |||
| dir_t dir; | |||
| if (!dirEntry(&dir)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| printFatDate(pr, dir.lastWriteDate); | |||
| pr->write(' '); | |||
| printFatTime(pr, dir.lastWriteTime); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a file's name | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print stream for output. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t SdBaseFile::printName(Print* pr) { | |||
| char name[13]; | |||
| if (!getFilename(name)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| return pr->print(name); | |||
| fail: | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a file's name to stdOut | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t SdBaseFile::printName() { | |||
| return printName(SdFat::stdOut()); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| size_t SdBaseFile::printFileSize(Print* pr) { | |||
| char buf[10]; | |||
| char *ptr = fmtDec(fileSize(), buf + sizeof(buf)); | |||
| while (ptr > buf) *--ptr = ' '; | |||
| return pr->write(reinterpret_cast<uint8_t *>(buf), sizeof(buf)); | |||
| } | |||
+ 247
- 0
SdFat/SdFat.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,247 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #if USE_SERIAL_FOR_STD_OUT || !defined(UDR0) | |||
| Print* SdFat::m_stdOut = &Serial; | |||
| #else // USE_SERIAL_FOR_STD_OUT | |||
| #include <MinimumSerial.h> | |||
| Print* SdFat::m_stdOut = &MiniSerial; | |||
| #endif // USE_SERIAL_FOR_STD_OUT | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Initialize an SdFat object. | |||
| * | |||
| * Initializes the SD card, SD volume, and root directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] chipSelectPin SD chip select pin. See Sd2Card::init(). | |||
| * \param[in] sckDivisor value for SPI SCK divisor. See Sd2Card::init(). | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::begin(uint8_t chipSelectPin, uint8_t sckDivisor) { | |||
| return m_card.begin(chipSelectPin, sckDivisor) | |||
| && m_vol.init(&m_card) && chdir(1); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Change a volume's working directory to root | |||
| * | |||
| * Changes the volume's working directory to the SD's root directory. | |||
| * Optionally set the current working directory to the volume's | |||
| * working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] set_cwd Set the current working directory to this volume's | |||
| * working directory if true. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::chdir(bool set_cwd) { | |||
| if (set_cwd) SdBaseFile::setCwd(&m_vwd); | |||
| if (m_vwd.isOpen()) m_vwd.close(); | |||
| return m_vwd.openRoot(&m_vol); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Change a volume's working directory | |||
| * | |||
| * Changes the volume working directory to the \a path subdirectory. | |||
| * Optionally set the current working directory to the volume's | |||
| * working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * Example: If the volume's working directory is "/DIR", chdir("SUB") | |||
| * will change the volume's working directory from "/DIR" to "/DIR/SUB". | |||
| * | |||
| * If path is "/", the volume's working directory will be changed to the | |||
| * root directory | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path The name of the subdirectory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] set_cwd Set the current working directory to this volume's | |||
| * working directory if true. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::chdir(const char *path, bool set_cwd) { | |||
| SdBaseFile dir; | |||
| dir.open(&m_vwd, path, O_READ); | |||
| // Check for correctly open directory. | |||
| if (!dir.isDir()) goto fail; | |||
| m_vwd = dir; | |||
| if (set_cwd) SdBaseFile::setCwd(&m_vwd); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Set the current working directory to a volume's working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * This is useful with multiple SD cards. | |||
| * | |||
| * The current working directory is changed to this volume's working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * This is like the Windows/DOS \<drive letter>: command. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::chvol() { | |||
| SdBaseFile::setCwd(&m_vwd); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Test for the existence of a file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] name Name of the file to be tested for. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true if the file exists else false. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::exists(const char* name) { | |||
| return m_vwd.exists(name); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** List the directory contents of the volume working directory to stdOut. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] flags The inclusive OR of | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_DATE - %Print file modification date | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_SIZE - %Print file size. | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_R - Recursive list of subdirectories. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::ls(uint8_t flags) { | |||
| m_vwd.ls(m_stdOut, flags); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** List the directory contents of the volume working directory to stdOut. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path directory to list. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] flags The inclusive OR of | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_DATE - %Print file modification date | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_SIZE - %Print file size. | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_R - Recursive list of subdirectories. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::ls(const char* path, uint8_t flags) { | |||
| ls(m_stdOut, path, flags); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** List the directory contents of the volume working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print stream for list. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] flags The inclusive OR of | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_DATE - %Print file modification date | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_SIZE - %Print file size. | |||
| * | |||
| * LS_R - Recursive list of subdirectories. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::ls(Print* pr, uint8_t flags) { | |||
| m_vwd.ls(pr, flags); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdFat::ls(Print* pr, const char* path, uint8_t flags) { | |||
| SdBaseFile dir(path, O_READ); | |||
| dir.ls(pr, flags); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Make a subdirectory in the volume working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path A path with a valid 8.3 DOS name for the subdirectory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pFlag Create missing parent directories if true. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::mkdir(const char* path, bool pFlag) { | |||
| SdBaseFile sub; | |||
| return sub.mkdir(&m_vwd, path, pFlag); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Remove a file from the volume working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path A path with a valid 8.3 DOS name for the file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::remove(const char* path) { | |||
| return SdBaseFile::remove(&m_vwd, path); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Rename a file or subdirectory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] oldPath Path name to the file or subdirectory to be renamed. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] newPath New path name of the file or subdirectory. | |||
| * | |||
| * The \a newPath object must not exist before the rename call. | |||
| * | |||
| * The file to be renamed must not be open. The directory entry may be | |||
| * moved and file system corruption could occur if the file is accessed by | |||
| * a file object that was opened before the rename() call. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::rename(const char *oldPath, const char *newPath) { | |||
| SdBaseFile file; | |||
| if (!file.open(oldPath, O_READ)) return false; | |||
| return file.rename(&m_vwd, newPath); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Remove a subdirectory from the volume's working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path A path with a valid 8.3 DOS name for the subdirectory. | |||
| * | |||
| * The subdirectory file will be removed only if it is empty. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::rmdir(const char* path) { | |||
| SdBaseFile sub; | |||
| if (!sub.open(path, O_READ)) return false; | |||
| return sub.rmdir(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Truncate a file to a specified length. The current file position | |||
| * will be maintained if it is less than or equal to \a length otherwise | |||
| * it will be set to end of file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path A path with a valid 8.3 DOS name for the file. | |||
| * \param[in] length The desired length for the file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. | |||
| * Reasons for failure include file is read only, file is a directory, | |||
| * \a length is greater than the current file size or an I/O error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdFat::truncate(const char* path, uint32_t length) { | |||
| SdBaseFile file; | |||
| if (!file.open(path, O_WRITE)) return false; | |||
| return file.truncate(length); | |||
| } | |||
+ 99
- 0
SdFat/SdFat.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,99 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdFat_h | |||
| #define SdFat_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief SdFat class | |||
| */ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Macro for debug. */ | |||
| #define DBG_FAIL_MACRO // Serial.print(__FILE__);Serial.println(__LINE__) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SdFat version YYYYMMDD */ | |||
| #define SD_FAT_VERSION 20140824 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** error if old IDE */ | |||
| #if !defined(ARDUINO) || ARDUINO < 100 | |||
| #error Arduino IDE must be 1.0 or greater | |||
| #endif // ARDUINO < 100 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #include <SdFile.h> | |||
| #include <SdStream.h> | |||
| #include <ArduinoStream.h> | |||
| #include <MinimumSerial.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class SdFat | |||
| * \brief Integration class for the %SdFat library. | |||
| */ | |||
| class SdFat { | |||
| public: | |||
| SdFat() {} | |||
| /** \return a pointer to the Sd2Card object. */ | |||
| Sd2Card* card() {return &m_card;} | |||
| bool chdir(bool set_cwd = false); | |||
| bool chdir(const char* path, bool set_cwd = false); | |||
| void chvol(); | |||
| void errorHalt(); | |||
| void errorHalt(char const *msg); | |||
| void errorPrint(); | |||
| void errorPrint(char const *msg); | |||
| bool exists(const char* name); | |||
| bool begin(uint8_t chipSelectPin = SD_CHIP_SELECT_PIN, | |||
| uint8_t sckDivisor = SPI_FULL_SPEED); | |||
| void initErrorHalt(); | |||
| void initErrorHalt(char const *msg); | |||
| void initErrorPrint(); | |||
| void initErrorPrint(char const *msg); | |||
| void ls(uint8_t flags = 0); | |||
| void ls(const char* path, uint8_t flags = 0); | |||
| void ls(Print* pr, uint8_t flags = 0); | |||
| void ls(Print* pr, const char* path, uint8_t flags = 0); | |||
| bool mkdir(const char* path, bool pFlag = true); | |||
| bool remove(const char* path); | |||
| bool rename(const char *oldPath, const char *newPath); | |||
| bool rmdir(const char* path); | |||
| bool truncate(const char* path, uint32_t length); | |||
| /** \return a pointer to the SdVolume object. */ | |||
| SdVolume* vol() {return &m_vol;} | |||
| /** \return a pointer to the volume working directory. */ | |||
| SdBaseFile* vwd() {return &m_vwd;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| void errorHalt_P(PGM_P msg); | |||
| void errorPrint_P(PGM_P msg); | |||
| void initErrorHalt_P(PGM_P msg); | |||
| void initErrorPrint_P(PGM_P msg); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set stdOut Print stream for messages. | |||
| * \param[in] stream The new Print stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| static void setStdOut(Print* stream) {m_stdOut = stream;} | |||
| /** \return Print stream for messages. */ | |||
| static Print* stdOut() {return m_stdOut;} | |||
| private: | |||
| Sd2Card m_card; | |||
| SdVolume m_vol; | |||
| SdBaseFile m_vwd; | |||
| static Print* m_stdOut; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // SdFat_h | |||
+ 196
- 0
SdFat/SdFatConfig.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,196 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief configuration definitions | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdFatConfig_h | |||
| #define SdFatConfig_h | |||
| #include <stdint.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE nonzero to use a second 512 byte cache | |||
| * for FAT table entries. Improves performance for large writes that | |||
| * are not a multiple of 512 bytes. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifdef __arm__ | |||
| #define USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE 1 | |||
| #else // __arm__ | |||
| #define USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE 0 | |||
| #endif // __arm__ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set USE_MULTI_BLOCK_SD_IO nonzero to use multi-block SD read/write. | |||
| * | |||
| * Don't use mult-block read/write on small AVR boards. | |||
| */ | |||
| #if defined(RAMEND) && RAMEND < 3000 | |||
| #define USE_MULTI_BLOCK_SD_IO 0 | |||
| #else | |||
| #define USE_MULTI_BLOCK_SD_IO 1 | |||
| #endif | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * To enable SD card CRC checking set USE_SD_CRC nonzero. | |||
| * | |||
| * Set USE_SD_CRC to 1 to use a smaller slower CRC-CCITT function. | |||
| * | |||
| * Set USE_SD_CRC to 2 to used a larger faster table driven CRC-CCITT function. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define USE_SD_CRC 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * To use multiple SD cards set USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS nonzero. | |||
| * | |||
| * Using multiple cards costs about 200 bytes of flash. | |||
| * | |||
| * Each card requires about 550 bytes of SRAM so use of a Mega is recommended. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE nonzero to close a file in its destructor. | |||
| * | |||
| * Causes use of lots of heap in ARM. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * For AVR | |||
| * | |||
| * Set USE_SERIAL_FOR_STD_OUT nonzero to use Serial (the HardwareSerial class) | |||
| * for error messages and output from print functions like ls(). | |||
| * | |||
| * If USE_SERIAL_FOR_STD_OUT is zero, a small non-interrupt driven class | |||
| * is used to output messages to serial port zero. This allows an alternate | |||
| * Serial library like SerialPort to be used with SdFat. | |||
| * | |||
| * You can redirect stdOut with SdFat::setStdOut(Print* stream) and | |||
| * get the current stream with SdFat::stdOut(). | |||
| */ | |||
| #define USE_SERIAL_FOR_STD_OUT 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Call flush for endl if ENDL_CALLS_FLUSH is nonzero | |||
| * | |||
| * The standard for iostreams is to call flush. This is very costly for | |||
| * SdFat. Each call to flush causes 2048 bytes of I/O to the SD. | |||
| * | |||
| * SdFat has a single 512 byte buffer for SD I/O so it must write the current | |||
| * data block to the SD, read the directory block from the SD, update the | |||
| * directory entry, write the directory block to the SD and read the data | |||
| * block back into the buffer. | |||
| * | |||
| * The SD flash memory controller is not designed for this many rewrites | |||
| * so performance may be reduced by more than a factor of 100. | |||
| * | |||
| * If ENDL_CALLS_FLUSH is zero, you must call flush and/or close to force | |||
| * all data to be written to the SD. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define ENDL_CALLS_FLUSH 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Allow FAT12 volumes if FAT12_SUPPORT is nonzero. | |||
| * FAT12 has not been well tested. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define FAT12_SUPPORT 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * SPI SCK divisor for SD initialization commands. | |||
| * or greater | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifdef __AVR__ | |||
| const uint8_t SPI_SCK_INIT_DIVISOR = 64; | |||
| #else | |||
| const uint8_t SPI_SCK_INIT_DIVISOR = 128; | |||
| #endif | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION nonzero to enable the SPI transaction feature | |||
| * of the standard Arduino SPI library. You must include SPI.h in your | |||
| * sketches when ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION is nonzero. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set ENABLE_SPI_YIELD nonzero to enable release of the SPI bus during | |||
| * SD card busy waits. | |||
| * | |||
| * This will allow interrupt routines to access the SPI bus if | |||
| * ENABLE_SPI_TRANSACTION is nonzero. | |||
| * | |||
| * Setting ENABLE_SPI_YIELD will introduce some extra overhead and will | |||
| * slightly slow transfer rates. A few older SD cards may fail when | |||
| * ENABLE_SPI_YIELD is nonzero. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define ENABLE_SPI_YIELD 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Force use of Arduino Standard SPI library if USE_ARDUINO_SPI_LIBRARY | |||
| * is nonzero. This will override native and software SPI for all boards. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define USE_ARDUINO_SPI_LIBRARY 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Define AVR_SOF_SPI nonzero to use software SPI on all AVR Arduinos. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define AVR_SOFT_SPI 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Define DUE_SOFT_SPI nonzero to use software SPI on Due Arduinos. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define DUE_SOFT_SPI 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Define LEONARDO_SOFT_SPI nonzero to use software SPI on Leonardo Arduinos. | |||
| * LEONARDO_SOFT_SPI allows an unmodified 328 Shield to be used | |||
| * on Leonardo Arduinos. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define LEONARDO_SOFT_SPI 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Define MEGA_SOFT_SPI nonzero to use software SPI on Mega Arduinos. | |||
| * MEGA_SOFT_SPI allows an unmodified 328 Shield to be used | |||
| * on Mega Arduinos. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define MEGA_SOFT_SPI 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set TEENSY3_SOFT_SPI nonzero to use software SPI on Teensy 3.x boards. | |||
| */ | |||
| #define TEENSY3_SOFT_SPI 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Define software SPI pins. Default allows Uno shields to be used on other | |||
| * boards. | |||
| */ | |||
| // define software SPI pins | |||
| /** Default Software SPI chip select pin */ | |||
| uint8_t const SOFT_SPI_CS_PIN = 10; | |||
| /** Software SPI Master Out Slave In pin */ | |||
| uint8_t const SOFT_SPI_MOSI_PIN = 11; | |||
| /** Software SPI Master In Slave Out pin */ | |||
| uint8_t const SOFT_SPI_MISO_PIN = 12; | |||
| /** Software SPI Clock pin */ | |||
| uint8_t const SOFT_SPI_SCK_PIN = 13; | |||
| #endif // SdFatConfig_h | |||
+ 145
- 0
SdFat/SdFatErrorPrint.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,145 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #ifndef PSTR | |||
| #define PSTR(x) x | |||
| #define PGM_P const char* | |||
| #endif | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| static void pstrPrint(PGM_P str) { | |||
| for (uint8_t c; (c = pgm_read_byte(str)); str++) SdFat::stdOut()->write(c); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| static void pstrPrintln(PGM_P str) { | |||
| pstrPrint(str); | |||
| SdFat::stdOut()->println(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print any SD error code and halt. */ | |||
| void SdFat::errorHalt() { | |||
| errorPrint(); | |||
| while (1) {} | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print msg, any SD error code, and halt. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::errorHalt(char const* msg) { | |||
| errorPrint(msg); | |||
| while (1) {} | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print msg, any SD error code, and halt. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message in program space (flash memory) to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::errorHalt_P(PGM_P msg) { | |||
| errorPrint_P(msg); | |||
| while (1) {} | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print any SD error code. */ | |||
| void SdFat::errorPrint() { | |||
| if (!m_card.errorCode()) return; | |||
| pstrPrint(PSTR("SD errorCode: 0X")); | |||
| m_stdOut->print(m_card.errorCode(), HEX); | |||
| pstrPrint(PSTR(",0X")); | |||
| m_stdOut->println(m_card.errorData(), HEX); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print msg, any SD error code. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::errorPrint(char const* msg) { | |||
| pstrPrint(PSTR("error: ")); | |||
| m_stdOut->println(msg); | |||
| errorPrint(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print msg, any SD error code. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message in program space (flash memory) to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::errorPrint_P(PGM_P msg) { | |||
| pstrPrint(PSTR("error: ")); | |||
| pstrPrintln(msg); | |||
| errorPrint(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print error details and halt after SdFat::init() fails. */ | |||
| void SdFat::initErrorHalt() { | |||
| initErrorPrint(); | |||
| while (1) {} | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /**Print message, error details, and halt after SdFat::init() fails. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::initErrorHalt(char const *msg) { | |||
| m_stdOut->println(msg); | |||
| initErrorHalt(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /**Print message, error details, and halt after SdFat::init() fails. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message in program space (flash memory) to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::initErrorHalt_P(PGM_P msg) { | |||
| pstrPrintln(msg); | |||
| initErrorHalt(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print error details after SdFat::init() fails. */ | |||
| void SdFat::initErrorPrint() { | |||
| if (m_card.errorCode()) { | |||
| pstrPrintln(PSTR("Can't access SD card. Do not reformat.")); | |||
| if (m_card.errorCode() == SD_CARD_ERROR_CMD0) { | |||
| pstrPrintln(PSTR("No card, wrong chip select pin, or SPI problem?")); | |||
| } | |||
| errorPrint(); | |||
| } else if (m_vol.fatType() == 0) { | |||
| pstrPrintln(PSTR("Invalid format, reformat SD.")); | |||
| } else if (!m_vwd.isOpen()) { | |||
| pstrPrintln(PSTR("Can't open root directory.")); | |||
| } else { | |||
| pstrPrintln(PSTR("No error found.")); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /**Print message and error details and halt after SdFat::init() fails. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::initErrorPrint(char const *msg) { | |||
| m_stdOut->println(msg); | |||
| initErrorPrint(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /**Print message and error details after SdFat::init() fails. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] msg Message in program space (flash memory) to print. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFat::initErrorPrint_P(PGM_P msg) { | |||
| pstrPrintln(msg); | |||
| initErrorHalt(); | |||
| } | |||
+ 76
- 0
SdFat/SdFatUtil.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,76 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <stdlib.h> | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| #ifdef __arm__ | |||
| // should use uinstd.h to define sbrk but Due causes a conflict | |||
| extern "C" char* sbrk(int incr); | |||
| #else // __ARM__ | |||
| extern char *__brkval; | |||
| extern char __bss_end; | |||
| #endif // __arm__ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Amount of free RAM | |||
| * \return The number of free bytes. | |||
| */ | |||
| int SdFatUtil::FreeRam() { | |||
| char top; | |||
| #ifdef __arm__ | |||
| return &top - reinterpret_cast<char*>(sbrk(0)); | |||
| #else // __arm__ | |||
| return __brkval ? &top - __brkval : &top - &__bss_end; | |||
| #endif // __arm__ | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a string in flash memory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print object for output. | |||
| * \param[in] str Pointer to string stored in flash memory. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFatUtil::print_P(Print* pr, PGM_P str) { | |||
| for (uint8_t c; (c = pgm_read_byte(str)); str++) pr->write(c); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a string in flash memory followed by a CR/LF. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] pr Print object for output. | |||
| * \param[in] str Pointer to string stored in flash memory. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFatUtil::println_P(Print* pr, PGM_P str) { | |||
| print_P(pr, str); | |||
| pr->println(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a string in flash memory to Serial. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] str Pointer to string stored in flash memory. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFatUtil::SerialPrint_P(PGM_P str) { | |||
| print_P(SdFat::stdOut(), str); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** %Print a string in flash memory to Serial followed by a CR/LF. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] str Pointer to string stored in flash memory. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFatUtil::SerialPrintln_P(PGM_P str) { | |||
| println_P(SdFat::stdOut(), str); | |||
| } | |||
+ 40
- 0
SdFat/SdFatUtil.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdFatUtil_h | |||
| #define SdFatUtil_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief Useful utility functions. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| /** Store and print a string in flash memory.*/ | |||
| #define PgmPrint(x) SerialPrint_P(PSTR(x)) | |||
| /** Store and print a string in flash memory followed by a CR/LF.*/ | |||
| #define PgmPrintln(x) SerialPrintln_P(PSTR(x)) | |||
| namespace SdFatUtil { | |||
| int FreeRam(); | |||
| void print_P(Print* pr, PGM_P str); | |||
| void println_P(Print* pr, PGM_P str); | |||
| void SerialPrint_P(PGM_P str); | |||
| void SerialPrintln_P(PGM_P str); | |||
| } | |||
| using namespace SdFatUtil; // NOLINT | |||
| #endif // #define SdFatUtil_h | |||
+ 219
- 0
SdFat/SdFatmainpage.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,219 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| /** | |||
| \mainpage Arduino %SdFat Library | |||
| <CENTER>Copyright © 2012, 2013, 2014 by William Greiman | |||
| </CENTER> | |||
| \section Intro Introduction | |||
| The Arduino %SdFat Library is a minimal implementation of FAT16 and FAT32 | |||
| file systems on SD flash memory cards. Standard SD and high capacity SDHC | |||
| cards are supported. | |||
| Experimental support for FAT12 can be enabled by setting FAT12_SUPPORT | |||
| nonzero in SdFatConfig.h. | |||
| The %SdFat library only supports short 8.3 names. | |||
| The main classes in %SdFat are SdFat, SdFile, StdioStream, \ref fstream, | |||
| \ref ifstream, and \ref ofstream. | |||
| The SdFat class maintains a volume working directories, a current working | |||
| directory, and simplifies initialization of other classes. | |||
| The SdFile class provides binary file access functions such as open(), read(), | |||
| remove(), write(), close() and sync(). This class supports access to the root | |||
| directory and subdirectories. | |||
| The StdioStream class implements functions similar to Linux/Unix standard | |||
| buffered input/output. | |||
| The \ref fstream class implements C++ iostreams for both reading and writing | |||
| text files. | |||
| The \ref ifstream class implements the C++ iostreams for reading text files. | |||
| The \ref ofstream class implements the C++ iostreams for writing text files. | |||
| The classes \ref ibufstream and \ref obufstream format and parse character | |||
| strings in memory buffers. | |||
| the classes ArduinoInStream and ArduinoOutStream provide iostream functions | |||
| for Serial, LiquidCrystal, and other devices. | |||
| The SdVolume class supports FAT16 and FAT32 partitions. Most applications | |||
| will not need to call SdVolume member function. | |||
| The Sd2Card class supports access to standard SD cards and SDHC cards. Most | |||
| applications will not need to call Sd2Card functions. The Sd2Card class can | |||
| be used for raw access to the SD card. | |||
| A number of example are provided in the %SdFat/examples folder. These were | |||
| developed to test %SdFat and illustrate its use. | |||
| %SdFat was developed for high speed data recording. %SdFat was used to | |||
| implement an audio record/play class, WaveRP, for the Adafruit Wave Shield. | |||
| This application uses special Sd2Card calls to write to contiguous files in | |||
| raw mode. These functions reduce write latency so that audio can be | |||
| recorded with the small amount of RAM in the Arduino. | |||
| \section SDcard SD\SDHC Cards | |||
| Arduinos access SD cards using the cards SPI protocol. PCs, Macs, and | |||
| most consumer devices use the 4-bit parallel SD protocol. A card that | |||
| functions well on A PC or Mac may not work well on the Arduino. | |||
| Most cards have good SPI read performance but cards vary widely in SPI | |||
| write performance. Write performance is limited by how efficiently the | |||
| card manages internal erase/remapping operations. The Arduino cannot | |||
| optimize writes to reduce erase operations because of its limit RAM. | |||
| SanDisk cards generally have good write performance. They seem to have | |||
| more internal RAM buffering than other cards and therefore can limit | |||
| the number of flash erase operations that the Arduino forces due to its | |||
| limited RAM. | |||
| \section Hardware Hardware Configuration | |||
| %SdFat was developed using an | |||
| <A HREF = "http://www.adafruit.com/"> Adafruit Industries</A> | |||
| Data Logging Shield. | |||
| The hardware interface to the SD card should not use a resistor based level | |||
| shifter. %SdFat sets the SPI bus frequency to 8 MHz which results in signal | |||
| rise times that are too slow for the edge detectors in many newer SD card | |||
| controllers when resistor voltage dividers are used. | |||
| The 5 to 3.3 V level shifter for 5 V Arduinos should be IC based like the | |||
| 74HC4050N based circuit shown in the file SdLevel.png. The Adafruit Wave Shield | |||
| uses a 74AHC125N. Gravitech sells SD and MicroSD Card Adapters based on the | |||
| 74LCX245. | |||
| If you are using a resistor based level shifter and are having problems try | |||
| setting the SPI bus frequency to 4 MHz. This can be done by using | |||
| card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED) to initialize the SD card. | |||
| \section comment Bugs and Comments | |||
| If you wish to report bugs or have comments, send email to fat16lib@sbcglobal.net. | |||
| \section SdFatClass SdFat Usage | |||
| %SdFat uses a slightly restricted form of short names. | |||
| Only printable ASCII characters are supported. No characters with code point | |||
| values greater than 127 are allowed. Space is not allowed even though space | |||
| was allowed in the API of early versions of DOS. | |||
| Short names are limited to 8 characters followed by an optional period (.) | |||
| and extension of up to 3 characters. The characters may be any combination | |||
| of letters and digits. The following special characters are also allowed: | |||
| $ % ' - _ @ ~ ` ! ( ) { } ^ # & | |||
| Short names are always converted to upper case and their original case | |||
| value is lost. | |||
| \par | |||
| An application which writes to a file using print(), println() or | |||
| \link SdFile::write write() \endlink must call \link SdFile::sync() sync() \endlink | |||
| at the appropriate time to force data and directory information to be written | |||
| to the SD Card. Data and directory information are also written to the SD card | |||
| when \link SdFile::close() close() \endlink is called. | |||
| \par | |||
| Applications must use care calling \link SdFile::sync() sync() \endlink | |||
| since 2048 bytes of I/O is required to update file and | |||
| directory information. This includes writing the current data block, reading | |||
| the block that contains the directory entry for update, writing the directory | |||
| block back and reading back the current data block. | |||
| It is possible to open a file with two or more instances of SdFile. A file may | |||
| be corrupted if data is written to the file by more than one instance of SdFile. | |||
| \section HowTo How to format SD Cards as FAT Volumes | |||
| You should use a freshly formatted SD card for best performance. FAT | |||
| file systems become slower if many files have been created and deleted. | |||
| This is because the directory entry for a deleted file is marked as deleted, | |||
| but is not deleted. When a new file is created, these entries must be scanned | |||
| before creating the file, a flaw in the FAT design. Also files can become | |||
| fragmented which causes reads and writes to be slower. | |||
| A formatter sketch, SdFormatter.pde, is included in the | |||
| %SdFat/examples/SdFormatter directory. This sketch attempts to | |||
| emulate SD Association's SDFormatter. | |||
| The best way to restore an SD card's format on a PC is to use SDFormatter | |||
| which can be downloaded from: | |||
| http://www.sdcard.org/consumers/formatter/ | |||
| SDFormatter aligns flash erase boundaries with file | |||
| system structures which reduces write latency and file system overhead. | |||
| SDFormatter does not have an option for FAT type so it may format | |||
| small cards as FAT12. | |||
| After the MBR is restored by SDFormatter you may need to reformat small | |||
| cards that have been formatted FAT12 to force the volume type to be FAT16. | |||
| If you reformat the SD card with an OS utility, choose a cluster size that | |||
| will result in: | |||
| 4084 < CountOfClusters && CountOfClusters < 65525 | |||
| The volume will then be FAT16. | |||
| If you are formatting an SD card on OS X or Linux, be sure to use the first | |||
| partition. Format this partition with a cluster count in above range for FAT16. | |||
| SDHC cards should be formatted FAT32 with a cluster size of 32 KB. | |||
| Microsoft operating systems support removable media formatted with a | |||
| Master Boot Record, MBR, or formatted as a super floppy with a FAT Boot Sector | |||
| in block zero. | |||
| Microsoft operating systems expect MBR formatted removable media | |||
| to have only one partition. The first partition should be used. | |||
| Microsoft operating systems do not support partitioning SD flash cards. | |||
| If you erase an SD card with a program like KillDisk, Most versions of | |||
| Windows will format the card as a super floppy. | |||
| \section References References | |||
| The Arduino site: | |||
| http://www.arduino.cc/ | |||
| For more information about FAT file systems see: | |||
| http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/system/platform/firmware/fatgen.mspx | |||
| For information about using SD cards as SPI devices see: | |||
| http://www.sdcard.org/developers/tech/sdcard/pls/Simplified_Physical_Layer_Spec.pdf | |||
| The ATmega328 datasheet: | |||
| http://www.atmel.com/dyn/resources/prod_documents/doc8161.pdf | |||
| */ | |||
+ 83
- 0
SdFat/SdFile.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,83 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFile.h> | |||
| /** Create a file object and open it in the current working directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path A path with a valid 8.3 DOS name for a file to be opened. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] oflag Values for \a oflag are constructed by a bitwise-inclusive | |||
| * OR of open flags. see SdBaseFile::open(SdBaseFile*, const char*, uint8_t). | |||
| */ | |||
| SdFile::SdFile(const char* path, uint8_t oflag) : SdBaseFile(path, oflag) { | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Write data to an open file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \note Data is moved to the cache but may not be written to the | |||
| * storage device until sync() is called. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] buf Pointer to the location of the data to be written. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] nbyte Number of bytes to write. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return For success write() returns the number of bytes written, always | |||
| * \a nbyte. If an error occurs, write() returns -1. Possible errors | |||
| * include write() is called before a file has been opened, write is called | |||
| * for a read-only file, device is full, a corrupt file system or an I/O error. | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| int SdFile::write(const void* buf, size_t nbyte) { | |||
| return SdBaseFile::write(buf, nbyte); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Write a byte to a file. Required by the Arduino Print class. | |||
| * \param[in] b the byte to be written. | |||
| * Use getWriteError to check for errors. | |||
| * \return 1 for success and 0 for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t SdFile::write(uint8_t b) { | |||
| return SdBaseFile::write(&b, 1) == 1 ? 1 : 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Write a string to a file. Used by the Arduino Print class. | |||
| * \param[in] str Pointer to the string. | |||
| * Use getWriteError to check for errors. | |||
| * \return count of characters written for success or -1 for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| int SdFile::write(const char* str) { | |||
| return SdBaseFile::write(str, strlen(str)); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Write a PROGMEM string to a file. | |||
| * \param[in] str Pointer to the PROGMEM string. | |||
| * Use getWriteError to check for errors. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFile::write_P(PGM_P str) { | |||
| for (uint8_t c; (c = pgm_read_byte(str)); str++) write(c); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Write a PROGMEM string followed by CR/LF to a file. | |||
| * \param[in] str Pointer to the PROGMEM string. | |||
| * Use getWriteError to check for errors. | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdFile::writeln_P(PGM_P str) { | |||
| write_P(str); | |||
| write_P(PSTR("\r\n")); | |||
| } | |||
+ 51
- 0
SdFat/SdFile.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,51 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief SdFile class | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdBaseFile.h> | |||
| #ifndef SdFile_h | |||
| #define SdFile_h | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class SdFile | |||
| * \brief SdBaseFile with Print. | |||
| */ | |||
| class SdFile : public SdBaseFile, public Print { | |||
| public: | |||
| SdFile() {} | |||
| SdFile(const char* name, uint8_t oflag); | |||
| #if DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| ~SdFile() {} | |||
| #endif // DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| /** \return value of writeError */ | |||
| bool getWriteError() {return SdBaseFile::getWriteError();} | |||
| /** Set writeError to zero */ | |||
| void clearWriteError() {SdBaseFile::clearWriteError();} | |||
| size_t write(uint8_t b); | |||
| int write(const char* str); | |||
| int write(const void* buf, size_t nbyte); | |||
| size_t write(const uint8_t *buf, size_t size) { | |||
| return SdBaseFile::write(buf, size);} | |||
| void write_P(PGM_P str); | |||
| void writeln_P(PGM_P str); | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // SdFile_h | |||
+ 303
- 0
SdFat/SdInfo.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,303 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino Sd2Card Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino Sd2Card Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino Sd2Card Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdInfo_h | |||
| #define SdInfo_h | |||
| #include <stdint.h> | |||
| // Based on the document: | |||
| // | |||
| // SD Specifications | |||
| // Part 1 | |||
| // Physical Layer | |||
| // Simplified Specification | |||
| // Version 3.01 | |||
| // May 18, 2010 | |||
| // | |||
| // http://www.sdcard.org/developers/tech/sdcard/pls/simplified_specs | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // SPI divisor constants | |||
| /** Set SCK to max rate of F_CPU/2. */ | |||
| uint8_t const SPI_FULL_SPEED = 2; | |||
| /** Set SCK rate to F_CPU/3 for Due */ | |||
| uint8_t const SPI_DIV3_SPEED = 3; | |||
| /** Set SCK rate to F_CPU/4. */ | |||
| uint8_t const SPI_HALF_SPEED = 4; | |||
| /** Set SCK rate to F_CPU/6 for Due */ | |||
| uint8_t const SPI_DIV6_SPEED = 6; | |||
| /** Set SCK rate to F_CPU/8. */ | |||
| uint8_t const SPI_QUARTER_SPEED = 8; | |||
| /** Set SCK rate to F_CPU/16. */ | |||
| uint8_t const SPI_EIGHTH_SPEED = 16; | |||
| /** Set SCK rate to F_CPU/32. */ | |||
| uint8_t const SPI_SIXTEENTH_SPEED = 32; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // SD operation timeouts | |||
| /** init timeout ms */ | |||
| uint16_t const SD_INIT_TIMEOUT = 2000; | |||
| /** erase timeout ms */ | |||
| uint16_t const SD_ERASE_TIMEOUT = 10000; | |||
| /** read timeout ms */ | |||
| uint16_t const SD_READ_TIMEOUT = 300; | |||
| /** write time out ms */ | |||
| uint16_t const SD_WRITE_TIMEOUT = 600; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // SD card commands | |||
| /** GO_IDLE_STATE - init card in spi mode if CS low */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD0 = 0X00; | |||
| /** SEND_IF_COND - verify SD Memory Card interface operating condition.*/ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD8 = 0X08; | |||
| /** SEND_CSD - read the Card Specific Data (CSD register) */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD9 = 0X09; | |||
| /** SEND_CID - read the card identification information (CID register) */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD10 = 0X0A; | |||
| /** STOP_TRANSMISSION - end multiple block read sequence */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD12 = 0X0C; | |||
| /** SEND_STATUS - read the card status register */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD13 = 0X0D; | |||
| /** READ_SINGLE_BLOCK - read a single data block from the card */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD17 = 0X11; | |||
| /** READ_MULTIPLE_BLOCK - read a multiple data blocks from the card */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD18 = 0X12; | |||
| /** WRITE_BLOCK - write a single data block to the card */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD24 = 0X18; | |||
| /** WRITE_MULTIPLE_BLOCK - write blocks of data until a STOP_TRANSMISSION */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD25 = 0X19; | |||
| /** ERASE_WR_BLK_START - sets the address of the first block to be erased */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD32 = 0X20; | |||
| /** ERASE_WR_BLK_END - sets the address of the last block of the continuous | |||
| range to be erased*/ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD33 = 0X21; | |||
| /** ERASE - erase all previously selected blocks */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD38 = 0X26; | |||
| /** APP_CMD - escape for application specific command */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD55 = 0X37; | |||
| /** READ_OCR - read the OCR register of a card */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD58 = 0X3A; | |||
| /** CRC_ON_OFF - enable or disable CRC checking */ | |||
| uint8_t const CMD59 = 0X3B; | |||
| /** SET_WR_BLK_ERASE_COUNT - Set the number of write blocks to be | |||
| pre-erased before writing */ | |||
| uint8_t const ACMD23 = 0X17; | |||
| /** SD_SEND_OP_COMD - Sends host capacity support information and | |||
| activates the card's initialization process */ | |||
| uint8_t const ACMD41 = 0X29; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** status for card in the ready state */ | |||
| uint8_t const R1_READY_STATE = 0X00; | |||
| /** status for card in the idle state */ | |||
| uint8_t const R1_IDLE_STATE = 0X01; | |||
| /** status bit for illegal command */ | |||
| uint8_t const R1_ILLEGAL_COMMAND = 0X04; | |||
| /** start data token for read or write single block*/ | |||
| uint8_t const DATA_START_BLOCK = 0XFE; | |||
| /** stop token for write multiple blocks*/ | |||
| uint8_t const STOP_TRAN_TOKEN = 0XFD; | |||
| /** start data token for write multiple blocks*/ | |||
| uint8_t const WRITE_MULTIPLE_TOKEN = 0XFC; | |||
| /** mask for data response tokens after a write block operation */ | |||
| uint8_t const DATA_RES_MASK = 0X1F; | |||
| /** write data accepted token */ | |||
| uint8_t const DATA_RES_ACCEPTED = 0X05; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Card IDentification (CID) register */ | |||
| typedef struct CID { | |||
| // byte 0 | |||
| /** Manufacturer ID */ | |||
| unsigned char mid; | |||
| // byte 1-2 | |||
| /** OEM/Application ID */ | |||
| char oid[2]; | |||
| // byte 3-7 | |||
| /** Product name */ | |||
| char pnm[5]; | |||
| // byte 8 | |||
| /** Product revision least significant digit */ | |||
| unsigned char prv_m : 4; | |||
| /** Product revision most significant digit */ | |||
| unsigned char prv_n : 4; | |||
| // byte 9-12 | |||
| /** Product serial number */ | |||
| uint32_t psn; | |||
| // byte 13 | |||
| /** Manufacturing date year low digit */ | |||
| unsigned char mdt_year_high : 4; | |||
| /** not used */ | |||
| unsigned char reserved : 4; | |||
| // byte 14 | |||
| /** Manufacturing date month */ | |||
| unsigned char mdt_month : 4; | |||
| /** Manufacturing date year low digit */ | |||
| unsigned char mdt_year_low :4; | |||
| // byte 15 | |||
| /** not used always 1 */ | |||
| unsigned char always1 : 1; | |||
| /** CRC7 checksum */ | |||
| unsigned char crc : 7; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)) cid_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** CSD for version 1.00 cards */ | |||
| typedef struct CSDV1 { | |||
| // byte 0 | |||
| unsigned char reserved1 : 6; | |||
| unsigned char csd_ver : 2; | |||
| // byte 1 | |||
| unsigned char taac; | |||
| // byte 2 | |||
| unsigned char nsac; | |||
| // byte 3 | |||
| unsigned char tran_speed; | |||
| // byte 4 | |||
| unsigned char ccc_high; | |||
| // byte 5 | |||
| unsigned char read_bl_len : 4; | |||
| unsigned char ccc_low : 4; | |||
| // byte 6 | |||
| unsigned char c_size_high : 2; | |||
| unsigned char reserved2 : 2; | |||
| unsigned char dsr_imp : 1; | |||
| unsigned char read_blk_misalign :1; | |||
| unsigned char write_blk_misalign : 1; | |||
| unsigned char read_bl_partial : 1; | |||
| // byte 7 | |||
| unsigned char c_size_mid; | |||
| // byte 8 | |||
| unsigned char vdd_r_curr_max : 3; | |||
| unsigned char vdd_r_curr_min : 3; | |||
| unsigned char c_size_low :2; | |||
| // byte 9 | |||
| unsigned char c_size_mult_high : 2; | |||
| unsigned char vdd_w_cur_max : 3; | |||
| unsigned char vdd_w_curr_min : 3; | |||
| // byte 10 | |||
| unsigned char sector_size_high : 6; | |||
| unsigned char erase_blk_en : 1; | |||
| unsigned char c_size_mult_low : 1; | |||
| // byte 11 | |||
| unsigned char wp_grp_size : 7; | |||
| unsigned char sector_size_low : 1; | |||
| // byte 12 | |||
| unsigned char write_bl_len_high : 2; | |||
| unsigned char r2w_factor : 3; | |||
| unsigned char reserved3 : 2; | |||
| unsigned char wp_grp_enable : 1; | |||
| // byte 13 | |||
| unsigned char reserved4 : 5; | |||
| unsigned char write_partial : 1; | |||
| unsigned char write_bl_len_low : 2; | |||
| // byte 14 | |||
| unsigned char reserved5: 2; | |||
| unsigned char file_format : 2; | |||
| unsigned char tmp_write_protect : 1; | |||
| unsigned char perm_write_protect : 1; | |||
| unsigned char copy : 1; | |||
| /** Indicates the file format on the card */ | |||
| unsigned char file_format_grp : 1; | |||
| // byte 15 | |||
| unsigned char always1 : 1; | |||
| unsigned char crc : 7; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)) csd1_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** CSD for version 2.00 cards */ | |||
| typedef struct CSDV2 { | |||
| // byte 0 | |||
| unsigned char reserved1 : 6; | |||
| unsigned char csd_ver : 2; | |||
| // byte 1 | |||
| /** fixed to 0X0E */ | |||
| unsigned char taac; | |||
| // byte 2 | |||
| /** fixed to 0 */ | |||
| unsigned char nsac; | |||
| // byte 3 | |||
| unsigned char tran_speed; | |||
| // byte 4 | |||
| unsigned char ccc_high; | |||
| // byte 5 | |||
| /** This field is fixed to 9h, which indicates READ_BL_LEN=512 Byte */ | |||
| unsigned char read_bl_len : 4; | |||
| unsigned char ccc_low : 4; | |||
| // byte 6 | |||
| /** not used */ | |||
| unsigned char reserved2 : 4; | |||
| unsigned char dsr_imp : 1; | |||
| /** fixed to 0 */ | |||
| unsigned char read_blk_misalign :1; | |||
| /** fixed to 0 */ | |||
| unsigned char write_blk_misalign : 1; | |||
| /** fixed to 0 - no partial read */ | |||
| unsigned char read_bl_partial : 1; | |||
| // byte 7 | |||
| /** high part of card size */ | |||
| unsigned char c_size_high : 6; | |||
| /** not used */ | |||
| unsigned char reserved3 : 2; | |||
| // byte 8 | |||
| /** middle part of card size */ | |||
| unsigned char c_size_mid; | |||
| // byte 9 | |||
| /** low part of card size */ | |||
| unsigned char c_size_low; | |||
| // byte 10 | |||
| /** sector size is fixed at 64 KB */ | |||
| unsigned char sector_size_high : 6; | |||
| /** fixed to 1 - erase single is supported */ | |||
| unsigned char erase_blk_en : 1; | |||
| /** not used */ | |||
| unsigned char reserved4 : 1; | |||
| // byte 11 | |||
| unsigned char wp_grp_size : 7; | |||
| /** sector size is fixed at 64 KB */ | |||
| unsigned char sector_size_low : 1; | |||
| // byte 12 | |||
| /** write_bl_len fixed for 512 byte blocks */ | |||
| unsigned char write_bl_len_high : 2; | |||
| /** fixed value of 2 */ | |||
| unsigned char r2w_factor : 3; | |||
| /** not used */ | |||
| unsigned char reserved5 : 2; | |||
| /** fixed value of 0 - no write protect groups */ | |||
| unsigned char wp_grp_enable : 1; | |||
| // byte 13 | |||
| unsigned char reserved6 : 5; | |||
| /** always zero - no partial block read*/ | |||
| unsigned char write_partial : 1; | |||
| /** write_bl_len fixed for 512 byte blocks */ | |||
| unsigned char write_bl_len_low : 2; | |||
| // byte 14 | |||
| unsigned char reserved7: 2; | |||
| /** Do not use always 0 */ | |||
| unsigned char file_format : 2; | |||
| unsigned char tmp_write_protect : 1; | |||
| unsigned char perm_write_protect : 1; | |||
| unsigned char copy : 1; | |||
| /** Do not use always 0 */ | |||
| unsigned char file_format_grp : 1; | |||
| // byte 15 | |||
| /** not used always 1 */ | |||
| unsigned char always1 : 1; | |||
| /** checksum */ | |||
| unsigned char crc : 7; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)) csd2_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** union of old and new style CSD register */ | |||
| union csd_t { | |||
| csd1_t v1; | |||
| csd2_t v2; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // SdInfo_h | |||
+ 173
- 0
SdFat/SdSpi.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,173 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdSpi Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief SdSpi class for V2 SD/SDHC cards | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdSpi_h | |||
| #define SdSpi_h | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatConfig.h> | |||
| #if !USE_ARDUINO_SPI_LIBRARY | |||
| // AVR Arduinos | |||
| #ifdef __AVR__ | |||
| #if AVR_SOFT_SPI | |||
| #define USE_SOFTWARE_SPI 1 | |||
| #elif LEONARDO_SOFT_SPI && defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) && !defined(CORE_TEENSY) | |||
| #define USE_SOFTWARE_SPI 1 | |||
| #elif MEGA_SOFT_SPI && (defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__)\ | |||
| ||defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__)) | |||
| #define USE_SOFTWARE_SPI 1 | |||
| #else // USE_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| #define USE_NATIVE_AVR_SPI 1 | |||
| #endif // USE_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| #endif // __AVR__ | |||
| // Due | |||
| #if defined(__arm__) && !defined(CORE_TEENSY) | |||
| #if DUE_SOFT_SPI | |||
| #define USE_SOFTWARE_SPI 1 | |||
| #else // DUE_SOFT_SPI | |||
| /** Nonzero - use native SAM3X SPI */ | |||
| #define USE_NATIVE_SAM3X_SPI 1 | |||
| #endif // DUE_SOFT_SPI | |||
| #endif // defined(__arm__) && !defined(CORE_TEENSY) | |||
| // Teensy 3.0 | |||
| #if defined(__arm__) && defined(CORE_TEENSY) | |||
| #if TEENSY3_SOFT_SPI | |||
| #define USE_SOFTWARE_SPI 1 | |||
| #else // TEENSY3_SOFT_SPI | |||
| /** Nonzero - use native MK20DX128 SPI */ | |||
| #define USE_NATIVE_TEENSY3_SPI 1 | |||
| #endif // TEENSY3_SOFT_SPI | |||
| #endif // defined(__arm__) && defined(CORE_TEENSY) | |||
| #endif // !USE_ARDUINO_SPI_LIBRARY | |||
| #ifndef USE_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| #define USE_SOFTWARE_SPI 0 | |||
| #endif // USE_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| #ifndef USE_NATIVE_AVR_SPI | |||
| #define USE_NATIVE_AVR_SPI 0 | |||
| #endif | |||
| #ifndef USE_NATIVE_SAM3X_SPI | |||
| #define USE_NATIVE_SAM3X_SPI 0 | |||
| #endif // USE_NATIVE_SAM3X_SPI | |||
| #ifndef USE_NATIVE_TEENSY3_SPI | |||
| #define USE_NATIVE_TEENSY3_SPI 0 | |||
| #endif // USE_NATIVE_TEENSY3_SPI | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // define default chip select pin | |||
| // | |||
| #if !USE_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| /** The default chip select pin for the SD card is SS. */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CHIP_SELECT_PIN = SS; | |||
| #else // USE_AVR_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| /** SPI chip select pin for software SPI. */ | |||
| uint8_t const SD_CHIP_SELECT_PIN = SOFT_SPI_CS_PIN; | |||
| #endif // USE_AVR_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class SdSpi | |||
| * \brief SPI class for access to SD and SDHC flash memory cards. | |||
| */ | |||
| class SdSpi { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** Initialize the SPI bus */ | |||
| void begin(); | |||
| /** Set SPI options for access to SD/SDHC cards. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] spiDivisor SCK clock divider relative to the system clock. | |||
| */ | |||
| void init(uint8_t spiDivisor); | |||
| /** Receive a byte. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The byte. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t receive(); | |||
| /** Receive multiple bytes. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] buf Buffer to receive the data. | |||
| * \param[in] n Number of bytes to receive. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Zero for no error or nonzero error code. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t receive(uint8_t* buf, size_t n); | |||
| /** Send a byte. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] data Byte to send | |||
| */ | |||
| void send(uint8_t data); | |||
| /** Send multiple bytes. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] buf Buffer for data to be sent. | |||
| * \param[in] n Number of bytes to send. | |||
| */ | |||
| void send(const uint8_t* buf, size_t n); | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Use of inline for AVR results in up to 10% better write performance. | |||
| // Inline also save a little flash memory. | |||
| /** inline avr native functions if nonzero. */ | |||
| #define USE_AVR_NATIVE_SPI_INLINE 1 | |||
| #if USE_NATIVE_AVR_SPI && USE_AVR_NATIVE_SPI_INLINE | |||
| inline uint8_t SdSpi::receive() { | |||
| SPDR = 0XFF; | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| return SPDR; | |||
| } | |||
| inline uint8_t SdSpi::receive(uint8_t* buf, size_t n) { | |||
| if (n-- == 0) return 0; | |||
| SPDR = 0XFF; | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| uint8_t b = SPDR; | |||
| SPDR = 0XFF; | |||
| buf[i] = b; | |||
| } | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| buf[n] = SPDR; | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| inline void SdSpi::send(uint8_t data) { | |||
| SPDR = data; | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| } | |||
| inline void SdSpi::send(const uint8_t* buf , size_t n) { | |||
| if (n == 0) return; | |||
| SPDR = buf[0]; | |||
| if (n > 1) { | |||
| uint8_t b = buf[1]; | |||
| size_t i = 2; | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| SPDR = b; | |||
| if (i == n) break; | |||
| b = buf[i++]; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_NATIVE_AVR_SPI && USE_AVR_NATIVE_SPI_INLINE | |||
| #endif // SdSpi_h | |||
+ 86
- 0
SdFat/SdSpiAVR.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,86 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdSpi Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdSpi.h> | |||
| #if USE_NATIVE_AVR_SPI | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::begin() { | |||
| // set SS high - may be chip select for another SPI device | |||
| digitalWrite(SS, HIGH); | |||
| // SS must be in output mode even it is not chip select | |||
| pinMode(SS, OUTPUT); | |||
| pinMode(MISO, INPUT); | |||
| pinMode(MOSI, OUTPUT); | |||
| pinMode(SCK, OUTPUT); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::init(uint8_t sckDivisor) { | |||
| uint8_t r = 0; | |||
| for (uint8_t b = 2; sckDivisor > b && r < 6; b <<= 1, r++) {} | |||
| // See avr processor documentation | |||
| SPCR = (1 << SPE) | (1 << MSTR) | (r >> 1); | |||
| SPSR = r & 1 || r == 6 ? 0 : 1 << SPI2X; | |||
| } | |||
| #if !USE_AVR_NATIVE_SPI_INLINE | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive() { | |||
| SPDR = 0XFF; | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| return SPDR; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive(uint8_t* buf, size_t n) { | |||
| if (n-- == 0) return 0; | |||
| SPDR = 0XFF; | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| uint8_t b = SPDR; | |||
| SPDR = 0XFF; | |||
| buf[i] = b; | |||
| } | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| buf[n] = SPDR; | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(uint8_t data) { | |||
| SPDR = data; | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(const uint8_t* buf , size_t n) { | |||
| if (n == 0) return; | |||
| SPDR = buf[0]; | |||
| if (n > 1) { | |||
| uint8_t b = buf[1]; | |||
| size_t i = 2; | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| SPDR = b; | |||
| if (i == n) break; | |||
| b = buf[i++]; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| while (!(SPSR & (1 << SPIF))) {} | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // !USE_AVR_NATIVE_SPI_INLINE | |||
| #endif // USE_NATIVE_AVR_SPI | |||
+ 70
- 0
SdFat/SdSpiArduino.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,70 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdSpi Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdSpi.h> | |||
| #if USE_ARDUINO_SPI_LIBRARY | |||
| #include <SPI.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::begin() { | |||
| SPI.begin(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::init(uint8_t sckDivisor) { | |||
| SPI.setBitOrder(MSBFIRST); | |||
| SPI.setDataMode(SPI_MODE0); | |||
| #ifndef SPI_CLOCK_DIV128 | |||
| SPI.setClockDivider(sckDivisor); | |||
| #else // SPI_CLOCK_DIV128 | |||
| int v; | |||
| if (sckDivisor <= 2) v = SPI_CLOCK_DIV2; | |||
| else if (sckDivisor <= 4) v = SPI_CLOCK_DIV4; | |||
| else if (sckDivisor <= 8) v = SPI_CLOCK_DIV8; | |||
| else if (sckDivisor <= 16) v = SPI_CLOCK_DIV16; | |||
| else if (sckDivisor <= 32) v = SPI_CLOCK_DIV32; | |||
| else if (sckDivisor <= 64) v = SPI_CLOCK_DIV64; | |||
| else v = SPI_CLOCK_DIV128; | |||
| SPI.setClockDivider(v); | |||
| #endif // SPI_CLOCK_DIV128 | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI receive a byte */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive() { | |||
| return SPI.transfer(0XFF); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI receive multiple bytes */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive(uint8_t* buf, size_t n) { | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| buf[i] = SPI.transfer(0XFF); | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI send a byte */ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(uint8_t b) { | |||
| SPI.transfer(b); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI send multiple bytes */ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(const uint8_t* buf , size_t n) { | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| SPI.transfer(buf[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_ARDUINO_SPI_LIBRARY | |||
+ 216
- 0
SdFat/SdSpiSAM3X.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,216 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdSpi Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdSpi.h> | |||
| #if USE_NATIVE_SAM3X_SPI | |||
| /** Use SAM3X DMAC if nonzero */ | |||
| #define USE_SAM3X_DMAC 1 | |||
| /** Use extra Bus Matrix arbitration fix if nonzero */ | |||
| #define USE_SAM3X_BUS_MATRIX_FIX 0 | |||
| /** Time in ms for DMA receive timeout */ | |||
| #define SAM3X_DMA_TIMEOUT 100 | |||
| /** chip select register number */ | |||
| #define SPI_CHIP_SEL 3 | |||
| /** DMAC receive channel */ | |||
| #define SPI_DMAC_RX_CH 1 | |||
| /** DMAC transmit channel */ | |||
| #define SPI_DMAC_TX_CH 0 | |||
| /** DMAC Channel HW Interface Number for SPI TX. */ | |||
| #define SPI_TX_IDX 1 | |||
| /** DMAC Channel HW Interface Number for SPI RX. */ | |||
| #define SPI_RX_IDX 2 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Disable DMA Controller. */ | |||
| static void dmac_disable() { | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_EN &= (~DMAC_EN_ENABLE); | |||
| } | |||
| /** Enable DMA Controller. */ | |||
| static void dmac_enable() { | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_EN = DMAC_EN_ENABLE; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Disable DMA Channel. */ | |||
| static void dmac_channel_disable(uint32_t ul_num) { | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CHDR = DMAC_CHDR_DIS0 << ul_num; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Enable DMA Channel. */ | |||
| static void dmac_channel_enable(uint32_t ul_num) { | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CHER = DMAC_CHER_ENA0 << ul_num; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Poll for transfer complete. */ | |||
| static bool dmac_channel_transfer_done(uint32_t ul_num) { | |||
| return (DMAC->DMAC_CHSR & (DMAC_CHSR_ENA0 << ul_num)) ? false : true; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::begin() { | |||
| PIO_Configure( | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MOSI].pPort, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MOSI].ulPinType, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MOSI].ulPin, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MOSI].ulPinConfiguration); | |||
| PIO_Configure( | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MISO].pPort, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MISO].ulPinType, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MISO].ulPin, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_MISO].ulPinConfiguration); | |||
| PIO_Configure( | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_SCK].pPort, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_SCK].ulPinType, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_SCK].ulPin, | |||
| g_APinDescription[PIN_SPI_SCK].ulPinConfiguration); | |||
| pmc_enable_periph_clk(ID_SPI0); | |||
| #if USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| pmc_enable_periph_clk(ID_DMAC); | |||
| dmac_disable(); | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_GCFG = DMAC_GCFG_ARB_CFG_FIXED; | |||
| dmac_enable(); | |||
| #if USE_SAM3X_BUS_MATRIX_FIX | |||
| MATRIX->MATRIX_WPMR = 0x4d415400; | |||
| MATRIX->MATRIX_MCFG[1] = 1; | |||
| MATRIX->MATRIX_MCFG[2] = 1; | |||
| MATRIX->MATRIX_SCFG[0] = 0x01000010; | |||
| MATRIX->MATRIX_SCFG[1] = 0x01000010; | |||
| MATRIX->MATRIX_SCFG[7] = 0x01000010; | |||
| #endif // USE_SAM3X_BUS_MATRIX_FIX | |||
| #endif // USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // start RX DMA | |||
| static void spiDmaRX(uint8_t* dst, uint16_t count) { | |||
| dmac_channel_disable(SPI_DMAC_RX_CH); | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_RX_CH].DMAC_SADDR = (uint32_t)&SPI0->SPI_RDR; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_RX_CH].DMAC_DADDR = (uint32_t)dst; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_RX_CH].DMAC_DSCR = 0; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_RX_CH].DMAC_CTRLA = count | | |||
| DMAC_CTRLA_SRC_WIDTH_BYTE | DMAC_CTRLA_DST_WIDTH_BYTE; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_RX_CH].DMAC_CTRLB = DMAC_CTRLB_SRC_DSCR | | |||
| DMAC_CTRLB_DST_DSCR | DMAC_CTRLB_FC_PER2MEM_DMA_FC | | |||
| DMAC_CTRLB_SRC_INCR_FIXED | DMAC_CTRLB_DST_INCR_INCREMENTING; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_RX_CH].DMAC_CFG = DMAC_CFG_SRC_PER(SPI_RX_IDX) | | |||
| DMAC_CFG_SRC_H2SEL | DMAC_CFG_SOD | DMAC_CFG_FIFOCFG_ASAP_CFG; | |||
| dmac_channel_enable(SPI_DMAC_RX_CH); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // start TX DMA | |||
| static void spiDmaTX(const uint8_t* src, uint16_t count) { | |||
| static uint8_t ff = 0XFF; | |||
| uint32_t src_incr = DMAC_CTRLB_SRC_INCR_INCREMENTING; | |||
| if (!src) { | |||
| src = &ff; | |||
| src_incr = DMAC_CTRLB_SRC_INCR_FIXED; | |||
| } | |||
| dmac_channel_disable(SPI_DMAC_TX_CH); | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_TX_CH].DMAC_SADDR = (uint32_t)src; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_TX_CH].DMAC_DADDR = (uint32_t)&SPI0->SPI_TDR; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_TX_CH].DMAC_DSCR = 0; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_TX_CH].DMAC_CTRLA = count | | |||
| DMAC_CTRLA_SRC_WIDTH_BYTE | DMAC_CTRLA_DST_WIDTH_BYTE; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_TX_CH].DMAC_CTRLB = DMAC_CTRLB_SRC_DSCR | | |||
| DMAC_CTRLB_DST_DSCR | DMAC_CTRLB_FC_MEM2PER_DMA_FC | | |||
| src_incr | DMAC_CTRLB_DST_INCR_FIXED; | |||
| DMAC->DMAC_CH_NUM[SPI_DMAC_TX_CH].DMAC_CFG = DMAC_CFG_DST_PER(SPI_TX_IDX) | | |||
| DMAC_CFG_DST_H2SEL | DMAC_CFG_SOD | DMAC_CFG_FIFOCFG_ALAP_CFG; | |||
| dmac_channel_enable(SPI_DMAC_TX_CH); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // initialize SPI controller | |||
| void SdSpi::init(uint8_t sckDivisor) { | |||
| uint8_t scbr = sckDivisor; | |||
| Spi* pSpi = SPI0; | |||
| // disable SPI | |||
| pSpi->SPI_CR = SPI_CR_SPIDIS; | |||
| // reset SPI | |||
| pSpi->SPI_CR = SPI_CR_SWRST; | |||
| // no mode fault detection, set master mode | |||
| pSpi->SPI_MR = SPI_PCS(SPI_CHIP_SEL) | SPI_MR_MODFDIS | SPI_MR_MSTR; | |||
| // mode 0, 8-bit, | |||
| pSpi->SPI_CSR[SPI_CHIP_SEL] = SPI_CSR_SCBR(scbr) | SPI_CSR_NCPHA; | |||
| // enable SPI | |||
| pSpi->SPI_CR |= SPI_CR_SPIEN; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| static inline uint8_t spiTransfer(uint8_t b) { | |||
| Spi* pSpi = SPI0; | |||
| pSpi->SPI_TDR = b; | |||
| while ((pSpi->SPI_SR & SPI_SR_RDRF) == 0) {} | |||
| b = pSpi->SPI_RDR; | |||
| return b; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI receive a byte */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive() { | |||
| return spiTransfer(0XFF); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI receive multiple bytes */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive(uint8_t* buf, size_t n) { | |||
| Spi* pSpi = SPI0; | |||
| int rtn = 0; | |||
| #if USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| // clear overrun error | |||
| uint32_t s = pSpi->SPI_SR; | |||
| spiDmaRX(buf, n); | |||
| spiDmaTX(0, n); | |||
| uint32_t m = millis(); | |||
| while (!dmac_channel_transfer_done(SPI_DMAC_RX_CH)) { | |||
| if ((millis() - m) > SAM3X_DMA_TIMEOUT) { | |||
| dmac_channel_disable(SPI_DMAC_RX_CH); | |||
| dmac_channel_disable(SPI_DMAC_TX_CH); | |||
| rtn = 2; | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (pSpi->SPI_SR & SPI_SR_OVRES) rtn |= 1; | |||
| #else // USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| pSpi->SPI_TDR = 0XFF; | |||
| while ((pSpi->SPI_SR & SPI_SR_RDRF) == 0) {} | |||
| buf[i] = pSpi->SPI_RDR; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| return rtn; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI send a byte */ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(uint8_t b) { | |||
| spiTransfer(b); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(const uint8_t* buf , size_t n) { | |||
| Spi* pSpi = SPI0; | |||
| #if USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| spiDmaTX(buf, n); | |||
| while (!dmac_channel_transfer_done(SPI_DMAC_TX_CH)) {} | |||
| #else // #if USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| while ((pSpi->SPI_SR & SPI_SR_TXEMPTY) == 0) {} | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| pSpi->SPI_TDR = buf[i]; | |||
| while ((pSpi->SPI_SR & SPI_SR_TDRE) == 0) {} | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // #if USE_SAM3X_DMAC | |||
| while ((pSpi->SPI_SR & SPI_SR_TXEMPTY) == 0) {} | |||
| // leave RDR empty | |||
| uint8_t b = pSpi->SPI_RDR; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_NATIVE_SAM3X_SPI | |||
+ 61
- 0
SdFat/SdSpiSoft.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,61 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdSpi Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdSpi.h> | |||
| #if USE_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
| #include <SoftSPI.h> | |||
| static | |||
| SoftSPI<SOFT_SPI_MISO_PIN, SOFT_SPI_MOSI_PIN, SOFT_SPI_SCK_PIN, 0> softSpiBus; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * initialize SPI pins | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdSpi::begin() { | |||
| softSpiBus.begin(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Initialize hardware SPI - dummy for soft SPI | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdSpi::init(uint8_t sckDivisor) {} | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Soft SPI receive byte */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive() { | |||
| return softSpiBus.receive(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Soft SPI read data */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive(uint8_t* buf, size_t n) { | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| buf[i] = receive(); | |||
| } | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Soft SPI send byte */ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(uint8_t data) { | |||
| softSpiBus.send(data); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(const uint8_t* buf , size_t n) { | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| send(buf[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_SOFTWARE_SPI | |||
+ 223
- 0
SdFat/SdSpiTeensy3.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,223 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdSpi Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdSpi Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdSpi.h> | |||
| #if USE_NATIVE_TEENSY3_SPI | |||
| // Teensy 3.0 functions | |||
| #include <mk20dx128.h> | |||
| // use 16-bit frame if SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME is zero | |||
| #define SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME 0 | |||
| // Limit initial fifo to three entries to avoid fifo overrun | |||
| #define SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH 3 | |||
| // define some symbols that are not in mk20dx128.h | |||
| #ifndef SPI_SR_RXCTR | |||
| #define SPI_SR_RXCTR 0XF0 | |||
| #endif // SPI_SR_RXCTR | |||
| #ifndef SPI_PUSHR_CONT | |||
| #define SPI_PUSHR_CONT 0X80000000 | |||
| #endif // SPI_PUSHR_CONT | |||
| #ifndef SPI_PUSHR_CTAS | |||
| #define SPI_PUSHR_CTAS(n) (((n) & 7) << 28) | |||
| #endif // SPI_PUSHR_CTAS | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * initialize SPI pins | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdSpi::begin() { | |||
| SIM_SCGC6 |= SIM_SCGC6_SPI0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Initialize hardware SPI | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| void SdSpi::init(uint8_t sckDivisor) { | |||
| uint32_t ctar, ctar0, ctar1; | |||
| if (sckDivisor <= 2) { | |||
| // 1/2 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_DBR | SPI_CTAR_BR(0) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(0); | |||
| } else if (sckDivisor <= 4) { | |||
| // 1/4 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_BR(0) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(0); | |||
| } else if (sckDivisor <= 8) { | |||
| // 1/8 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_BR(1) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(1); | |||
| } else if (sckDivisor <= 12) { | |||
| // 1/12 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_BR(2) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(2); | |||
| } else if (sckDivisor <= 16) { | |||
| // 1/16 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_BR(3) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(3); | |||
| } else if (sckDivisor <= 32) { | |||
| // 1/32 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_PBR(1) | SPI_CTAR_BR(4) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(4); | |||
| } else if (sckDivisor <= 64) { | |||
| // 1/64 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_PBR(1) | SPI_CTAR_BR(5) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(5); | |||
| } else { | |||
| // 1/128 speed | |||
| ctar = SPI_CTAR_PBR(1) | SPI_CTAR_BR(6) | SPI_CTAR_CSSCK(6); | |||
| } | |||
| // CTAR0 - 8 bit transfer | |||
| ctar0 = ctar | SPI_CTAR_FMSZ(7); | |||
| // CTAR1 - 16 bit transfer | |||
| ctar1 = ctar | SPI_CTAR_FMSZ(15); | |||
| if (SPI0_CTAR0 != ctar0 || SPI0_CTAR1 != ctar1) { | |||
| SPI0_MCR = SPI_MCR_MSTR | SPI_MCR_MDIS | SPI_MCR_HALT | SPI_MCR_PCSIS(0x1F); | |||
| SPI0_CTAR0 = ctar0; | |||
| SPI0_CTAR1 = ctar1; | |||
| } | |||
| SPI0_MCR = SPI_MCR_MSTR | SPI_MCR_PCSIS(0x1F); | |||
| CORE_PIN11_CONFIG = PORT_PCR_DSE | PORT_PCR_MUX(2); | |||
| CORE_PIN12_CONFIG = PORT_PCR_MUX(2); | |||
| CORE_PIN13_CONFIG = PORT_PCR_DSE | PORT_PCR_MUX(2); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI receive a byte */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive() { | |||
| SPI0_MCR |= SPI_MCR_CLR_RXF; | |||
| SPI0_SR = SPI_SR_TCF; | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = 0xFF; | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_TCF)) {} | |||
| return SPI0_POPR; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI receive multiple bytes */ | |||
| uint8_t SdSpi::receive(uint8_t* buf, size_t n) { | |||
| // clear any data in RX FIFO | |||
| SPI0_MCR = SPI_MCR_MSTR | SPI_MCR_CLR_RXF | SPI_MCR_PCSIS(0x1F); | |||
| #if SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME | |||
| // initial number of bytes to push into TX FIFO | |||
| int nf = n < SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH ? n : SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH; | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < nf; i++) { | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = 0XFF; | |||
| } | |||
| // limit for pushing dummy data into TX FIFO | |||
| uint8_t* limit = buf + n - nf; | |||
| while (buf < limit) { | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = 0XFF; | |||
| *buf++ = SPI0_POPR; | |||
| } | |||
| // limit for rest of RX data | |||
| limit += nf; | |||
| while (buf < limit) { | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| *buf++ = SPI0_POPR; | |||
| } | |||
| #else // SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME | |||
| // use 16 bit frame to avoid TD delay between frames | |||
| // get one byte if n is odd | |||
| if (n & 1) { | |||
| *buf++ = receive(); | |||
| n--; | |||
| } | |||
| // initial number of words to push into TX FIFO | |||
| int nf = n/2 < SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH ? n/2 : SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH; | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < nf; i++) { | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = SPI_PUSHR_CONT | SPI_PUSHR_CTAS(1) | 0XFFFF; | |||
| } | |||
| uint8_t* limit = buf + n - 2*nf; | |||
| while (buf < limit) { | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = SPI_PUSHR_CONT | SPI_PUSHR_CTAS(1) | 0XFFFF; | |||
| uint16_t w = SPI0_POPR; | |||
| *buf++ = w >> 8; | |||
| *buf++ = w & 0XFF; | |||
| } | |||
| // limit for rest of RX data | |||
| limit += 2*nf; | |||
| while (buf < limit) { | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| uint16_t w = SPI0_POPR; | |||
| *buf++ = w >> 8; | |||
| *buf++ = w & 0XFF; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI send a byte */ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(uint8_t b) { | |||
| SPI0_MCR |= SPI_MCR_CLR_RXF; | |||
| SPI0_SR = SPI_SR_TCF; | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = b; | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_TCF)) {} | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** SPI send multiple bytes */ | |||
| void SdSpi::send(const uint8_t* buf , size_t n) { | |||
| // clear any data in RX FIFO | |||
| SPI0_MCR = SPI_MCR_MSTR | SPI_MCR_CLR_RXF | SPI_MCR_PCSIS(0x1F); | |||
| #if SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME | |||
| // initial number of bytes to push into TX FIFO | |||
| int nf = n < SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH ? n : SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH; | |||
| // limit for pushing data into TX fifo | |||
| const uint8_t* limit = buf + n; | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < nf; i++) { | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = *buf++; | |||
| } | |||
| // write data to TX FIFO | |||
| while (buf < limit) { | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = *buf++; | |||
| SPI0_POPR; | |||
| } | |||
| // wait for data to be sent | |||
| while (nf) { | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| SPI0_POPR; | |||
| nf--; | |||
| } | |||
| #else // SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME | |||
| // use 16 bit frame to avoid TD delay between frames | |||
| // send one byte if n is odd | |||
| if (n & 1) { | |||
| send(*buf++); | |||
| n--; | |||
| } | |||
| // initial number of words to push into TX FIFO | |||
| int nf = n/2 < SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH ? n/2 : SPI_INITIAL_FIFO_DEPTH; | |||
| // limit for pushing data into TX fifo | |||
| const uint8_t* limit = buf + n; | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < nf; i++) { | |||
| uint16_t w = (*buf++) << 8; | |||
| w |= *buf++; | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = SPI_PUSHR_CONT | SPI_PUSHR_CTAS(1) | w; | |||
| } | |||
| // write data to TX FIFO | |||
| while (buf < limit) { | |||
| uint16_t w = *buf++ << 8; | |||
| w |= *buf++; | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| SPI0_PUSHR = SPI_PUSHR_CONT | SPI_PUSHR_CTAS(1) | w; | |||
| SPI0_POPR; | |||
| } | |||
| // wait for data to be sent | |||
| while (nf) { | |||
| while (!(SPI0_SR & SPI_SR_RXCTR)) {} | |||
| SPI0_POPR; | |||
| nf--; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // SPI_USE_8BIT_FRAME | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_NATIVE_TEENSY3_SPI | |||
+ 151
- 0
SdFat/SdStream.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,151 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| int16_t SdStreamBase::getch() { | |||
| uint8_t c; | |||
| int8_t s = read(&c, 1); | |||
| if (s != 1) { | |||
| if (s < 0) { | |||
| setstate(badbit); | |||
| } else { | |||
| setstate(eofbit); | |||
| } | |||
| return -1; | |||
| } | |||
| if (c != '\r' || (getmode() & ios::binary)) return c; | |||
| s = read(&c, 1); | |||
| if (s == 1 && c == '\n') return c; | |||
| if (s == 1) seekCur(-1); | |||
| return '\r'; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdStreamBase::open(const char* path, ios::openmode mode) { | |||
| uint8_t flags; | |||
| switch (mode & (app | in | out | trunc)) { | |||
| case app | in: | |||
| case app | in | out: | |||
| flags = O_RDWR | O_APPEND | O_CREAT; | |||
| break; | |||
| case app: | |||
| case app | out: | |||
| flags = O_WRITE | O_APPEND | O_CREAT; | |||
| break; | |||
| case in: | |||
| flags = O_READ; | |||
| break; | |||
| case in | out: | |||
| flags = O_RDWR; | |||
| break; | |||
| case in | out | trunc: | |||
| flags = O_RDWR | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT; | |||
| break; | |||
| case out: | |||
| case out | trunc: | |||
| flags = O_WRITE | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT; | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (mode & ios::ate) flags |= O_AT_END; | |||
| if (!SdBaseFile::open(path, flags)) goto fail; | |||
| setmode(mode); | |||
| clear(); | |||
| return; | |||
| fail: | |||
| SdBaseFile::close(); | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdStreamBase::putch(char c) { | |||
| if (c == '\n' && !(getmode() & ios::binary)) { | |||
| write('\r'); | |||
| } | |||
| write(c); | |||
| if (writeError) setstate(badbit); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdStreamBase::putstr(const char* str) { | |||
| size_t n = 0; | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| char c = str[n]; | |||
| if (c == '\0' || (c == '\n' && !(getmode() & ios::binary))) { | |||
| if (n > 0) write(str, n); | |||
| if (c == '\0') break; | |||
| write('\r'); | |||
| str += n; | |||
| n = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| n++; | |||
| } | |||
| if (writeError) setstate(badbit); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Internal do not use | |||
| * \param[in] off | |||
| * \param[in] way | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdStreamBase::seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) { | |||
| pos_type pos; | |||
| switch (way) { | |||
| case beg: | |||
| pos = off; | |||
| break; | |||
| case cur: | |||
| pos = curPosition() + off; | |||
| break; | |||
| case end: | |||
| pos = fileSize() + off; | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| return seekpos(pos); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Internal do not use | |||
| * \param[in] pos | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdStreamBase::seekpos(pos_type pos) { | |||
| return seekSet(pos); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int SdStreamBase::write(const void* buf, size_t n) { | |||
| return SdBaseFile::write(buf, n); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdStreamBase::write(char c) { | |||
| write(&c, 1); | |||
| } | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
+ 263
- 0
SdFat/SdStream.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,263 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdStream_h | |||
| #define SdStream_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief \ref fstream, \ref ifstream, and \ref ofstream classes | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdBaseFile.h> | |||
| #include <iostream.h> | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class SdStreamBase | |||
| * \brief Base class for SD streams | |||
| */ | |||
| class SdStreamBase : protected SdBaseFile, virtual public ios { | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| int16_t getch(); | |||
| void putch(char c); | |||
| void putstr(const char *str); | |||
| void open(const char* path, ios::openmode mode); | |||
| /** Internal do not use | |||
| * \return mode | |||
| */ | |||
| ios::openmode getmode() {return m_mode;} | |||
| /** Internal do not use | |||
| * \param[in] mode | |||
| */ | |||
| void setmode(ios::openmode mode) {m_mode = mode;} | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way); | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos); | |||
| int write(const void* buf, size_t n); | |||
| void write(char c); | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| private: | |||
| ios::openmode m_mode; | |||
| }; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class fstream | |||
| * \brief SD file input/output stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| class fstream : public iostream, SdStreamBase { | |||
| public: | |||
| using iostream::peek; | |||
| fstream() {} | |||
| /** Constructor with open | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] path path to open | |||
| * \param[in] mode open mode | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit fstream(const char* path, openmode mode = in | out) { | |||
| open(path, mode); | |||
| } | |||
| #if DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| ~fstream() {} | |||
| #endif // DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| /** Clear state and writeError | |||
| * \param[in] state new state for stream | |||
| */ | |||
| void clear(iostate state = goodbit) { | |||
| ios::clear(state); | |||
| SdBaseFile::writeError = false; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Close a file and force cached data and directory information | |||
| * to be written to the storage device. | |||
| */ | |||
| void close() {SdBaseFile::close();} | |||
| /** Open a fstream | |||
| * \param[in] path file to open | |||
| * \param[in] mode open mode | |||
| * | |||
| * Valid open modes are (at end, ios::ate, and/or ios::binary may be added): | |||
| * | |||
| * ios::in - Open file for reading. | |||
| * | |||
| * ios::out or ios::out | ios::trunc - Truncate to 0 length, if existent, | |||
| * or create a file for writing only. | |||
| * | |||
| * ios::app or ios::out | ios::app - Append; open or create file for | |||
| * writing at end-of-file. | |||
| * | |||
| * ios::in | ios::out - Open file for update (reading and writing). | |||
| * | |||
| * ios::in | ios::out | ios::trunc - Truncate to zero length, if existent, | |||
| * or create file for update. | |||
| * | |||
| * ios::in | ios::app or ios::in | ios::out | ios::app - Append; open or | |||
| * create text file for update, writing at end of file. | |||
| */ | |||
| void open(const char* path, openmode mode = in | out) { | |||
| SdStreamBase::open(path, mode); | |||
| } | |||
| /** \return True if stream is open else false. */ | |||
| bool is_open () {return SdBaseFile::isOpen();} | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \return | |||
| */ | |||
| int16_t getch() {return SdStreamBase::getch();} | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[out] pos | |||
| */ | |||
| void getpos(FatPos_t* pos) {SdBaseFile::getpos(pos);} | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[in] c | |||
| */ | |||
| void putch(char c) {SdStreamBase::putch(c);} | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[in] str | |||
| */ | |||
| void putstr(const char *str) {SdStreamBase::putstr(str);} | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[in] pos | |||
| */ | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) { | |||
| return SdStreamBase::seekoff(off, way); | |||
| } | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos) {return SdStreamBase::seekpos(pos);} | |||
| void setpos(FatPos_t* pos) {SdBaseFile::setpos(pos);} | |||
| bool sync() {return SdStreamBase::sync();} | |||
| pos_type tellpos() {return SdStreamBase::curPosition();} | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| }; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ifstream | |||
| * \brief SD file input stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| class ifstream : public istream, SdStreamBase { | |||
| public: | |||
| using istream::peek; | |||
| ifstream() {} | |||
| /** Constructor with open | |||
| * \param[in] path file to open | |||
| * \param[in] mode open mode | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit ifstream(const char* path, openmode mode = in) { | |||
| open(path, mode); | |||
| } | |||
| #if DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| ~ifstream() {} | |||
| #endif // DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| /** Close a file and force cached data and directory information | |||
| * to be written to the storage device. | |||
| */ | |||
| void close() {SdBaseFile::close();} | |||
| /** \return True if stream is open else false. */ | |||
| bool is_open() {return SdBaseFile::isOpen();} | |||
| /** Open an ifstream | |||
| * \param[in] path file to open | |||
| * \param[in] mode open mode | |||
| * | |||
| * \a mode See fstream::open() for valid modes. | |||
| */ | |||
| void open(const char* path, openmode mode = in) { | |||
| SdStreamBase::open(path, mode | in); | |||
| } | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \return | |||
| */ | |||
| int16_t getch() {return SdStreamBase::getch();} | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[out] pos | |||
| */ | |||
| void getpos(FatPos_t* pos) {SdBaseFile::getpos(pos);} | |||
| /** Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[in] pos | |||
| */ | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) { | |||
| return SdStreamBase::seekoff(off, way); | |||
| } | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos) {return SdStreamBase::seekpos(pos);} | |||
| void setpos(FatPos_t* pos) {SdBaseFile::setpos(pos);} | |||
| pos_type tellpos() {return SdStreamBase::curPosition();} | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| }; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ofstream | |||
| * \brief SD card output stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| class ofstream : public ostream, SdStreamBase { | |||
| public: | |||
| ofstream() {} | |||
| /** Constructor with open | |||
| * \param[in] path file to open | |||
| * \param[in] mode open mode | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit ofstream(const char* path, ios::openmode mode = out) { | |||
| open(path, mode); | |||
| } | |||
| #if DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| ~ofstream() {} | |||
| #endif // DESTRUCTOR_CLOSES_FILE | |||
| /** Clear state and writeError | |||
| * \param[in] state new state for stream | |||
| */ | |||
| void clear(iostate state = goodbit) { | |||
| ios::clear(state); | |||
| SdBaseFile::writeError = false; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Close a file and force cached data and directory information | |||
| * to be written to the storage device. | |||
| */ | |||
| void close() {SdBaseFile::close();} | |||
| /** Open an ofstream | |||
| * \param[in] path file to open | |||
| * \param[in] mode open mode | |||
| * | |||
| * \a mode See fstream::open() for valid modes. | |||
| */ | |||
| void open(const char* path, openmode mode = out) { | |||
| SdStreamBase::open(path, mode | out); | |||
| } | |||
| /** \return True if stream is open else false. */ | |||
| bool is_open() {return SdBaseFile::isOpen();} | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| /** | |||
| * Internal do not use | |||
| * \param[in] c | |||
| */ | |||
| void putch(char c) {SdStreamBase::putch(c);} | |||
| void putstr(const char* str) {SdStreamBase::putstr(str);} | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) { | |||
| return SdStreamBase::seekoff(off, way); | |||
| } | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos) {return SdStreamBase::seekpos(pos);} | |||
| /** | |||
| * Internal do not use | |||
| * \param[in] b | |||
| */ | |||
| bool sync() {return SdStreamBase::sync();} | |||
| pos_type tellpos() {return SdStreamBase::curPosition();} | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #endif // SdStream_h | |||
+ 595
- 0
SdFat/SdVolume.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,595 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #if !USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| // raw block cache | |||
| uint8_t SdVolume::m_fatCount; // number of FATs on volume | |||
| uint32_t SdVolume::m_blocksPerFat; // FAT size in blocks | |||
| cache_t SdVolume::m_cacheBuffer; // 512 byte cache for Sd2Card | |||
| uint32_t SdVolume::m_cacheBlockNumber; // current block number | |||
| uint8_t SdVolume::m_cacheStatus; // status of cache block | |||
| #if USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| cache_t SdVolume::m_cacheFatBuffer; // 512 byte cache for FAT | |||
| uint32_t SdVolume::m_cacheFatBlockNumber; // current Fat block number | |||
| uint8_t SdVolume::m_cacheFatStatus; // status of cache Fatblock | |||
| #endif // USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| Sd2Card* SdVolume::m_sdCard; // pointer to SD card object | |||
| #endif // USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // find a contiguous group of clusters | |||
| bool SdVolume::allocContiguous(uint32_t count, uint32_t* curCluster) { | |||
| // start of group | |||
| uint32_t bgnCluster; | |||
| // end of group | |||
| uint32_t endCluster; | |||
| // last cluster of FAT | |||
| uint32_t fatEnd = m_clusterCount + 1; | |||
| // flag to save place to start next search | |||
| bool setStart; | |||
| // set search start cluster | |||
| if (*curCluster) { | |||
| // try to make file contiguous | |||
| bgnCluster = *curCluster + 1; | |||
| // don't save new start location | |||
| setStart = false; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // start at likely place for free cluster | |||
| bgnCluster = m_allocSearchStart; | |||
| // save next search start if no holes. | |||
| setStart = true; | |||
| } | |||
| // end of group | |||
| endCluster = bgnCluster; | |||
| // search the FAT for free clusters | |||
| for (uint32_t n = 0;; n++, endCluster++) { | |||
| // can't find space checked all clusters | |||
| if (n >= m_clusterCount) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // past end - start from beginning of FAT | |||
| if (endCluster > fatEnd) { | |||
| bgnCluster = endCluster = 2; | |||
| } | |||
| uint32_t f; | |||
| if (!fatGet(endCluster, &f)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (f != 0) { | |||
| // don't update search start if unallocated clusters before endCluster. | |||
| if (bgnCluster != endCluster) setStart = false; | |||
| // cluster in use try next cluster as bgnCluster | |||
| bgnCluster = endCluster + 1; | |||
| } else if ((endCluster - bgnCluster + 1) == count) { | |||
| // done - found space | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // remember possible next free cluster | |||
| if (setStart) m_allocSearchStart = endCluster + 1; | |||
| // mark end of chain | |||
| if (!fatPutEOC(endCluster)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // link clusters | |||
| while (endCluster > bgnCluster) { | |||
| if (!fatPut(endCluster - 1, endCluster)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| endCluster--; | |||
| } | |||
| if (*curCluster != 0) { | |||
| // connect chains | |||
| if (!fatPut(*curCluster, bgnCluster)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // return first cluster number to caller | |||
| *curCluster = bgnCluster; | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // cache functions | |||
| #if USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| cache_t* SdVolume::cacheFetch(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options) { | |||
| return cacheFetchData(blockNumber, options); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| cache_t* SdVolume::cacheFetchData(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options) { | |||
| if (m_cacheBlockNumber != blockNumber) { | |||
| if (!cacheWriteData()) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!(options & CACHE_OPTION_NO_READ)) { | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->readBlock(blockNumber, m_cacheBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheStatus = 0; | |||
| m_cacheBlockNumber = blockNumber; | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheStatus |= options & CACHE_STATUS_MASK; | |||
| return &m_cacheBuffer; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| cache_t* SdVolume::cacheFetchFat(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options) { | |||
| if (m_cacheFatBlockNumber != blockNumber) { | |||
| if (!cacheWriteFat()) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!(options & CACHE_OPTION_NO_READ)) { | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->readBlock(blockNumber, m_cacheFatBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheFatStatus = 0; | |||
| m_cacheFatBlockNumber = blockNumber; | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheFatStatus |= options & CACHE_STATUS_MASK; | |||
| return &m_cacheFatBuffer; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool SdVolume::cacheSync() { | |||
| return cacheWriteData() && cacheWriteFat(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool SdVolume::cacheWriteData() { | |||
| if (m_cacheStatus & CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY) { | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->writeBlock(m_cacheBlockNumber, m_cacheBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheStatus &= ~CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool SdVolume::cacheWriteFat() { | |||
| if (m_cacheFatStatus & CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY) { | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->writeBlock(m_cacheFatBlockNumber, m_cacheFatBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // mirror second FAT | |||
| if (m_fatCount > 1) { | |||
| uint32_t lbn = m_cacheFatBlockNumber + m_blocksPerFat; | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->writeBlock(lbn, m_cacheFatBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheFatStatus &= ~CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| #else // USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| cache_t* SdVolume::cacheFetch(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options) { | |||
| if (m_cacheBlockNumber != blockNumber) { | |||
| if (!cacheSync()) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!(options & CACHE_OPTION_NO_READ)) { | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->readBlock(blockNumber, m_cacheBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheStatus = 0; | |||
| m_cacheBlockNumber = blockNumber; | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheStatus |= options & CACHE_STATUS_MASK; | |||
| return &m_cacheBuffer; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| cache_t* SdVolume::cacheFetchFat(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options) { | |||
| return cacheFetch(blockNumber, options | CACHE_STATUS_FAT_BLOCK); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool SdVolume::cacheSync() { | |||
| if (m_cacheStatus & CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY) { | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->writeBlock(m_cacheBlockNumber, m_cacheBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // mirror second FAT | |||
| if ((m_cacheStatus & CACHE_STATUS_FAT_BLOCK) && m_fatCount > 1) { | |||
| uint32_t lbn = m_cacheBlockNumber + m_blocksPerFat; | |||
| if (!m_sdCard->writeBlock(lbn, m_cacheBuffer.data)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| m_cacheStatus &= ~CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool SdVolume::cacheWriteData() { | |||
| return cacheSync(); | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void SdVolume::cacheInvalidate() { | |||
| m_cacheBlockNumber = 0XFFFFFFFF; | |||
| m_cacheStatus = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| uint32_t SdVolume::clusterStartBlock(uint32_t cluster) const { | |||
| return m_dataStartBlock + ((cluster - 2) << m_clusterSizeShift); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Fetch a FAT entry | |||
| bool SdVolume::fatGet(uint32_t cluster, uint32_t* value) { | |||
| uint32_t lba; | |||
| cache_t* pc; | |||
| // error if reserved cluster of beyond FAT | |||
| if (cluster < 2 || cluster > (m_clusterCount + 1)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (FAT12_SUPPORT && m_fatType == 12) { | |||
| uint16_t index = cluster; | |||
| index += index >> 1; | |||
| lba = m_fatStartBlock + (index >> 9); | |||
| pc = cacheFetchFat(lba, CACHE_FOR_READ); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| index &= 0X1FF; | |||
| uint16_t tmp = pc->data[index]; | |||
| index++; | |||
| if (index == 512) { | |||
| pc = cacheFetchFat(lba + 1, CACHE_FOR_READ); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| index = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| tmp |= pc->data[index] << 8; | |||
| *value = cluster & 1 ? tmp >> 4 : tmp & 0XFFF; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_fatType == 16) { | |||
| lba = m_fatStartBlock + (cluster >> 8); | |||
| } else if (m_fatType == 32) { | |||
| lba = m_fatStartBlock + (cluster >> 7); | |||
| } else { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| pc = cacheFetchFat(lba, CACHE_FOR_READ); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_fatType == 16) { | |||
| *value = pc->fat16[cluster & 0XFF]; | |||
| } else { | |||
| *value = pc->fat32[cluster & 0X7F] & FAT32MASK; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Store a FAT entry | |||
| bool SdVolume::fatPut(uint32_t cluster, uint32_t value) { | |||
| uint32_t lba; | |||
| cache_t* pc; | |||
| // error if reserved cluster of beyond FAT | |||
| if (cluster < 2 || cluster > (m_clusterCount + 1)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (FAT12_SUPPORT && m_fatType == 12) { | |||
| uint16_t index = cluster; | |||
| index += index >> 1; | |||
| lba = m_fatStartBlock + (index >> 9); | |||
| pc = cacheFetchFat(lba, CACHE_FOR_WRITE); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| index &= 0X1FF; | |||
| uint8_t tmp = value; | |||
| if (cluster & 1) { | |||
| tmp = (pc->data[index] & 0XF) | tmp << 4; | |||
| } | |||
| pc->data[index] = tmp; | |||
| index++; | |||
| if (index == 512) { | |||
| lba++; | |||
| index = 0; | |||
| pc = cacheFetchFat(lba, CACHE_FOR_WRITE); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| tmp = value >> 4; | |||
| if (!(cluster & 1)) { | |||
| tmp = ((pc->data[index] & 0XF0)) | tmp >> 4; | |||
| } | |||
| pc->data[index] = tmp; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_fatType == 16) { | |||
| lba = m_fatStartBlock + (cluster >> 8); | |||
| } else if (m_fatType == 32) { | |||
| lba = m_fatStartBlock + (cluster >> 7); | |||
| } else { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| pc = cacheFetchFat(lba, CACHE_FOR_WRITE); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // store entry | |||
| if (m_fatType == 16) { | |||
| pc->fat16[cluster & 0XFF] = value; | |||
| } else { | |||
| pc->fat32[cluster & 0X7F] = value; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // free a cluster chain | |||
| bool SdVolume::freeChain(uint32_t cluster) { | |||
| uint32_t next; | |||
| do { | |||
| if (!fatGet(cluster, &next)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| // free cluster | |||
| if (!fatPut(cluster, 0)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (cluster < m_allocSearchStart) m_allocSearchStart = cluster; | |||
| cluster = next; | |||
| } while (!isEOC(cluster)); | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Volume free space in clusters. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Count of free clusters for success or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int32_t SdVolume::freeClusterCount() { | |||
| uint32_t free = 0; | |||
| uint32_t lba; | |||
| uint32_t todo = m_clusterCount + 2; | |||
| uint16_t n; | |||
| if (FAT12_SUPPORT && m_fatType == 12) { | |||
| for (unsigned i = 2; i < todo; i++) { | |||
| uint32_t c; | |||
| if (!fatGet(i, &c)) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| if (c == 0) free++; | |||
| } | |||
| } else if (m_fatType == 16 || m_fatType == 32) { | |||
| lba = m_fatStartBlock; | |||
| while (todo) { | |||
| cache_t* pc = cacheFetchFat(lba++, CACHE_FOR_READ); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| n = m_fatType == 16 ? 256 : 128; | |||
| if (todo < n) n = todo; | |||
| if (m_fatType == 16) { | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| if (pc->fat16[i] == 0) free++; | |||
| } | |||
| } else { | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| if (pc->fat32[i] == 0) free++; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| todo -= n; | |||
| } | |||
| } else { | |||
| // invalid FAT type | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| return free; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return -1; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Initialize a FAT volume. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] dev The SD card where the volume is located. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] part The partition to be used. Legal values for \a part are | |||
| * 1-4 to use the corresponding partition on a device formatted with | |||
| * a MBR, Master Boot Record, or zero if the device is formatted as | |||
| * a super floppy with the FAT boot sector in block zero. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. Reasons for | |||
| * failure include not finding a valid partition, not finding a valid | |||
| * FAT file system in the specified partition or an I/O error. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool SdVolume::init(Sd2Card* dev, uint8_t part) { | |||
| uint8_t tmp; | |||
| uint32_t totalBlocks; | |||
| uint32_t volumeStartBlock = 0; | |||
| fat32_boot_t* fbs; | |||
| cache_t* pc; | |||
| m_sdCard = dev; | |||
| m_fatType = 0; | |||
| m_allocSearchStart = 2; | |||
| m_cacheStatus = 0; // cacheSync() will write block if true | |||
| m_cacheBlockNumber = 0XFFFFFFFF; | |||
| #if USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| m_cacheFatStatus = 0; // cacheSync() will write block if true | |||
| m_cacheFatBlockNumber = 0XFFFFFFFF; | |||
| #endif // USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| // if part == 0 assume super floppy with FAT boot sector in block zero | |||
| // if part > 0 assume mbr volume with partition table | |||
| if (part) { | |||
| if (part > 4) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| pc = cacheFetch(volumeStartBlock, CACHE_FOR_READ); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| part_t* p = &pc->mbr.part[part-1]; | |||
| if ((p->boot & 0X7F) != 0 || p->firstSector == 0) { | |||
| // not a valid partition | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| volumeStartBlock = p->firstSector; | |||
| } | |||
| pc = cacheFetch(volumeStartBlock, CACHE_FOR_READ); | |||
| if (!pc) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| fbs = &(pc->fbs32); | |||
| if (fbs->bytesPerSector != 512 || | |||
| fbs->fatCount == 0 || | |||
| fbs->reservedSectorCount == 0) { | |||
| // not valid FAT volume | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| m_fatCount = fbs->fatCount; | |||
| m_blocksPerCluster = fbs->sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| m_clusterBlockMask = m_blocksPerCluster - 1; | |||
| // determine shift that is same as multiply by m_blocksPerCluster | |||
| m_clusterSizeShift = 0; | |||
| for (tmp = 1; m_blocksPerCluster != tmp; m_clusterSizeShift++) { | |||
| tmp <<= 1; | |||
| if (tmp == 0) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| m_blocksPerFat = fbs->sectorsPerFat16 ? | |||
| fbs->sectorsPerFat16 : fbs->sectorsPerFat32; | |||
| m_fatStartBlock = volumeStartBlock + fbs->reservedSectorCount; | |||
| // count for FAT16 zero for FAT32 | |||
| m_rootDirEntryCount = fbs->rootDirEntryCount; | |||
| // directory start for FAT16 dataStart for FAT32 | |||
| m_rootDirStart = m_fatStartBlock + fbs->fatCount * m_blocksPerFat; | |||
| // data start for FAT16 and FAT32 | |||
| m_dataStartBlock = m_rootDirStart + ((32 * fbs->rootDirEntryCount + 511)/512); | |||
| // total blocks for FAT16 or FAT32 | |||
| totalBlocks = fbs->totalSectors16 ? | |||
| fbs->totalSectors16 : fbs->totalSectors32; | |||
| // total data blocks | |||
| m_clusterCount = totalBlocks - (m_dataStartBlock - volumeStartBlock); | |||
| // divide by cluster size to get cluster count | |||
| m_clusterCount >>= m_clusterSizeShift; | |||
| // FAT type is determined by cluster count | |||
| if (m_clusterCount < 4085) { | |||
| m_fatType = 12; | |||
| if (!FAT12_SUPPORT) { | |||
| DBG_FAIL_MACRO; | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } else if (m_clusterCount < 65525) { | |||
| m_fatType = 16; | |||
| } else { | |||
| m_rootDirStart = fbs->fat32RootCluster; | |||
| m_fatType = 32; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
+ 216
- 0
SdFat/SdVolume.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,216 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SdVolume_h | |||
| #define SdVolume_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief SdVolume class | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFatConfig.h> | |||
| #include <Sd2Card.h> | |||
| #include <utility/FatStructs.h> | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // SdVolume class | |||
| /** | |||
| * \brief Cache for an SD data block | |||
| */ | |||
| union cache_t { | |||
| /** Used to access cached file data blocks. */ | |||
| uint8_t data[512]; | |||
| /** Used to access cached FAT16 entries. */ | |||
| uint16_t fat16[256]; | |||
| /** Used to access cached FAT32 entries. */ | |||
| uint32_t fat32[128]; | |||
| /** Used to access cached directory entries. */ | |||
| dir_t dir[16]; | |||
| /** Used to access a cached Master Boot Record. */ | |||
| mbr_t mbr; | |||
| /** Used to access to a cached FAT boot sector. */ | |||
| fat_boot_t fbs; | |||
| /** Used to access to a cached FAT32 boot sector. */ | |||
| fat32_boot_t fbs32; | |||
| /** Used to access to a cached FAT32 FSINFO sector. */ | |||
| fat32_fsinfo_t fsinfo; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class SdVolume | |||
| * \brief Access FAT16 and FAT32 volumes on SD and SDHC cards. | |||
| */ | |||
| class SdVolume { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** Create an instance of SdVolume */ | |||
| SdVolume() : m_fatType(0) {} | |||
| /** Clear the cache and returns a pointer to the cache. Used by the WaveRP | |||
| * recorder to do raw write to the SD card. Not for normal apps. | |||
| * \return A pointer to the cache buffer or zero if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| cache_t* cacheClear() { | |||
| if (!cacheSync()) return 0; | |||
| m_cacheBlockNumber = 0XFFFFFFFF; | |||
| return &m_cacheBuffer; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Initialize a FAT volume. Try partition one first then try super | |||
| * floppy format. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] dev The Sd2Card where the volume is located. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The value one, true, is returned for success and | |||
| * the value zero, false, is returned for failure. Reasons for | |||
| * failure include not finding a valid partition, not finding a valid | |||
| * FAT file system or an I/O error. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool init(Sd2Card* dev) { return init(dev, 1) ? true : init(dev, 0);} | |||
| bool init(Sd2Card* dev, uint8_t part); | |||
| // inline functions that return volume info | |||
| /** \return The volume's cluster size in blocks. */ | |||
| uint8_t blocksPerCluster() const {return m_blocksPerCluster;} | |||
| /** \return The number of blocks in one FAT. */ | |||
| uint32_t blocksPerFat() const {return m_blocksPerFat;} | |||
| /** \return The total number of clusters in the volume. */ | |||
| uint32_t clusterCount() const {return m_clusterCount;} | |||
| /** \return The shift count required to multiply by blocksPerCluster. */ | |||
| uint8_t clusterSizeShift() const {return m_clusterSizeShift;} | |||
| /** \return The logical block number for the start of file data. */ | |||
| uint32_t dataStartBlock() const {return clusterStartBlock(2);} | |||
| /** \return The number of FAT structures on the volume. */ | |||
| uint8_t fatCount() const {return m_fatCount;} | |||
| /** \return The logical block number for the start of the first FAT. */ | |||
| uint32_t fatStartBlock() const {return m_fatStartBlock;} | |||
| /** \return The FAT type of the volume. Values are 12, 16 or 32. */ | |||
| uint8_t fatType() const {return m_fatType;} | |||
| int32_t freeClusterCount(); | |||
| /** \return The number of entries in the root directory for FAT16 volumes. */ | |||
| uint32_t rootDirEntryCount() const {return m_rootDirEntryCount;} | |||
| /** \return The logical block number for the start of the root directory | |||
| on FAT16 volumes or the first cluster number on FAT32 volumes. */ | |||
| uint32_t rootDirStart() const {return m_rootDirStart;} | |||
| /** Sd2Card object for this volume | |||
| * \return pointer to Sd2Card object. | |||
| */ | |||
| Sd2Card* sdCard() {return m_sdCard;} | |||
| /** Debug access to FAT table | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] n cluster number. | |||
| * \param[out] v value of entry | |||
| * \return true for success or false for failure | |||
| */ | |||
| bool dbgFat(uint32_t n, uint32_t* v) {return fatGet(n, v);} | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| private: | |||
| // Allow SdBaseFile access to SdVolume private data. | |||
| friend class SdBaseFile; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| uint32_t m_allocSearchStart; // Start cluster for alloc search. | |||
| uint8_t m_blocksPerCluster; // Cluster size in blocks. | |||
| uint8_t m_clusterBlockMask; // Mask to extract block of cluster. | |||
| uint32_t m_clusterCount; // Clusters in one FAT. | |||
| uint8_t m_clusterSizeShift; // Cluster count to block count shift. | |||
| uint32_t m_dataStartBlock; // First data block number. | |||
| uint32_t m_fatStartBlock; // Start block for first FAT. | |||
| uint8_t m_fatType; // Volume type (12, 16, OR 32). | |||
| uint16_t m_rootDirEntryCount; // Number of entries in FAT16 root dir. | |||
| uint32_t m_rootDirStart; // Start block for FAT16, cluster for FAT32. | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // block caches | |||
| // use of static functions save a bit of flash - maybe not worth complexity | |||
| // | |||
| static const uint8_t CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY = 1; | |||
| static const uint8_t CACHE_STATUS_FAT_BLOCK = 2; | |||
| static const uint8_t CACHE_STATUS_MASK | |||
| = CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY | CACHE_STATUS_FAT_BLOCK; | |||
| static const uint8_t CACHE_OPTION_NO_READ = 4; | |||
| // value for option argument in cacheFetch to indicate read from cache | |||
| static uint8_t const CACHE_FOR_READ = 0; | |||
| // value for option argument in cacheFetch to indicate write to cache | |||
| static uint8_t const CACHE_FOR_WRITE = CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY; | |||
| // reserve cache block with no read | |||
| static uint8_t const CACHE_RESERVE_FOR_WRITE | |||
| = CACHE_STATUS_DIRTY | CACHE_OPTION_NO_READ; | |||
| #if USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| uint8_t m_fatCount; // number of FATs on volume | |||
| uint32_t m_blocksPerFat; // FAT size in blocks | |||
| cache_t m_cacheBuffer; // 512 byte cache for device blocks | |||
| uint32_t m_cacheBlockNumber; // Logical number of block in the cache | |||
| Sd2Card* m_sdCard; // Sd2Card object for cache | |||
| uint8_t m_cacheStatus; // status of cache block | |||
| #if USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| cache_t m_cacheFatBuffer; // 512 byte cache for FAT | |||
| uint32_t m_cacheFatBlockNumber; // current Fat block number | |||
| uint8_t m_cacheFatStatus; // status of cache Fatblock | |||
| #endif // USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| #else // USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| static uint8_t m_fatCount; // number of FATs on volume | |||
| static uint32_t m_blocksPerFat; // FAT size in blocks | |||
| static cache_t m_cacheBuffer; // 512 byte cache for device blocks | |||
| static uint32_t m_cacheBlockNumber; // Logical number of block in the cache | |||
| static uint8_t m_cacheStatus; // status of cache block | |||
| #if USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| static cache_t m_cacheFatBuffer; // 512 byte cache for FAT | |||
| static uint32_t m_cacheFatBlockNumber; // current Fat block number | |||
| static uint8_t m_cacheFatStatus; // status of cache Fatblock | |||
| #endif // USE_SEPARATE_FAT_CACHE | |||
| static Sd2Card* m_sdCard; // Sd2Card object for cache | |||
| #endif // USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| cache_t *cacheAddress() {return &m_cacheBuffer;} | |||
| uint32_t cacheBlockNumber() {return m_cacheBlockNumber;} | |||
| #if USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| cache_t* cacheFetch(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options); | |||
| cache_t* cacheFetchData(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options); | |||
| cache_t* cacheFetchFat(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options); | |||
| void cacheInvalidate(); | |||
| bool cacheSync(); | |||
| bool cacheWriteData(); | |||
| bool cacheWriteFat(); | |||
| #else // USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| static cache_t* cacheFetch(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options); | |||
| static cache_t* cacheFetchData(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options); | |||
| static cache_t* cacheFetchFat(uint32_t blockNumber, uint8_t options); | |||
| static void cacheInvalidate(); | |||
| static bool cacheSync(); | |||
| static bool cacheWriteData(); | |||
| static bool cacheWriteFat(); | |||
| #endif // USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool allocContiguous(uint32_t count, uint32_t* curCluster); | |||
| uint8_t blockOfCluster(uint32_t position) const { | |||
| return (position >> 9) & m_clusterBlockMask;} | |||
| uint32_t clusterStartBlock(uint32_t cluster) const; | |||
| bool fatGet(uint32_t cluster, uint32_t* value); | |||
| bool fatPut(uint32_t cluster, uint32_t value); | |||
| bool fatPutEOC(uint32_t cluster) { | |||
| return fatPut(cluster, 0x0FFFFFFF); | |||
| } | |||
| bool freeChain(uint32_t cluster); | |||
| bool isEOC(uint32_t cluster) const { | |||
| if (FAT12_SUPPORT && m_fatType == 12) return cluster >= FAT12EOC_MIN; | |||
| if (m_fatType == 16) return cluster >= FAT16EOC_MIN; | |||
| return cluster >= FAT32EOC_MIN; | |||
| } | |||
| bool readBlock(uint32_t block, uint8_t* dst) { | |||
| return m_sdCard->readBlock(block, dst);} | |||
| bool writeBlock(uint32_t block, const uint8_t* dst) { | |||
| return m_sdCard->writeBlock(block, dst); | |||
| } | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // SdVolume | |||
+ 535
- 0
SdFat/StdioStream.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,535 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino RamDisk Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2014 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino RamDisk Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino RamDisk Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * StdioStream implementation | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| #include <StdioStream.h> | |||
| #include <utility/FmtNumber.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::fclose() { | |||
| int rtn = 0; | |||
| if (!m_flags) { | |||
| return EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_flags & F_SWR) { | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) rtn = EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!SdBaseFile::close()) rtn = EOF; | |||
| m_r = 0; | |||
| m_w = 0; | |||
| m_flags = 0; | |||
| return rtn; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::fflush() { | |||
| if ((m_flags & (F_SWR | F_SRW)) && !(m_flags & F_SRD)) { | |||
| if (flushBuf() && SdBaseFile::sync()) return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| return EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| char* StdioStream::fgets(char* str, int num, size_t* len) { | |||
| char* s = str; | |||
| size_t n; | |||
| if (num-- <= 0) return 0; | |||
| while (num) { | |||
| if ((n = m_r) == 0) { | |||
| if (!fillBuf()) { | |||
| if (s == str) return 0; | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| n = m_r; | |||
| } | |||
| if (n > num) n = num; | |||
| uint8_t* end = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(memchr(m_p, '\n', n)); | |||
| if (end != 0) { | |||
| n = ++end - m_p; | |||
| memcpy(s, m_p, n); | |||
| m_r -= n; | |||
| m_p = end; | |||
| s += n; | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| memcpy(s, m_p, n); | |||
| m_r -= n; | |||
| m_p += n; | |||
| s += n; | |||
| num -= n; | |||
| } | |||
| *s = 0; | |||
| if (len) *len = s - str; | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool StdioStream::fopen(const char* filename, const char* mode) { | |||
| uint8_t oflags; | |||
| switch (*mode++) { | |||
| case 'a': | |||
| m_flags = F_SWR; | |||
| oflags = O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_APPEND | O_AT_END; | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'r': | |||
| m_flags = F_SRD; | |||
| oflags = O_READ; | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'w': | |||
| m_flags = F_SWR; | |||
| oflags = O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC; | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| while (*mode) { | |||
| switch (*mode++) { | |||
| case '+': | |||
| m_flags |= F_SRW; | |||
| oflags |= O_RDWR; | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'b': | |||
| break; | |||
| case 'x': | |||
| oflags |= O_EXCL; | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if ((oflags & O_EXCL) && !(oflags & O_WRITE)) goto fail; | |||
| if (!SdBaseFile::open(filename, oflags)) goto fail; | |||
| m_r = 0; | |||
| m_w = 0; | |||
| m_p = m_buf; | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| m_flags = 0; | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::fputs(const char* str) { | |||
| size_t len = strlen(str); | |||
| return fwrite(str, 1, len) == len ? len : EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::fputs_P(PGM_P str) { | |||
| PGM_P bgn = str; | |||
| for (char c; (c = pgm_read_byte(str)); str++) { | |||
| if (putc(c) < 0) return EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| return str - bgn; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| size_t StdioStream::fread(void* ptr, size_t size, size_t count) { | |||
| uint8_t* dst = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(ptr); | |||
| size_t total = size*count; | |||
| if (total == 0) return 0; | |||
| size_t need = total; | |||
| while (need > m_r) { | |||
| memcpy(dst, m_p, m_r); | |||
| dst += m_r; | |||
| m_p += m_r; | |||
| need -= m_r; | |||
| if (!fillBuf()) { | |||
| return (total - need)/size; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| memcpy(dst, m_p, need); | |||
| m_r -= need; | |||
| m_p += need; | |||
| return count; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::fseek(int32_t offset, int origin) { | |||
| int32_t pos; | |||
| if (m_flags & F_SWR) { | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) { | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| switch (origin) { | |||
| case SEEK_CUR: | |||
| pos = ftell(); | |||
| if (pos < 0) { | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| pos += offset; | |||
| if (!SdBaseFile::seekCur(pos)) { | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case SEEK_SET: | |||
| if (!SdBaseFile::seekSet(offset)) { | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case SEEK_END: | |||
| if (!SdBaseFile::seekEnd(offset)) { | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| goto fail; | |||
| } | |||
| m_r = 0; | |||
| m_p = m_buf; | |||
| return 0; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int32_t StdioStream::ftell() { | |||
| uint32_t pos = SdBaseFile::curPosition(); | |||
| if (m_flags & F_SRD) { | |||
| if (m_r > pos) return -1L; | |||
| pos -= m_r; | |||
| } else if (m_flags & F_SWR) { | |||
| pos += m_p - m_buf; | |||
| } | |||
| return pos; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| size_t StdioStream::fwrite(const void* ptr, size_t size, size_t count) { | |||
| return write(ptr, count*size) < 0 ? EOF : count; | |||
| #if 0 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// | |||
| const uint8_t* src = static_cast<const uint8_t*>(ptr); | |||
| size_t total = count*size; | |||
| if (total == 0) return 0; | |||
| size_t todo = total; | |||
| while (todo > m_w) { | |||
| memcpy(m_p, src, m_w); | |||
| m_p += m_w; | |||
| src += m_w; | |||
| todo -= m_w; | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) { | |||
| return (total - todo)/size; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| memcpy(m_p, src, todo); | |||
| m_p += todo; | |||
| m_w -= todo; | |||
| return count; | |||
| #endif ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::write(const void* buf, size_t count) { | |||
| const uint8_t* src = static_cast<const uint8_t*>(buf); | |||
| size_t todo = count; | |||
| while (todo > m_w) { | |||
| memcpy(m_p, src, m_w); | |||
| m_p += m_w; | |||
| src += m_w; | |||
| todo -= m_w; | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) return EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| memcpy(m_p, src, todo); | |||
| m_p += todo; | |||
| m_w -= todo; | |||
| return count; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| size_t StdioStream::print(const __FlashStringHelper *str) { | |||
| const char PROGMEM *p = (const char PROGMEM *)str; | |||
| uint8_t c; | |||
| while (c = pgm_read_byte(p)) { | |||
| if (putc(c) < 0) return 0; | |||
| p++; | |||
| } | |||
| return p - (const char PROGMEM *)str; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::printDec(float value, uint8_t prec) { | |||
| #define FLOAT_NEW_WAY | |||
| #ifdef FLOAT_NEW_WAY | |||
| char buf[24]; | |||
| char *ptr = fmtFloat(value, buf + sizeof(buf), prec); | |||
| // return fputs(ptr); | |||
| // uint8_t len = buf + sizeof(buf) - ptr; | |||
| return write(ptr, buf + sizeof(buf) - ptr); | |||
| #else | |||
| char* ptr; | |||
| uint8_t rtn = 0; | |||
| uint8_t sign = 0; | |||
| if (value < 0) { | |||
| value = -value; | |||
| sign = '-'; | |||
| } | |||
| // check for NaN INF OVF | |||
| if (isnan(value)) { | |||
| if (fputs_P(PSTR("nan")) < 0) return -1; | |||
| rtn += 3; | |||
| } else if (isinf(value)) { | |||
| if (fputs_P(PSTR("inf")) < 0) return -1; | |||
| rtn += 3; | |||
| } else if (value > 4294967040.0) { | |||
| if (fputs_P(PSTR("ovf")) < 0) return -1;; | |||
| rtn += 3; | |||
| } else { | |||
| if (sign) { | |||
| if (putc(sign) < 0) return -1; | |||
| rtn++; | |||
| } | |||
| if (prec > 9) prec = 9; | |||
| /* | |||
| uint32_t s = 1; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < prec; i++) { | |||
| // s *= 10; | |||
| s = ((s << 2) + s) << 1; | |||
| } | |||
| // round value | |||
| value += 0.5/s; | |||
| */ | |||
| value += scale10(0.5, -prec); | |||
| uint32_t whole = value; | |||
| int np; | |||
| if ((np = printDec(whole)) < 0) return -1; | |||
| rtn += np; | |||
| if (prec) { | |||
| if (putc('.') < 0) return -1; | |||
| char* str = fmtSpace(prec); | |||
| if (!str) return -1; | |||
| char* tmp = str - prec; | |||
| // uint32_t fraction = s*(value - whole); | |||
| uint32_t fraction = scale10(value - whole, prec); | |||
| ptr = fmtDec(fraction, str); | |||
| while (ptr > tmp) *--ptr = '0'; | |||
| rtn += prec + 1; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| return rtn; | |||
| #endif | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::printDec(signed char n) { | |||
| uint8_t s = 0; | |||
| if (n < 0) { | |||
| if (fputc('-') < 0) return -1; | |||
| n = -n; | |||
| s = 1; | |||
| } | |||
| printDec((unsigned char)n); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::printDec(int16_t n) { | |||
| int s; | |||
| uint8_t rtn = 0; | |||
| if (n < 0) { | |||
| if (fputc('-') < 0) return -1; | |||
| n = -n; | |||
| rtn++; | |||
| } | |||
| if ((s = printDec((uint16_t)n)) < 0) return s; | |||
| return rtn; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::printDec(uint16_t n) { | |||
| #define NEW_WAY | |||
| #ifdef NEW_WAY | |||
| char buf[5]; | |||
| char *ptr = fmtDec(n, buf + sizeof(buf)); | |||
| uint8_t len = buf + sizeof(buf) - ptr; | |||
| return write(ptr, len); | |||
| #else | |||
| uint8_t len; | |||
| if (n < 100) { | |||
| len = n < 10 ? 1 : 2; | |||
| } else { | |||
| len = n < 1000 ? 3 : n < 10000 ? 4 : 5; | |||
| } | |||
| char* str = fmtSpace(len); | |||
| if (!str) return -1; | |||
| fmtDec(n, str); | |||
| return len; | |||
| #endif | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::printDec(int32_t n) { | |||
| uint8_t s = 0; | |||
| if (n < 0) { | |||
| if (fputc('-') < 0) return -1; | |||
| n = -n; | |||
| s = 1; | |||
| } | |||
| int rtn = printDec((uint32_t)n); | |||
| return rtn > 0 ? rtn + s : -1; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::printDec(uint32_t n) { | |||
| #ifdef NEW_WAY | |||
| char buf[10]; | |||
| char *ptr = fmtDec(n, buf + sizeof(buf)); | |||
| uint8_t len = buf + sizeof(buf) - ptr; | |||
| return write(ptr, len); | |||
| #else | |||
| uint8_t len; | |||
| if (n < 0X10000) { | |||
| return printDec((uint16_t)n); | |||
| } | |||
| if (n < 10000000) { | |||
| len = n < 100000 ? 5 : n < 1000000 ? 6 : 7; | |||
| } else { | |||
| len = n < 100000000 ? 8 : n < 1000000000 ? 9 : 10; | |||
| } | |||
| char* str = fmtSpace(len); | |||
| if (!str) return -1; | |||
| fmtDec(n, str); | |||
| return len; | |||
| #endif | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::printHex(uint32_t n) { | |||
| #ifdef NEW_WAY | |||
| char buf[8]; | |||
| char *ptr = fmtHex(n, buf + sizeof(buf)); | |||
| uint8_t len = buf + sizeof(buf) - ptr; | |||
| return write(ptr, len); | |||
| #else | |||
| size_t len; | |||
| if (n < 0X10000) { | |||
| len = n < 0X10 ? 1 : n < 0X100 ? 2 : n < 0X1000 ? 3 : 4; | |||
| } else { | |||
| len = n < 0X100000 ? 5 : n < 0X1000000 ? 6 : n < 0X10000000 ? 7 : 8; | |||
| } | |||
| char* str = fmtSpace(len); | |||
| if (!str) return -1; | |||
| do { | |||
| uint8_t h = n & 0XF; | |||
| *str-- = h + (h < 10 ? '0' : 'A' - 10); | |||
| n >>= 4; | |||
| } while (n); | |||
| return len; | |||
| #endif | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool StdioStream::rewind() { | |||
| if (m_flags & F_SWR) { | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) return false; | |||
| } | |||
| SdBaseFile::seekSet(0); | |||
| m_r = 0; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::ungetc(int c) { | |||
| // error if EOF. | |||
| if (c == EOF) return EOF; | |||
| // error if not reading. | |||
| if ((m_flags & F_SRD) == 0) return EOF; | |||
| // error if no space. | |||
| if (m_p == m_buf) return EOF; | |||
| m_r++; | |||
| m_flags &= ~F_EOF; | |||
| return *--m_p = (uint8_t)c; | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // private | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::fillGet() { | |||
| if (!fillBuf()) { | |||
| return EOF; | |||
| } | |||
| m_r--; | |||
| return *m_p++; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // private | |||
| bool StdioStream::fillBuf() { | |||
| if (!(m_flags & F_SRD)) { /////////////check for F_ERR and F_EOF ??///////////////// | |||
| if (!(m_flags & F_SRW)) { | |||
| m_flags |= F_ERR; | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_flags & F_SWR) { | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) { | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| m_flags &= ~F_SWR; | |||
| m_flags |= F_SRD; | |||
| m_w = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| m_p = m_buf + UNGETC_BUF_SIZE; | |||
| int nr = SdBaseFile::read(m_p, sizeof(m_buf) - UNGETC_BUF_SIZE); | |||
| if (nr <= 0) { | |||
| m_flags |= nr < 0 ? F_ERR : F_EOF; | |||
| m_r = 0; | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| m_r = nr; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // private | |||
| bool StdioStream::flushBuf() { | |||
| if (!(m_flags & F_SWR)) { /////////////////check for F_ERR ??//////////////////////// | |||
| if (!(m_flags & F_SRW)) { | |||
| m_flags |= F_ERR; | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| m_flags &= ~F_SRD; | |||
| m_flags |= F_SWR; | |||
| m_r = 0; | |||
| m_w = sizeof(m_buf); | |||
| m_p = m_buf; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| uint8_t n = m_p - m_buf; | |||
| m_p = m_buf; | |||
| m_w = sizeof(m_buf); | |||
| if (SdBaseFile::write(m_buf, n) == n) return true; | |||
| m_flags |= F_ERR; | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int StdioStream::flushPut(uint8_t c) { | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) return EOF; | |||
| m_w--; | |||
| return *m_p++ = c; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| char* StdioStream::fmtSpace(uint8_t len) { | |||
| if (m_w < len) { | |||
| if (!flushBuf() || m_w < len) { | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (len > m_w) return 0; | |||
| m_p += len; | |||
| m_w -= len; | |||
| return reinterpret_cast<char*>(m_p); | |||
| } | |||
+ 656
- 0
SdFat/StdioStream.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,656 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino RamDisk Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2014 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino RamDisk Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino RamDisk Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef StdioStream_h | |||
| #define StdioStream_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * StdioStream class | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <limits.h> | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdBaseFile.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Total size of stream buffer. The entire buffer is used for output. | |||
| * During input UNGETC_BUF_SIZE of this space is reserved for ungetc. | |||
| */ | |||
| const uint8_t STREAM_BUF_SIZE = 64; | |||
| /** Amount of buffer allocated for ungetc during input. */ | |||
| const uint8_t UNGETC_BUF_SIZE = 2; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Get rid of any macros defined in <stdio.h>. | |||
| #include <stdio.h> | |||
| #undef clearerr | |||
| #undef fclose | |||
| #undef feof | |||
| #undef ferror | |||
| #undef fflush | |||
| #undef fgetc | |||
| #undef fgetpos | |||
| #undef fgets | |||
| #undef fopen | |||
| #undef fprintf | |||
| #undef fputc | |||
| #undef fputs | |||
| #undef fread | |||
| #undef freopen | |||
| #undef fscanf | |||
| #undef fseek | |||
| #undef fsetpos | |||
| #undef ftell | |||
| #undef fwrite | |||
| #undef getc | |||
| #undef getchar | |||
| #undef gets | |||
| #undef perror | |||
| #undef printf | |||
| #undef putc | |||
| #undef putchar | |||
| #undef puts | |||
| #undef remove | |||
| #undef rename | |||
| #undef rewind | |||
| #undef scanf | |||
| #undef setbuf | |||
| #undef setvbuf | |||
| #undef sprintf // NOLINT | |||
| #undef sscanf | |||
| #undef tmpfile | |||
| #undef tmpnam | |||
| #undef ungetc | |||
| #undef vfprintf | |||
| #undef vprintf | |||
| #undef vsprintf | |||
| // make sure needed macros are defined | |||
| #ifndef EOF | |||
| /** End-of-file return value. */ | |||
| #define EOF (-1) | |||
| #endif // EOF | |||
| #ifndef NULL | |||
| /** Null pointer */ | |||
| #define NULL 0 | |||
| #endif // NULL | |||
| #ifndef SEEK_CUR | |||
| /** Seek relative to current position. */ | |||
| #define SEEK_CUR 1 | |||
| #endif // SEEK_CUR | |||
| #ifndef SEEK_END | |||
| /** Seek relative to end-of-file. */ | |||
| #define SEEK_END 2 | |||
| #endif // SEEK_END | |||
| #ifndef SEEK_SET | |||
| /** Seek relative to start-of-file. */ | |||
| #define SEEK_SET 0 | |||
| #endif // SEEK_SET | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** \class StdioStream | |||
| * \brief StdioStream implements a minimal stdio stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * StdioStream does not support subdirectories or long file names. | |||
| */ | |||
| class StdioStream : private SdBaseFile { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** Constructor | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| StdioStream() { | |||
| m_w = m_r = 0; | |||
| m_p = m_buf; | |||
| m_flags = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Clear the stream's end-of-file and error indicators. */ | |||
| void clearerr() {m_flags &= ~(F_ERR | F_EOF);} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Close a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * A successful call to the fclose function causes the stream to be | |||
| * flushed and the associated file to be closed. Any unwritten buffered | |||
| * data is written to the file; any unread buffered data is discarded. | |||
| * Whether or not the call succeeds, the stream is disassociated from | |||
| * the file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return zero if the stream was successfully closed, or EOF if any any | |||
| * errors are detected. | |||
| */ | |||
| int fclose(); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Test the stream's end-of-file indicator. | |||
| * \return non-zero if and only if the end-of-file indicator is set. | |||
| */ | |||
| int feof() {return (m_flags & F_EOF) != 0;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Test the stream's error indicator. | |||
| * \return return non-zero if and only if the error indicator is set. | |||
| */ | |||
| int ferror() {return (m_flags & F_ERR) != 0;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Flush the stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * If stream is an output stream or an update stream in which the most | |||
| * recent operation was not input, any unwritten data is written to the | |||
| * file; otherwise the call is an error since any buffered input data | |||
| * would be lost. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return sets the error indicator for the stream and returns EOF if an | |||
| * error occurs, otherwise it returns zero. | |||
| */ | |||
| int fflush(); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Get a byte from the stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return If the end-of-file indicator for the stream is set, or if the | |||
| * stream is at end-of-file, the end-of-file indicator for the stream is | |||
| * set and the fgetc function returns EOF. Otherwise, the fgetc function | |||
| * returns the next character from the input stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| int fgetc() {return m_r-- == 0 ? fillGet() : *m_p++;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Get a string from a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * The fgets function reads at most one less than the number of | |||
| * characters specified by num from the stream into the array pointed | |||
| * to by str. No additional characters are read after a new-line | |||
| * character (which is retained) or after end-of-file. A null character | |||
| * is written immediately after the last character read into the array. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] str Pointer to an array of where the string is copied. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] num Maximum number of characters including the null | |||
| * character. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] len If len is not null and fgets is successful, the | |||
| * length of the string is returned. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return str if successful. If end-of-file is encountered and no | |||
| * characters have been read into the array, the contents of the array | |||
| * remain unchanged and a null pointer is returned. If a read error | |||
| * occurs during the operation, the array contents are indeterminate | |||
| * and a null pointer is returned. | |||
| */ | |||
| char* fgets(char* str, int num, size_t* len = 0); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Open a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * Open a file and associates the stream with it. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] filename name of the file to be opened. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] mode a string that indicates the open mode. | |||
| * | |||
| * <table> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"r" or "rb"</td> | |||
| * <td>Open a file for reading. The file must exist.</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"w" or "wb"</td> | |||
| * <td>Truncate an existing to zero length or create an empty file | |||
| * for writing.</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"wx" or "wbx"</td> | |||
| * <td>Create a file for writing. Fails if the file already exists.</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"a" or "ab"</td> | |||
| * <td>Append; open or create file for writing at end-of-file.</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"r+" or "rb+" or "r+b"</td> | |||
| * <td>Open a file for update (reading and writing).</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"w+" or "w+b" or "wb+"</td> | |||
| * <td>Truncate an existing to zero length or create a file for update.</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"w+x" or "w+bx" or "wb+x"</td> | |||
| * <td>Create a file for update. Fails if the file already exists.</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * <tr> | |||
| * <td>"a+" or "a+b" or "ab+"</td> | |||
| * <td>Append; open or create a file for update, writing at end-of-file.</td> | |||
| * </tr> | |||
| * </table> | |||
| * The character 'b' shall have no effect, but is allowed for ISO C | |||
| * standard conformance. | |||
| * | |||
| * Opening a file with append mode causes all subsequent writes to the | |||
| * file to be forced to the then current end-of-file, regardless of | |||
| * intervening calls to the fseek function. | |||
| * | |||
| * When a file is opened with update mode, both input and output may be | |||
| * performed on the associated stream. However, output shall not be | |||
| * directly followed by input without an intervening call to the fflush | |||
| * function or to a file positioning function (fseek, or rewind), and | |||
| * input shall not be directly followed by output without an intervening | |||
| * call to a file positioning function, unless the input operation | |||
| * encounters endof-file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true for success or false for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool fopen(const char* filename, const char * mode); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a byte to a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] c the byte to be written (converted to an unsigned char). | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Upon successful completion, fputc() returns the value it | |||
| * has written. Otherwise, it returns EOF and sets the error indicator for | |||
| * the stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| int fputc(int c) {return m_w-- == 0 ? flushPut(c) : *m_p++ = c;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a string to a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] str a pointer to the string to be written. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return for success, fputs() returns a non-negative | |||
| * number. Otherwise, it returns EOF and sets the error indicator for | |||
| * the stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| int fputs(const char* str); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a string stored in flash. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] str string to be written. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return for success, fputs() returns a non-negative | |||
| * number. Otherwise, it returns EOF and sets the error indicator for | |||
| * the stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| int fputs_P(PGM_P str); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Binary input. | |||
| * | |||
| * Reads an array of up to count elements, each one with a size of size | |||
| * bytes. | |||
| * \param[out] ptr pointer to area of at least (size*count) bytes where | |||
| * the data will be stored. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] size the size, in bytes, of each element to be read. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] count the number of elements to be read. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return number of elements successfully read, which may be less than | |||
| * count if a read error or end-of-file is encountered. If size or count | |||
| * is zero, fread returns zero and the contents of the array and the | |||
| * state of the stream remain unchanged. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t fread(void* ptr, size_t size, size_t count); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Set the file position for the stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] offset number of offset from the origin. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] origin position used as reference for the offset. It is | |||
| * specified by one of the following constants. | |||
| * | |||
| * SEEK_SET - Beginning of file. | |||
| * | |||
| * SEEK_CUR - Current position of the file pointer. | |||
| * | |||
| * SEEK_END - End of file. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return zero for success. Otherwise, it returns non-zero and sets the | |||
| * error indicator for the stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| int fseek(int32_t offset, int origin); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Get the current position in a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return If successful, ftell return the current value of the position | |||
| * indicator. On failure, ftell returns −1L. | |||
| */ | |||
| int32_t ftell(); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Binary output. | |||
| * | |||
| * Writes an array of up to count elements, each one with a size of size | |||
| * bytes. | |||
| * \param[in] ptr pointer to (size*count) bytes of data to be written. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] size the size, in bytes, of each element to be written. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] count the number of elements to be written. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return number of elements successfully written. if this number is | |||
| * less than count, an error has occured. If size or count is zero, | |||
| * fwrite returns zero. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t fwrite(const void * ptr, size_t size, size_t count); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Get a byte from the stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * getc and fgetc are equivalent but getc is inline so it is faster but | |||
| * require more flash memory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return If the end-of-file indicator for the stream is set, or if the | |||
| * stream is at end-of-file, the end-of-file indicator for the stream is | |||
| * set and the fgetc function returns EOF. Otherwise, the fgetc function | |||
| * returns the next character from the input stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| int getc() {return m_r-- == 0 ? fillGet() : *m_p++;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a byte to a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * putc and fputc are equivalent but putc is inline so it is faster but | |||
| * require more flash memory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] c the byte to be written (converted to an unsigned char). | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Upon successful completion, fputc() returns the value it | |||
| * has written. Otherwise, it returns EOF and sets the error indicator for | |||
| * the stream. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| int putc(int c) {return m_w-- == 0 ? flushPut(c) : *m_p++ = c;} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a CR/LF. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return two, the number of bytes written, for success or -1 for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| int putCRLF() { | |||
| if (m_w < 2) { | |||
| if (!flushBuf()) return -1; | |||
| } | |||
| *m_p++ = '\r'; | |||
| *m_p++ = '\n'; | |||
| m_w -= 2; | |||
| return 2; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a character. | |||
| * \param[in] c the character to write. | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t print(char c) { | |||
| return putc(c) < 0 ? 0 : 1; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a string. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] str the string to be written. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t print(const char* str) { | |||
| int n = fputs(str); | |||
| return n < 0 ? 0 : n; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a string stored in flash memory. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] str the string to print. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t print(const __FlashStringHelper *str); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a floating point number. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] val the number to be printed. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t print(double val, uint8_t prec = 2) { | |||
| return print(static_cast<float>(val), prec); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a floating point number. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] val the number to be printed. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t print(float val, uint8_t prec = 2) { | |||
| int n = printDec(val, prec); | |||
| return n > 0 ? n : 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a number. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] val the number to be printed. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| template <typename T> | |||
| size_t print(T val) { | |||
| int n = printDec(val); | |||
| return n > 0 ? n : 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write a CR/LF. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return two, the number of bytes written, for success or zero for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t println() { | |||
| return putCRLF() > 0 ? 2 : 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a floating point number followed by CR/LF. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] val the number to be printed. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t println(double val, uint8_t prec = 2) { | |||
| return println(static_cast<float>(val), prec); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a floating point number followed by CR/LF. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] val the number to be printed. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| size_t println(float val, uint8_t prec = 2) { | |||
| int n = printDec(val, prec); | |||
| return n > 0 && putCRLF() > 0 ? n + 2 : 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print an item followed by CR/LF | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] val the item to be printed. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return the number of bytes written. | |||
| */ | |||
| template <typename T> | |||
| size_t println(T val) { | |||
| int n = print(val); | |||
| return putCRLF() > 0 ? n + 2 : 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a char as a number. | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(char n) { | |||
| if (CHAR_MIN == 0) { | |||
| return printDec((unsigned char)n); | |||
| } else { | |||
| return printDec((signed char)n); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** print a signed 8-bit integer | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(signed char n); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print an unsigned 8-bit number. | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be print. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(unsigned char n) { | |||
| return printDec((uint16_t)n); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a int16_t | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(int16_t n); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** print a uint16_t. | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(uint16_t n); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a signed 32-bit integer. | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(int32_t n); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write an unsigned 32-bit number. | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(uint32_t n); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a double. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(double value, uint8_t prec) { | |||
| return printDec(static_cast<float>(value), prec); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a float. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printDec(float value, uint8_t prec); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] term The field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printField(double value, char term, uint8_t prec = 2) { | |||
| return printField(static_cast<float>(value), term, prec) > 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] term The field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printField(float value, char term, uint8_t prec = 2) { | |||
| int rtn = printDec(value, prec); | |||
| return rtn < 0 || putc(term) < 0 ? -1 : rtn + 1; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] term The field terminator. | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| template <typename T> | |||
| int printField(T value, char term) { | |||
| int rtn = printDec(value); | |||
| return rtn < 0 || putc(term) < 0 ? -1 : rtn + 1; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print HEX | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed as HEX. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printHex(uint32_t n); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Print HEX with CRLF | |||
| * \param[in] n number to be printed as HEX. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The number of bytes written or -1 if an error occurs. | |||
| */ | |||
| int printHexln(uint32_t n) { | |||
| int rtn = printHex(n); | |||
| return rtn < 0 || putCRLF() != 2 ? -1 : rtn + 2; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Set position of a stream to the beginning. | |||
| * | |||
| * The rewind function sets the file position to the beginning of the | |||
| * file. It is equivalent to fseek(0L, SEEK_SET) except that the error | |||
| * indicator for the stream is also cleared. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true for success or false for failure. | |||
| */ | |||
| bool rewind(); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Push a byte back into an input stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] c the byte (converted to an unsigned char) to be pushed back. | |||
| * | |||
| * One character of pushback is guaranteed. If the ungetc function is | |||
| * called too many times without an intervening read or file positioning | |||
| * operation on that stream, the operation may fail. | |||
| * | |||
| * A successful intervening call to a file positioning function (fseek, | |||
| * fsetpos, or rewind) discards any pushed-back characters for the stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Upon successful completion, ungetc() returns the byte pushed | |||
| * back after conversion. Otherwise it returns EOF. | |||
| */ | |||
| int ungetc(int c); | |||
| //============================================================================ | |||
| private: | |||
| bool fillBuf(); | |||
| int fillGet(); | |||
| bool flushBuf(); | |||
| int flushPut(uint8_t c); | |||
| char* fmtSpace(uint8_t len); | |||
| int write(const void* buf, size_t count); | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| // F_SRD and F_WR are never simultaneously asserted | |||
| static const uint8_t F_SRD = 0x01; // OK to read | |||
| static const uint8_t F_SWR = 0x02; // OK to write | |||
| static const uint8_t F_SRW = 0x04; // open for reading & writing | |||
| static const uint8_t F_EOF = 0x10; // found EOF | |||
| static const uint8_t F_ERR = 0x20; // found error | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| uint8_t m_flags; | |||
| uint8_t* m_p; | |||
| uint8_t m_r; | |||
| uint8_t m_w; | |||
| uint8_t m_buf[STREAM_BUF_SIZE]; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #endif // StdioStream_h | |||
+ 146
- 0
SdFat/bufstream.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,146 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef bufstream_h | |||
| #define bufstream_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief \ref ibufstream and \ref obufstream classes | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <iostream.h> | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ibufstream | |||
| * \brief parse a char string | |||
| */ | |||
| class ibufstream : public istream { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** Constructor */ | |||
| ibufstream() : m_buf(0), m_len(0) {} | |||
| /** Constructor | |||
| * \param[in] str pointer to string to be parsed | |||
| * Warning: The string will not be copied so must stay in scope. | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit ibufstream(const char* str) { | |||
| init(str); | |||
| } | |||
| /** Initialize an ibufstream | |||
| * \param[in] str pointer to string to be parsed | |||
| * Warning: The string will not be copied so must stay in scope. | |||
| */ | |||
| void init(const char* str) { | |||
| m_buf = str; | |||
| m_len = strlen(m_buf); | |||
| m_pos = 0; | |||
| clear(); | |||
| } | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| int16_t getch() { | |||
| if (m_pos < m_len) return m_buf[m_pos++]; | |||
| setstate(eofbit); | |||
| return -1; | |||
| } | |||
| void getpos(FatPos_t *pos) { | |||
| pos->position = m_pos; | |||
| } | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) {return false;} | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos) { | |||
| if (pos < m_len) { | |||
| m_pos = pos; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| void setpos(FatPos_t *pos) { | |||
| m_pos = pos->position; | |||
| } | |||
| pos_type tellpos() { | |||
| return m_pos; | |||
| } | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| private: | |||
| const char* m_buf; | |||
| size_t m_len; | |||
| size_t m_pos; | |||
| }; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class obufstream | |||
| * \brief format a char string | |||
| */ | |||
| class obufstream : public ostream { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** constructor */ | |||
| obufstream() : m_in(0) {} | |||
| /** Constructor | |||
| * \param[in] buf buffer for formatted string | |||
| * \param[in] size buffer size | |||
| */ | |||
| obufstream(char *buf, size_t size) { | |||
| init(buf, size); | |||
| } | |||
| /** Initialize an obufstream | |||
| * \param[in] buf buffer for formatted string | |||
| * \param[in] size buffer size | |||
| */ | |||
| void init(char *buf, size_t size) { | |||
| m_buf = buf; | |||
| buf[0] = '\0'; | |||
| m_size = size; | |||
| m_in = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| /** \return a pointer to the buffer */ | |||
| char* buf() {return m_buf;} | |||
| /** \return the length of the formatted string */ | |||
| size_t length() {return m_in;} | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| void putch(char c) { | |||
| if (m_in >= (m_size - 1)) { | |||
| setstate(badbit); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| m_buf[m_in++] = c; | |||
| m_buf[m_in]= '\0'; | |||
| } | |||
| void putstr(const char *str) { | |||
| while (*str) putch(*str++); | |||
| } | |||
| bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) {return false;} | |||
| bool seekpos(pos_type pos) { | |||
| if (pos > m_in) return false; | |||
| m_in = pos; | |||
| m_buf[m_in] = '\0'; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| bool sync() {return true;} | |||
| pos_type tellpos() { | |||
| return m_in; | |||
| } | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| private: | |||
| char *m_buf; | |||
| size_t m_size; | |||
| size_t m_in; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // bufstream_h | |||
+ 172
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/AnalogLogger/AnalogLogger.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,172 @@ | |||
| // A simple data logger for the Arduino analog pins with optional DS1307 | |||
| // uses RTClib from https://github.com/adafruit/RTClib | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> // define FreeRam() | |||
| #define SD_CHIP_SELECT SS // SD chip select pin | |||
| #define USE_DS1307 0 // set nonzero to use DS1307 RTC | |||
| #define LOG_INTERVAL 1000 // mills between entries | |||
| #define SENSOR_COUNT 3 // number of analog pins to log | |||
| #define ECHO_TO_SERIAL 1 // echo data to serial port if nonzero | |||
| #define WAIT_TO_START 1 // Wait for serial input in setup() | |||
| #define ADC_DELAY 10 // ADC delay for high impedence sensors | |||
| // file system object | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // text file for logging | |||
| ofstream logfile; | |||
| // Serial print stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| // buffer to format data - makes it eaiser to echo to Serial | |||
| char buf[80]; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #if SENSOR_COUNT > 6 | |||
| #error SENSOR_COUNT too large | |||
| #endif // SENSOR_COUNT | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #if USE_DS1307 | |||
| // use RTClib from Adafruit | |||
| // https://github.com/adafruit/RTClib | |||
| // The Arduino IDE has a bug that causes Wire and RTClib to be loaded even | |||
| // if USE_DS1307 is false. | |||
| #error remove this line and uncomment the next two lines. | |||
| //#include <Wire.h> | |||
| //#include <RTClib.h> | |||
| RTC_DS1307 RTC; // define the Real Time Clock object | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // call back for file timestamps | |||
| void dateTime(uint16_t* date, uint16_t* time) { | |||
| DateTime now = RTC.now(); | |||
| // return date using FAT_DATE macro to format fields | |||
| *date = FAT_DATE(now.year(), now.month(), now.day()); | |||
| // return time using FAT_TIME macro to format fields | |||
| *time = FAT_TIME(now.hour(), now.minute(), now.second()); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // format date/time | |||
| ostream& operator << (ostream& os, DateTime& dt) { | |||
| os << dt.year() << '/' << int(dt.month()) << '/' << int(dt.day()) << ','; | |||
| os << int(dt.hour()) << ':' << setfill('0') << setw(2) << int(dt.minute()); | |||
| os << ':' << setw(2) << int(dt.second()) << setfill(' '); | |||
| return os; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_DS1307 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial){} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << endl << pstr("FreeRam: ") << FreeRam() << endl; | |||
| #if WAIT_TO_START | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| #endif // WAIT_TO_START | |||
| #if USE_DS1307 | |||
| // connect to RTC | |||
| Wire.begin(); | |||
| if (!RTC.begin()) error("RTC failed"); | |||
| // set date time callback function | |||
| SdFile::dateTimeCallback(dateTime); | |||
| DateTime now = RTC.now(); | |||
| cout << now << endl; | |||
| #endif // USE_DS1307 | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CHIP_SELECT, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // create a new file in root, the current working directory | |||
| char name[] = "LOGGER00.CSV"; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 100; i++) { | |||
| name[6] = i/10 + '0'; | |||
| name[7] = i%10 + '0'; | |||
| if (sd.exists(name)) continue; | |||
| logfile.open(name); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!logfile.is_open()) error("file.open"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Logging to: ") << name << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to stop\n\n"); | |||
| // format header in buffer | |||
| obufstream bout(buf, sizeof(buf)); | |||
| bout << pstr("millis"); | |||
| #if USE_DS1307 | |||
| bout << pstr(",date,time"); | |||
| #endif // USE_DS1307 | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < SENSOR_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| bout << pstr(",sens") << int(i); | |||
| } | |||
| logfile << buf << endl; | |||
| #if ECHO_TO_SERIAL | |||
| cout << buf << endl; | |||
| #endif // ECHO_TO_SERIAL | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| uint32_t m; | |||
| // wait for time to be a multiple of interval | |||
| do { | |||
| m = millis(); | |||
| } while (m % LOG_INTERVAL); | |||
| // use buffer stream to format line | |||
| obufstream bout(buf, sizeof(buf)); | |||
| // start with time in millis | |||
| bout << m; | |||
| #if USE_DS1307 | |||
| DateTime now = RTC.now(); | |||
| bout << ',' << now; | |||
| #endif // USE_DS1307 | |||
| // read analog pins and format data | |||
| for (uint8_t ia = 0; ia < SENSOR_COUNT; ia++) { | |||
| #if ADC_DELAY | |||
| analogRead(ia); | |||
| delay(ADC_DELAY); | |||
| #endif // ADC_DELAY | |||
| bout << ',' << analogRead(ia); | |||
| } | |||
| bout << endl; | |||
| // log data and flush to SD | |||
| logfile << buf << flush; | |||
| // check for error | |||
| if (!logfile) error("write data failed"); | |||
| #if ECHO_TO_SERIAL | |||
| cout << buf; | |||
| #endif // ECHO_TO_SERIAL | |||
| // don't log two points in the same millis | |||
| if (m == millis()) delay(1); | |||
| if (!Serial.available()) return; | |||
| logfile.close(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Done!"); | |||
| while (1); | |||
| } | |||
+ 15
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/HelloWorld/HelloWorld.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // create a serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| delay(2000); | |||
| cout << "Hello, World!\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 18
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/MiniSerial/MiniSerial.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ | |||
| // This example illustrates use of SdFat's | |||
| // minimal unbuffered AVR Serial support. | |||
| // | |||
| // This is useful for debug and saves RAM | |||
| // Will not work on Due, Leonardo, or Teensy | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| #ifndef UDR0 | |||
| #error no AVR serial port0 | |||
| #endif | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| MiniSerial.begin(9600); | |||
| MiniSerial.println(FreeRam()); | |||
| MiniSerial.println(F("Type any Character")); | |||
| while(MiniSerial.read() < 0) {} | |||
| MiniSerial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 113
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/PrintBenchmarkSD/PrintBenchmarkSD.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,113 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch is a simple Print benchmark. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SD.h> | |||
| #include <SPI.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // number of lines to print | |||
| const uint16_t N_PRINT = 20000; | |||
| // test file | |||
| File file; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void error(char* s) { | |||
| Serial.println(s); | |||
| while(1); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) { | |||
| // wait for Leonardo | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| uint32_t maxLatency; | |||
| uint32_t minLatency; | |||
| uint32_t totalLatency; | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) { | |||
| } | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| Serial.println(F("Type any character to start")); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) { | |||
| } | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card | |||
| if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) error("begin"); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Starting print test. Please wait.\n")); | |||
| // do write test | |||
| for (int test = 0; test < 2; test++) { | |||
| file = SD.open("BENCH.TXT", FILE_WRITE); | |||
| if (!file) error("open failed"); | |||
| switch(test) { | |||
| case 0: | |||
| Serial.println(F("Test of println(uint16_t)")); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 1: | |||
| Serial.println(F("Test of println(double)")); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| maxLatency = 0; | |||
| minLatency = 999999; | |||
| totalLatency = 0; | |||
| uint32_t t = millis(); | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < N_PRINT; i++) { | |||
| uint32_t m = micros(); | |||
| switch(test) { | |||
| case 0: | |||
| file.println(i); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 1: | |||
| file.println((double)0.01*i); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| // if (file.writeError) { | |||
| // error("write failed"); | |||
| // } | |||
| m = micros() - m; | |||
| if (maxLatency < m) maxLatency = m; | |||
| if (minLatency > m) minLatency = m; | |||
| totalLatency += m; | |||
| } | |||
| file.flush(); | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| double s = file.size(); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Time ")); | |||
| Serial.print(0.001*t); | |||
| Serial.println(F(" sec")); | |||
| Serial.print(F("File size ")); | |||
| Serial.print(0.001*s); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" KB\n")); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Write ")); | |||
| Serial.print(s/t); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" KB/sec\n")); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Maximum latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(maxLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec, Minimum Latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(minLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec, Avg Latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(totalLatency/N_PRINT); | |||
| Serial.println(F(" usec\n")); | |||
| SD.remove("BENCH.TXT"); | |||
| } | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done!\n")); | |||
| } | |||
+ 26
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/SD_Size/SD_Size.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,26 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Sketch to compare size of Arduino SD library with SdFat V2. | |||
| * See SdFatSize.pde for SdFat sketch. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SPI.h> | |||
| #include <SD.h> | |||
| File file; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| if (!SD.begin()) { | |||
| Serial.println("begin failed"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| file = SD.open("TEST_SD.TXT", FILE_WRITE); | |||
| file.println("Hello"); | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| Serial.println("Done"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 28
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/SdFatSize/SdFatSize.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Sketch to compare size of SdFat V2 with Arduino SD library. | |||
| * See SD_Size.pde for Arduino SD sketch. | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| if (!sd.begin()) { | |||
| Serial.println("begin failed"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| file.open("SIZE_TST.TXT", O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_AT_END); | |||
| file.println("Hello"); | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| Serial.println("Done"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 135
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/TestMkdir/TestMkdir.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,135 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch is a test of subdirectory and file creation. | |||
| * It also tests allocation of clusters to directories. | |||
| * | |||
| * It will create two subdirectories and create enough files | |||
| * to force the allocation of a cluster to each directory. | |||
| * | |||
| * More than 3000 files may be created on a FAT32 volume. | |||
| * | |||
| * Note: Some cards may 'stutter' others just get slow due | |||
| * to the number of flash erases this program causes. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| const uint8_t SD_CHIP_SELECT = SS; | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| /* | |||
| * create enough files to force a cluster to be allocated to dir. | |||
| */ | |||
| void dirAllocTest(SdBaseFile* dir) { | |||
| char buf[13], name[13]; | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| uint16_t n; | |||
| uint32_t size = dir->fileSize(); | |||
| // create files and write name to file | |||
| for (n = 0; ; n++){ | |||
| // make file name | |||
| sprintf(name, "%u.TXT", n); | |||
| // open start time | |||
| uint32_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| if (!file.open(dir, name, O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_EXCL)) { | |||
| error("open for write failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // open end time and write start time | |||
| uint32_t t1 = millis(); | |||
| // write file name to file | |||
| file.print(name); | |||
| if (!file.close()) error("close write"); | |||
| // write end time | |||
| uint32_t t2 = millis(); | |||
| PgmPrint("WR "); | |||
| Serial.print(n); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| // print time to create file | |||
| Serial.print(t1 - t0); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| // print time to write file | |||
| Serial.println(t2 - t1); | |||
| // directory size will change when a cluster is added | |||
| if (dir->fileSize() != size) break; | |||
| } | |||
| // read files and check content | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i <= n; i++) { | |||
| sprintf(name, "%u.TXT", i); | |||
| // open start time | |||
| uint32_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| if (!file.open(dir, name, O_READ)) { | |||
| error("open for read failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // open end time and read start time | |||
| uint32_t t1 = millis(); | |||
| int16_t nr = file.read(buf, 13); | |||
| if (nr < 5) error("file.read failed"); | |||
| // read end time | |||
| uint32_t t2 = millis(); | |||
| // check file content | |||
| if (strlen(name) != nr || strncmp(name, buf, nr)) { | |||
| error("content compare failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| if (!file.close()) error("close read failed"); | |||
| PgmPrint("RD "); | |||
| Serial.print(i); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| // print open time | |||
| Serial.print(t1 - t0); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| // print read time | |||
| Serial.println(t2 - t1); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| PgmPrintln("Type any character to start"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(200); // Catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_FULL_SPEED for best performance. | |||
| // try SPI_HALF_SPEED if bus errors occur. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CHIP_SELECT, SPI_FULL_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // write files to root if FAT32 | |||
| if (sd.vol()->fatType() == 32) { | |||
| PgmPrintln("Writing files to root"); | |||
| dirAllocTest(sd.vwd()); | |||
| } | |||
| // create sub1 and write files | |||
| SdFile sub1; | |||
| if (!sub1.makeDir(sd.vwd(), "SUB1")) error("makdeDir SUB1 failed"); | |||
| PgmPrintln("Writing files to SUB1"); | |||
| dirAllocTest(&sub1); | |||
| // create sub2 and write files | |||
| SdFile sub2; | |||
| if (!sub2.makeDir(&sub1, "SUB2")) error("makeDir SUB2 failed"); | |||
| PgmPrintln("Writing files to SUB2"); | |||
| dirAllocTest(&sub2); | |||
| PgmPrintln("Done"); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() { } | |||
+ 97
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/TestRmdir/TestRmdir.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,97 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch will remove the files and directories | |||
| * created by the SdFatMakeDir.pde sketch. | |||
| * | |||
| * Performance is erratic due to the large number | |||
| * of flash erase operations caused by many random | |||
| * writes to file structures. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| const uint8_t SD_CHIP_SELECT = SS; | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| /* | |||
| * remove all files in dir. | |||
| */ | |||
| void deleteFiles(SdBaseFile* dir) { | |||
| char name[13]; | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| // open and delete files | |||
| for (uint16_t n = 0; ; n++){ | |||
| sprintf(name, "%u.TXT", n); | |||
| // open start time | |||
| uint32_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| // assume done if open fails | |||
| if (!file.open(dir, name, O_WRITE)) return; | |||
| // open end time and remove start time | |||
| uint32_t t1 = millis(); | |||
| if (!file.remove()) error("file.remove failed"); | |||
| // remove end time | |||
| uint32_t t2 = millis(); | |||
| PgmPrint("RM "); | |||
| Serial.print(n); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| // open time | |||
| Serial.print(t1 - t0); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| // remove time | |||
| Serial.println(t2 - t1); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| PgmPrintln("Type any character to start"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(200); // Catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_FULL_SPEED for best performance. | |||
| // try SPI_HALF_SPEED if bus errors occur. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CHIP_SELECT, SPI_FULL_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // delete files in root if FAT32 | |||
| if (sd.vol()->fatType() == 32) { | |||
| PgmPrintln("Remove files in root"); | |||
| deleteFiles(sd.vwd()); | |||
| } | |||
| // open SUB1 and delete files | |||
| SdFile sub1; | |||
| if (!sub1.open("SUB1", O_READ)) error("open SUB1 failed"); | |||
| PgmPrintln("Remove files in SUB1"); | |||
| deleteFiles(&sub1); | |||
| // open SUB2 and delete files | |||
| SdFile sub2; | |||
| if (!sub2.open(&sub1, "SUB2", O_READ)) error("open SUB2 failed"); | |||
| PgmPrintln("Remove files in SUB2"); | |||
| deleteFiles(&sub2); | |||
| // remove SUB2 | |||
| if (!sub2.rmDir()) error("sub2.rmDir failed"); | |||
| PgmPrintln("SUB2 removed"); | |||
| // remove SUB1 | |||
| if (!sub1.rmDir()) error("sub1.rmDir failed"); | |||
| PgmPrintln("SUB1 removed"); | |||
| PgmPrintln("Done"); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() { } | |||
+ 63
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/append/append.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,63 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Append Example | |||
| * | |||
| * This sketch shows how to use open for append. | |||
| * The sketch will append 100 line each time it opens the file. | |||
| * The sketch will open and close the file 100 times. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system object | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // create Serial stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| // filename for this example | |||
| char name[] = "APPEND.TXT"; | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| // pstr() stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << endl << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // Catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Appending to: ") << name; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 100; i++) { | |||
| // open stream for append | |||
| ofstream sdout(name, ios::out | ios::app); | |||
| if (!sdout) error("open failed"); | |||
| // append 100 lines to the file | |||
| for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 100; j++) { | |||
| // use int() so byte will print as decimal number | |||
| sdout << "line " << int(j) << " of pass " << int(i); | |||
| sdout << " millis = " << millis() << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| // close the stream | |||
| sdout.close(); | |||
| if (!sdout) error("append data failed"); | |||
| // output progress indicator | |||
| if (i % 25 == 0) cout << endl; | |||
| cout << '.'; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << endl << "Done" << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 70
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/average/average.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,70 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Calculate the sum and average of a list of floating point numbers | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // object for the SD file system | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // define a serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void writeTestFile() { | |||
| // open the output file | |||
| ofstream sdout("AVG_TEST.TXT"); | |||
| // write a series of float numbers | |||
| for (int16_t i = -1001; i < 2000; i += 13) { | |||
| sdout << 0.1 * i << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!sdout) sd.errorHalt("sdout failed"); | |||
| sdout.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void calcAverage() { | |||
| uint16_t n = 0; // count of input numbers | |||
| double num; // current input number | |||
| double sum = 0; // sum of input numbers | |||
| // open the input file | |||
| ifstream sdin("AVG_TEST.TXT"); | |||
| // check for an open failure | |||
| if (!sdin) sd.errorHalt("sdin failed"); | |||
| // read and sum the numbers | |||
| while (sdin >> num) { | |||
| n++; | |||
| sum += num; | |||
| } | |||
| // print the results | |||
| cout << "sum of " << n << " numbers = " << sum << endl; | |||
| cout << "average = " << sum/n << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // Catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // write the test file | |||
| writeTestFile(); | |||
| // read the test file and calculate the average | |||
| calcAverage(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 133
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/benchSD/benchSD.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,133 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch is a simple binary write/read benchmark | |||
| * for the standard Arduino SD.h library. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SPI.h> | |||
| #include <SD.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| #define FILE_SIZE_MB 5 | |||
| #define FILE_SIZE (1000000UL*FILE_SIZE_MB) | |||
| #define BUF_SIZE 100 | |||
| uint8_t buf[BUF_SIZE]; | |||
| // test file | |||
| File file; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void error(char* s) { | |||
| Serial.println(s); | |||
| while(1); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial){} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| uint32_t maxLatency; | |||
| uint32_t minLatency; | |||
| uint32_t totalLatency; | |||
| // discard any input | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| Serial.println(F("Type any character to start")); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) error("begin"); | |||
| // open or create file - truncate existing file. | |||
| file = SD.open("BENCH.DAT", FILE_WRITE | O_TRUNC); | |||
| // file = SD.open("BENCH.DAT", O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT); | |||
| if (!file) { | |||
| error("open failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // fill buf with known data | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < (BUF_SIZE-2); i++) { | |||
| buf[i] = 'A' + (i % 26); | |||
| } | |||
| buf[BUF_SIZE-2] = '\r'; | |||
| buf[BUF_SIZE-1] = '\n'; | |||
| Serial.print(F("File size ")); | |||
| Serial.print(FILE_SIZE_MB); | |||
| Serial.println(F("MB")); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Buffer size ")); | |||
| Serial.print(BUF_SIZE); | |||
| Serial.println(F(" bytes")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Starting write test. Please wait up to a minute")); | |||
| // do write test | |||
| uint32_t n = FILE_SIZE/sizeof(buf); | |||
| maxLatency = 0; | |||
| minLatency = 999999; | |||
| totalLatency = 0; | |||
| uint32_t t = millis(); | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| uint32_t m = micros(); | |||
| if (file.write(buf, sizeof(buf)) != sizeof(buf)) { | |||
| error("write failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| m = micros() - m; | |||
| if (maxLatency < m) maxLatency = m; | |||
| if (minLatency > m) minLatency = m; | |||
| totalLatency += m; | |||
| } | |||
| file.flush(); | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| double s = file.size(); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Write ")); | |||
| Serial.print(s/t); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" KB/sec\n")); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Maximum latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(maxLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec, Minimum Latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(minLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec, Avg Latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(totalLatency/n); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec\n\n")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Starting read test. Please wait up to a minute")); | |||
| // do read test | |||
| file.seek(0); | |||
| maxLatency = 0; | |||
| minLatency = 99999; | |||
| totalLatency = 0; | |||
| t = millis(); | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| buf[BUF_SIZE-1] = 0; | |||
| uint32_t m = micros(); | |||
| if (file.read(buf, sizeof(buf)) != sizeof(buf)) { | |||
| error("read failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| m = micros() - m; | |||
| if (maxLatency < m) maxLatency = m; | |||
| if (minLatency > m) minLatency = m; | |||
| totalLatency += m; | |||
| if (buf[BUF_SIZE-1] != '\n') { | |||
| error("data check"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| Serial.print(F("Read ")); | |||
| Serial.print(s/t); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" KB/sec\n")); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Maximum latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(maxLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec, Minimum Latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(minLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec, Avg Latency: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(totalLatency/n); | |||
| Serial.print(F(" usec\n\n")); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Done\n\n")); | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| } | |||
+ 33
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/bufstream/bufstream.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,33 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Use of ibufsteam to parse a line and obufstream to format a line | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // create a serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| char buf[20]; // buffer for formatted line | |||
| int i, j, k; // values from parsed line | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| delay(2000); | |||
| // initialize input string | |||
| ibufstream bin("123 456 789"); | |||
| // parse the string "123 456 789" | |||
| bin >> i >> j >> k; | |||
| // initialize output buffer | |||
| obufstream bout(buf, sizeof(buf)); | |||
| // format the output string | |||
| bout << k << ',' << j << ',' << i << endl; | |||
| // write the string to serial | |||
| cout << buf; | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 53
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/eventlog/eventlog.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Append a line to a file - demo of pathnames and streams | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system object | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // define a serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Append a line to LOGFILE.TXT | |||
| */ | |||
| void logEvent(const char *msg) { | |||
| // create dir if needed | |||
| sd.mkdir("LOGS/2011/JAN"); | |||
| // create or open a file for append | |||
| ofstream sdlog("LOGS/2011/JAN/LOGFILE.TXT", ios::out | ios::app); | |||
| // append a line to the file | |||
| sdlog << msg << endl; | |||
| // check for errors | |||
| if (!sdlog) sd.errorHalt("append failed"); | |||
| sdlog.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // append a line to the logfile | |||
| logEvent("Another line for the logfile"); | |||
| cout << "Done - check /LOGS/2011/JAN/LOGFILE.TXT on the SD" << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 91
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/fgetsRewrite/fgetsRewrite.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,91 @@ | |||
| // Demo of rewriting a line read by fgets | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD card chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // print stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash memory | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void demoFgets() { | |||
| char line[25]; | |||
| int c; | |||
| uint32_t pos; | |||
| // open test file | |||
| SdFile rdfile("FGETS.TXT", O_RDWR); | |||
| // check for open error | |||
| if (!rdfile.isOpen()) error("demoFgets"); | |||
| // list file | |||
| cout << pstr("-----Before Rewrite\r\n"); | |||
| while ((c = rdfile.read()) >= 0) Serial.write(c); | |||
| rdfile.rewind(); | |||
| // read lines from the file to get position | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| pos = rdfile.curPosition(); | |||
| if (rdfile.fgets(line, sizeof(line)) < 0) { | |||
| error("Line not found"); | |||
| } | |||
| // find line that contains "Line C" | |||
| if (strstr(line, "Line C"))break; | |||
| } | |||
| // rewrite line with 'C' | |||
| if (!rdfile.seekSet(pos))error("seekSet"); | |||
| rdfile.println("Line R"); | |||
| rdfile.rewind(); | |||
| // list file | |||
| cout << pstr("\r\n-----After Rewrite\r\n"); | |||
| while ((c = rdfile.read()) >= 0) Serial.write(c); | |||
| // close so rewrite is not lost | |||
| rdfile.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void makeTestFile() { | |||
| // create or open test file | |||
| SdFile wrfile("FGETS.TXT", O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC); | |||
| // check for open error | |||
| if (!wrfile.isOpen()) error("MakeTestFile"); | |||
| // write test file | |||
| wrfile.write_P(PSTR( | |||
| "Line A\r\n" | |||
| "Line B\r\n" | |||
| "Line C\r\n" | |||
| "Line D\r\n" | |||
| "Line E\r\n" | |||
| )); | |||
| wrfile.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial){} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| makeTestFile(); | |||
| demoFgets(); | |||
| cout << pstr("\nDone\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop(void) {} | |||
+ 40
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/readlog/readlog.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Read the logfile created by the eventlog.pde example. | |||
| * Demo of pathnames and working directories | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system object | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // define a serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| int c; | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // set current working directory | |||
| if (!sd.chdir("LOGS/2011/JAN/")) { | |||
| sd.errorHalt("chdir failed. Did you run eventlog.pde?"); | |||
| } | |||
| // open file in current working directory | |||
| ifstream file("LOGFILE.TXT"); | |||
| if (!file.is_open()) sd.errorHalt("open failed"); | |||
| // copy the file to Serial | |||
| while ((c = file.get()) >= 0) cout << (char)c; | |||
| cout << "Done" << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 30
- 0
SdFat/examples/#attic/readme.txt
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ | |||
| Old and debug examples. | |||
| AnalogLogger - A simple data logger for one or more analog pins. | |||
| append - This sketch creates a large file by successive | |||
| open/write/close operations. | |||
| average - A demonstration of parsing floating point numbers. | |||
| benchSD - A read/write benchmark for the standard Arduino SD.h library. | |||
| bufstream - ibufsteam to parse a line and obufstream to format a line. | |||
| eventlog - Append a line to a file - demo of pathnames and streams. | |||
| fgetsRewrite - Demo of rewriting a line read by fgets. | |||
| HelloWorld - Create a serial output stream. | |||
| MiniSerial - SdFat minimal serial support for debug. | |||
| PrintBenchmarkSD - Bench mark SD.h print. | |||
| readlog - Read file. Demo of pathnames and current working directory. | |||
| SD_Size - Determine flash used by SD.h example. | |||
| SdFatSize - Determine flash used by SdFat. | |||
| TestMkdirRmdir - Test mkdir, rmdir, and directory management. | |||
+ 39
- 0
SdFat/examples/AnalogBinLogger/AnalogBinLogger.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,39 @@ | |||
| #ifndef AnalogBinLogger_h | |||
| #define AnalogBinLogger_h | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // First block of file. | |||
| struct metadata_t { | |||
| unsigned long adcFrequency; // ADC clock frequency | |||
| unsigned long cpuFrequency; // CPU clock frequency | |||
| unsigned long sampleInterval; // Sample interval in CPU cycles. | |||
| unsigned long recordEightBits; // Size of ADC values, nonzero for 8-bits. | |||
| unsigned long pinCount; // Number of analog pins in a sample. | |||
| unsigned long pinNumber[123]; // List of pin numbers in a sample. | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Data block for 8-bit ADC mode. | |||
| const size_t DATA_DIM8 = 508; | |||
| struct block8_t { | |||
| unsigned short count; // count of data bytes | |||
| unsigned short overrun; // count of overruns since last block | |||
| unsigned char data[DATA_DIM8]; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Data block for 10-bit ADC mode. | |||
| const size_t DATA_DIM16 = 254; | |||
| struct block16_t { | |||
| unsigned short count; // count of data bytes | |||
| unsigned short overrun; // count of overruns since last block | |||
| unsigned short data[DATA_DIM16]; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Data block for PC use | |||
| struct adcdata_t { | |||
| unsigned short count; // count of data bytes | |||
| unsigned short overrun; // count of overruns since last block | |||
| union { | |||
| unsigned char u8[DATA_DIM8]; | |||
| unsigned short u16[DATA_DIM16]; | |||
| } data; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // AnalogBinLogger_h | |||
+ 787
- 0
SdFat/examples/AnalogBinLogger/AnalogBinLogger.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,787 @@ | |||
| /** | |||
| * This program logs data from the Arduino ADC to a binary file. | |||
| * | |||
| * Samples are logged at regular intervals. Each Sample consists of the ADC | |||
| * values for the analog pins defined in the PIN_LIST array. The pins numbers | |||
| * may be in any order. | |||
| * | |||
| * Edit the configuration constants below to set the sample pins, sample rate, | |||
| * and other configuration values. | |||
| * | |||
| * If your SD card has a long write latency, it may be necessary to use | |||
| * slower sample rates. Using a Mega Arduino helps overcome latency | |||
| * problems since 13 512 byte buffers will be used. | |||
| * | |||
| * Each 512 byte data block in the file has a four byte header followed by up | |||
| * to 508 bytes of data. (508 values in 8-bit mode or 254 values in 10-bit mode) | |||
| * Each block contains an integral number of samples with unused space at the | |||
| * end of the block. | |||
| * | |||
| * Data is written to the file using a SD multiple block write command. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| #include <StdioStream.h> | |||
| #include "AnalogBinLogger.h" | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Analog pin number list for a sample. Pins may be in any order and pin | |||
| // numbers may be repeated. | |||
| const uint8_t PIN_LIST[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Sample rate in samples per second. | |||
| const float SAMPLE_RATE = 5000; // Must be 0.25 or greater. | |||
| // The interval between samples in seconds, SAMPLE_INTERVAL, may be set to a | |||
| // constant instead of being calculated from SAMPLE_RATE. SAMPLE_RATE is not | |||
| // used in the code below. For example, setting SAMPLE_INTERVAL = 2.0e-4 | |||
| // will result in a 200 microsecond sample interval. | |||
| const float SAMPLE_INTERVAL = 1.0/SAMPLE_RATE; | |||
| // Setting ROUND_SAMPLE_INTERVAL non-zero will cause the sample interval to | |||
| // be rounded to a a multiple of the ADC clock period and will reduce sample | |||
| // time jitter. | |||
| #define ROUND_SAMPLE_INTERVAL 1 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // ADC clock rate. | |||
| // The ADC clock rate is normally calculated from the pin count and sample | |||
| // interval. The calculation attempts to use the lowest possible ADC clock | |||
| // rate. | |||
| // | |||
| // You can select an ADC clock rate by defining the symbol ADC_PRESCALER to | |||
| // one of these values. You must choose an appropriate ADC clock rate for | |||
| // your sample interval. | |||
| // #define ADC_PRESCALER 7 // F_CPU/128 125 kHz on an Uno | |||
| // #define ADC_PRESCALER 6 // F_CPU/64 250 kHz on an Uno | |||
| // #define ADC_PRESCALER 5 // F_CPU/32 500 kHz on an Uno | |||
| // #define ADC_PRESCALER 4 // F_CPU/16 1000 kHz on an Uno | |||
| // #define ADC_PRESCALER 3 // F_CPU/8 2000 kHz on an Uno (8-bit mode only) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Reference voltage. See the processor data-sheet for reference details. | |||
| // uint8_t const ADC_REF = 0; // External Reference AREF pin. | |||
| uint8_t const ADC_REF = (1 << REFS0); // Vcc Reference. | |||
| // uint8_t const ADC_REF = (1 << REFS1); // Internal 1.1 (only 644 1284P Mega) | |||
| // uint8_t const ADC_REF = (1 << REFS1) | (1 << REFS0); // Internal 1.1 or 2.56 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // File definitions. | |||
| // | |||
| // Maximum file size in blocks. | |||
| // The program creates a contiguous file with FILE_BLOCK_COUNT 512 byte blocks. | |||
| // This file is flash erased using special SD commands. The file will be | |||
| // truncated if logging is stopped early. | |||
| const uint32_t FILE_BLOCK_COUNT = 256000; | |||
| // log file base name. Must be six characters or less. | |||
| #define FILE_BASE_NAME "ANALOG" | |||
| // Set RECORD_EIGHT_BITS non-zero to record only the high 8-bits of the ADC. | |||
| #define RECORD_EIGHT_BITS 0 | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Pin definitions. | |||
| // | |||
| // Digital pin to indicate an error, set to -1 if not used. | |||
| // The led blinks for fatal errors. The led goes on solid for SD write | |||
| // overrun errors and logging continues. | |||
| const int8_t ERROR_LED_PIN = 3; | |||
| // SD chip select pin. | |||
| const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = SS; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Buffer definitions. | |||
| // | |||
| // The logger will use SdFat's buffer plus BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT additional | |||
| // buffers. QUEUE_DIM must be a power of two larger than | |||
| //(BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT + 1). | |||
| // | |||
| #if RAMEND < 0X8FF | |||
| #error Too little SRAM | |||
| // | |||
| #elif RAMEND < 0X10FF | |||
| // Use total of two 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 1; | |||
| // Dimension for queues of 512 byte SD blocks. | |||
| const uint8_t QUEUE_DIM = 4; // Must be a power of two! | |||
| // | |||
| #elif RAMEND < 0X20FF | |||
| // Use total of five 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 4; | |||
| // Dimension for queues of 512 byte SD blocks. | |||
| const uint8_t QUEUE_DIM = 8; // Must be a power of two! | |||
| // | |||
| #elif RAMEND < 0X40FF | |||
| // Use total of 13 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 12; | |||
| // Dimension for queues of 512 byte SD blocks. | |||
| const uint8_t QUEUE_DIM = 16; // Must be a power of two! | |||
| // | |||
| #else // RAMEND | |||
| // Use total of 29 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 28; | |||
| // Dimension for queues of 512 byte SD blocks. | |||
| const uint8_t QUEUE_DIM = 32; // Must be a power of two! | |||
| #endif // RAMEND | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // End of configuration constants. | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Temporary log file. Will be deleted if a reset or power failure occurs. | |||
| #define TMP_FILE_NAME "TMP_LOG.BIN" | |||
| // Size of file base name. Must not be larger than six. | |||
| const uint8_t BASE_NAME_SIZE = sizeof(FILE_BASE_NAME) - 1; | |||
| // Number of analog pins to log. | |||
| const uint8_t PIN_COUNT = sizeof(PIN_LIST)/sizeof(PIN_LIST[0]); | |||
| // Minimum ADC clock cycles per sample interval | |||
| const uint16_t MIN_ADC_CYCLES = 15; | |||
| // Extra cpu cycles to setup ADC with more than one pin per sample. | |||
| const uint16_t ISR_SETUP_ADC = 100; | |||
| // Maximum cycles for timer0 system interrupt, millis, micros. | |||
| const uint16_t ISR_TIMER0 = 160; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdBaseFile binFile; | |||
| char binName[13] = FILE_BASE_NAME "00.BIN"; | |||
| #if RECORD_EIGHT_BITS | |||
| const size_t SAMPLES_PER_BLOCK = DATA_DIM8/PIN_COUNT; | |||
| typedef block8_t block_t; | |||
| #else // RECORD_EIGHT_BITS | |||
| const size_t SAMPLES_PER_BLOCK = DATA_DIM16/PIN_COUNT; | |||
| typedef block16_t block_t; | |||
| #endif // RECORD_EIGHT_BITS | |||
| block_t* emptyQueue[QUEUE_DIM]; | |||
| uint8_t emptyHead; | |||
| uint8_t emptyTail; | |||
| block_t* fullQueue[QUEUE_DIM]; | |||
| volatile uint8_t fullHead; // volatile insures non-interrupt code sees changes. | |||
| uint8_t fullTail; | |||
| // queueNext assumes QUEUE_DIM is a power of two | |||
| inline uint8_t queueNext(uint8_t ht) {return (ht + 1) & (QUEUE_DIM -1);} | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Interrupt Service Routines | |||
| // Pointer to current buffer. | |||
| block_t* isrBuf; | |||
| // Need new buffer if true. | |||
| bool isrBufNeeded = true; | |||
| // overrun count | |||
| uint16_t isrOver = 0; | |||
| // ADC configuration for each pin. | |||
| uint8_t adcmux[PIN_COUNT]; | |||
| uint8_t adcsra[PIN_COUNT]; | |||
| uint8_t adcsrb[PIN_COUNT]; | |||
| uint8_t adcindex = 1; | |||
| // Insure no timer events are missed. | |||
| volatile bool timerError = false; | |||
| volatile bool timerFlag = false; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // ADC done interrupt. | |||
| ISR(ADC_vect) { | |||
| // Read ADC data. | |||
| #if RECORD_EIGHT_BITS | |||
| uint8_t d = ADCH; | |||
| #else // RECORD_EIGHT_BITS | |||
| // This will access ADCL first. | |||
| uint16_t d = ADC; | |||
| #endif // RECORD_EIGHT_BITS | |||
| if (isrBufNeeded && emptyHead == emptyTail) { | |||
| // no buffers - count overrun | |||
| if (isrOver < 0XFFFF) isrOver++; | |||
| // Avoid missed timer error. | |||
| timerFlag = false; | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| // Start ADC | |||
| if (PIN_COUNT > 1) { | |||
| ADMUX = adcmux[adcindex]; | |||
| ADCSRB = adcsrb[adcindex]; | |||
| ADCSRA = adcsra[adcindex]; | |||
| if (adcindex == 0) timerFlag = false; | |||
| adcindex = adcindex < (PIN_COUNT - 1) ? adcindex + 1 : 0; | |||
| } else { | |||
| timerFlag = false; | |||
| } | |||
| // Check for buffer needed. | |||
| if (isrBufNeeded) { | |||
| // Remove buffer from empty queue. | |||
| isrBuf = emptyQueue[emptyTail]; | |||
| emptyTail = queueNext(emptyTail); | |||
| isrBuf->count = 0; | |||
| isrBuf->overrun = isrOver; | |||
| isrBufNeeded = false; | |||
| } | |||
| // Store ADC data. | |||
| isrBuf->data[isrBuf->count++] = d; | |||
| // Check for buffer full. | |||
| if (isrBuf->count >= PIN_COUNT*SAMPLES_PER_BLOCK) { | |||
| // Put buffer isrIn full queue. | |||
| uint8_t tmp = fullHead; // Avoid extra fetch of volatile fullHead. | |||
| fullQueue[tmp] = (block_t*)isrBuf; | |||
| fullHead = queueNext(tmp); | |||
| // Set buffer needed and clear overruns. | |||
| isrBufNeeded = true; | |||
| isrOver = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // timer1 interrupt to clear OCF1B | |||
| ISR(TIMER1_COMPB_vect) { | |||
| // Make sure ADC ISR responded to timer event. | |||
| if (timerFlag) timerError = true; | |||
| timerFlag = true; | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Error messages stored in flash. | |||
| #define error(msg) error_P(PSTR(msg)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void error_P(const char* msg) { | |||
| sd.errorPrint_P(msg); | |||
| fatalBlink(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // | |||
| void fatalBlink() { | |||
| while (true) { | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, HIGH); | |||
| delay(200); | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, LOW); | |||
| delay(200); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| #if ADPS0 != 0 || ADPS1 != 1 || ADPS2 != 2 | |||
| #error unexpected ADC prescaler bits | |||
| #endif | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // initialize ADC and timer1 | |||
| void adcInit(metadata_t* meta) { | |||
| uint8_t adps; // prescaler bits for ADCSRA | |||
| uint32_t ticks = F_CPU*SAMPLE_INTERVAL + 0.5; // Sample interval cpu cycles. | |||
| if (ADC_REF & ~((1 << REFS0) | (1 << REFS1))) { | |||
| error("Invalid ADC reference"); | |||
| } | |||
| #ifdef ADC_PRESCALER | |||
| if (ADC_PRESCALER > 7 || ADC_PRESCALER < 2) { | |||
| error("Invalid ADC prescaler"); | |||
| } | |||
| adps = ADC_PRESCALER; | |||
| #else // ADC_PRESCALER | |||
| // Allow extra cpu cycles to change ADC settings if more than one pin. | |||
| int32_t adcCycles = (ticks - ISR_TIMER0)/PIN_COUNT; | |||
| - (PIN_COUNT > 1 ? ISR_SETUP_ADC : 0); | |||
| for (adps = 7; adps > 0; adps--) { | |||
| if (adcCycles >= (MIN_ADC_CYCLES << adps)) break; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // ADC_PRESCALER | |||
| meta->adcFrequency = F_CPU >> adps; | |||
| if (meta->adcFrequency > (RECORD_EIGHT_BITS ? 2000000 : 1000000)) { | |||
| error("Sample Rate Too High"); | |||
| } | |||
| #if ROUND_SAMPLE_INTERVAL | |||
| // Round so interval is multiple of ADC clock. | |||
| ticks += 1 << (adps - 1); | |||
| ticks >>= adps; | |||
| ticks <<= adps; | |||
| #endif // ROUND_SAMPLE_INTERVAL | |||
| if (PIN_COUNT > sizeof(meta->pinNumber)/sizeof(meta->pinNumber[0])) { | |||
| error("Too many pins"); | |||
| } | |||
| meta->pinCount = PIN_COUNT; | |||
| meta->recordEightBits = RECORD_EIGHT_BITS; | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < PIN_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| uint8_t pin = PIN_LIST[i]; | |||
| if (pin >= NUM_ANALOG_INPUTS) error("Invalid Analog pin number"); | |||
| meta->pinNumber[i] = pin; | |||
| // Set ADC reference and low three bits of analog pin number. | |||
| adcmux[i] = (pin & 7) | ADC_REF; | |||
| if (RECORD_EIGHT_BITS) adcmux[i] |= 1 << ADLAR; | |||
| // If this is the first pin, trigger on timer/counter 1 compare match B. | |||
| adcsrb[i] = i == 0 ? (1 << ADTS2) | (1 << ADTS0) : 0; | |||
| #ifdef MUX5 | |||
| if (pin > 7) adcsrb[i] |= (1 << MUX5); | |||
| #endif // MUX5 | |||
| adcsra[i] = (1 << ADEN) | (1 << ADIE) | adps; | |||
| adcsra[i] |= i == 0 ? 1 << ADATE : 1 << ADSC; | |||
| } | |||
| // Setup timer1 | |||
| TCCR1A = 0; | |||
| uint8_t tshift; | |||
| if (ticks < 0X10000) { | |||
| // no prescale, CTC mode | |||
| TCCR1B = (1 << WGM13) | (1 << WGM12) | (1 << CS10); | |||
| tshift = 0; | |||
| } else if (ticks < 0X10000*8) { | |||
| // prescale 8, CTC mode | |||
| TCCR1B = (1 << WGM13) | (1 << WGM12) | (1 << CS11); | |||
| tshift = 3; | |||
| } else if (ticks < 0X10000*64) { | |||
| // prescale 64, CTC mode | |||
| TCCR1B = (1 << WGM13) | (1 << WGM12) | (1 << CS11) | (1 << CS10); | |||
| tshift = 6; | |||
| } else if (ticks < 0X10000*256) { | |||
| // prescale 256, CTC mode | |||
| TCCR1B = (1 << WGM13) | (1 << WGM12) | (1 << CS12); | |||
| tshift = 8; | |||
| } else if (ticks < 0X10000*1024) { | |||
| // prescale 1024, CTC mode | |||
| TCCR1B = (1 << WGM13) | (1 << WGM12) | (1 << CS12) | (1 << CS10); | |||
| tshift = 10; | |||
| } else { | |||
| error("Sample Rate Too Slow"); | |||
| } | |||
| // divide by prescaler | |||
| ticks >>= tshift; | |||
| // set TOP for timer reset | |||
| ICR1 = ticks - 1; | |||
| // compare for ADC start | |||
| OCR1B = 0; | |||
| // multiply by prescaler | |||
| ticks <<= tshift; | |||
| // Sample interval in CPU clock ticks. | |||
| meta->sampleInterval = ticks; | |||
| meta->cpuFrequency = F_CPU; | |||
| float sampleRate = (float)meta->cpuFrequency/meta->sampleInterval; | |||
| Serial.print(F("Sample pins:")); | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < meta->pinCount; i++) { | |||
| Serial.print(' '); | |||
| Serial.print(meta->pinNumber[i], DEC); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.print(F("ADC bits: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(meta->recordEightBits ? 8 : 10); | |||
| Serial.print(F("ADC clock kHz: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(meta->adcFrequency/1000); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Sample Rate: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(sampleRate); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Sample interval usec: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(1000000.0/sampleRate, 4); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // enable ADC and timer1 interrupts | |||
| void adcStart() { | |||
| // initialize ISR | |||
| isrBufNeeded = true; | |||
| isrOver = 0; | |||
| adcindex = 1; | |||
| // Clear any pending interrupt. | |||
| ADCSRA |= 1 << ADIF; | |||
| // Setup for first pin. | |||
| ADMUX = adcmux[0]; | |||
| ADCSRB = adcsrb[0]; | |||
| ADCSRA = adcsra[0]; | |||
| // Enable timer1 interrupts. | |||
| timerError = false; | |||
| timerFlag = false; | |||
| TCNT1 = 0; | |||
| TIFR1 = 1 << OCF1B; | |||
| TIMSK1 = 1 << OCIE1B; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void adcStop() { | |||
| TIMSK1 = 0; | |||
| ADCSRA = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Convert binary file to CSV file. | |||
| void binaryToCsv() { | |||
| uint8_t lastPct = 0; | |||
| block_t buf; | |||
| metadata_t* pm; | |||
| uint32_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| char csvName[13]; | |||
| StdioStream csvStream; | |||
| if (!binFile.isOpen()) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("No current binary file")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| binFile.rewind(); | |||
| if (!binFile.read(&buf , 512) == 512) error("Read metadata failed"); | |||
| // Create a new CSV file. | |||
| strcpy(csvName, binName); | |||
| strcpy_P(&csvName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 3], PSTR("CSV")); | |||
| if (!csvStream.fopen(csvName, "w")) { | |||
| error("open csvStream failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Writing: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(csvName); | |||
| Serial.println(F(" - type any character to stop")); | |||
| pm = (metadata_t*)&buf; | |||
| csvStream.print(F("Interval,")); | |||
| float intervalMicros = 1.0e6*pm->sampleInterval/(float)pm->cpuFrequency; | |||
| csvStream.print(intervalMicros, 4); | |||
| csvStream.println(F(",usec")); | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < pm->pinCount; i++) { | |||
| if (i) csvStream.putc(','); | |||
| csvStream.print(F("pin")); | |||
| csvStream.print(pm->pinNumber[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| csvStream.println(); | |||
| uint32_t tPct = millis(); | |||
| while (!Serial.available() && binFile.read(&buf, 512) == 512) { | |||
| uint16_t i; | |||
| if (buf.count == 0) break; | |||
| if (buf.overrun) { | |||
| csvStream.print(F("OVERRUN,")); | |||
| csvStream.println(buf.overrun); | |||
| } | |||
| for (uint16_t j = 0; j < buf.count; j += PIN_COUNT) { | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < PIN_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| if (i) csvStream.putc(','); | |||
| csvStream.print(buf.data[i + j]); | |||
| } | |||
| csvStream.println(); | |||
| } | |||
| if ((millis() - tPct) > 1000) { | |||
| uint8_t pct = binFile.curPosition()/(binFile.fileSize()/100); | |||
| if (pct != lastPct) { | |||
| tPct = millis(); | |||
| lastPct = pct; | |||
| Serial.print(pct, DEC); | |||
| Serial.println('%'); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (Serial.available()) break; | |||
| } | |||
| csvStream.fclose(); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Done: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(0.001*(millis() - t0)); | |||
| Serial.println(F(" Seconds")); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // read data file and check for overruns | |||
| void checkOverrun() { | |||
| bool headerPrinted = false; | |||
| block_t buf; | |||
| uint32_t bgnBlock, endBlock; | |||
| uint32_t bn = 0; | |||
| if (!binFile.isOpen()) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("No current binary file")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!binFile.contiguousRange(&bgnBlock, &endBlock)) { | |||
| error("contiguousRange failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| binFile.rewind(); | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Checking overrun errors - type any character to stop")); | |||
| if (!binFile.read(&buf , 512) == 512) { | |||
| error("Read metadata failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| bn++; | |||
| while (binFile.read(&buf, 512) == 512) { | |||
| if (buf.count == 0) break; | |||
| if (buf.overrun) { | |||
| if (!headerPrinted) { | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Overruns:")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("fileBlockNumber,sdBlockNumber,overrunCount")); | |||
| headerPrinted = true; | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.print(bn); | |||
| Serial.print(','); | |||
| Serial.print(bgnBlock + bn); | |||
| Serial.print(','); | |||
| Serial.println(buf.overrun); | |||
| } | |||
| bn++; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!headerPrinted) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("No errors found")); | |||
| } else { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // dump data file to Serial | |||
| void dumpData() { | |||
| block_t buf; | |||
| if (!binFile.isOpen()) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("No current binary file")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| binFile.rewind(); | |||
| if (binFile.read(&buf , 512) != 512) { | |||
| error("Read metadata failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Type any character to stop")); | |||
| delay(1000); | |||
| while (!Serial.available() && binFile.read(&buf , 512) == 512) { | |||
| if (buf.count == 0) break; | |||
| if (buf.overrun) { | |||
| Serial.print(F("OVERRUN,")); | |||
| Serial.println(buf.overrun); | |||
| } | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < buf.count; i++) { | |||
| Serial.print(buf.data[i], DEC); | |||
| if ((i+1)%PIN_COUNT) { | |||
| Serial.print(','); | |||
| } else { | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // log data | |||
| // max number of blocks to erase per erase call | |||
| uint32_t const ERASE_SIZE = 262144L; | |||
| void logData() { | |||
| uint32_t bgnBlock, endBlock; | |||
| // Allocate extra buffer space. | |||
| block_t block[BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT]; | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| // Initialize ADC and timer1. | |||
| adcInit((metadata_t*) &block[0]); | |||
| // Find unused file name. | |||
| if (BASE_NAME_SIZE > 6) { | |||
| error("FILE_BASE_NAME too long"); | |||
| } | |||
| while (sd.exists(binName)) { | |||
| if (binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1] != '9') { | |||
| binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1]++; | |||
| } else { | |||
| binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1] = '0'; | |||
| if (binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE] == '9') { | |||
| error("Can't create file name"); | |||
| } | |||
| binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE]++; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Delete old tmp file. | |||
| if (sd.exists(TMP_FILE_NAME)) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Deleting tmp file")); | |||
| if (!sd.remove(TMP_FILE_NAME)) { | |||
| error("Can't remove tmp file"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Create new file. | |||
| Serial.println(F("Creating new file")); | |||
| binFile.close(); | |||
| if (!binFile.createContiguous(sd.vwd(), | |||
| TMP_FILE_NAME, 512 * FILE_BLOCK_COUNT)) { | |||
| error("createContiguous failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Get the address of the file on the SD. | |||
| if (!binFile.contiguousRange(&bgnBlock, &endBlock)) { | |||
| error("contiguousRange failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Use SdFat's internal buffer. | |||
| uint8_t* cache = (uint8_t*)sd.vol()->cacheClear(); | |||
| if (cache == 0) error("cacheClear failed"); | |||
| // Flash erase all data in the file. | |||
| Serial.println(F("Erasing all data")); | |||
| uint32_t bgnErase = bgnBlock; | |||
| uint32_t endErase; | |||
| while (bgnErase < endBlock) { | |||
| endErase = bgnErase + ERASE_SIZE; | |||
| if (endErase > endBlock) endErase = endBlock; | |||
| if (!sd.card()->erase(bgnErase, endErase)) { | |||
| error("erase failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| bgnErase = endErase + 1; | |||
| } | |||
| // Start a multiple block write. | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeStart(bgnBlock, FILE_BLOCK_COUNT)) { | |||
| error("writeBegin failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Write metadata. | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeData((uint8_t*)&block[0])) { | |||
| error("Write metadata failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Initialize queues. | |||
| emptyHead = emptyTail = 0; | |||
| fullHead = fullTail = 0; | |||
| // Use SdFat buffer for one block. | |||
| emptyQueue[emptyHead] = (block_t*)cache; | |||
| emptyHead = queueNext(emptyHead); | |||
| // Put rest of buffers in the empty queue. | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| emptyQueue[emptyHead] = &block[i]; | |||
| emptyHead = queueNext(emptyHead); | |||
| } | |||
| // Give SD time to prepare for big write. | |||
| delay(1000); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Logging - type any character to stop")); | |||
| // Wait for Serial Idle. | |||
| Serial.flush(); | |||
| delay(10); | |||
| uint32_t bn = 1; | |||
| uint32_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| uint32_t t1 = t0; | |||
| uint32_t overruns = 0; | |||
| uint32_t count = 0; | |||
| uint32_t maxLatency = 0; | |||
| // Start logging interrupts. | |||
| adcStart(); | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| if (fullHead != fullTail) { | |||
| // Get address of block to write. | |||
| block_t* pBlock = fullQueue[fullTail]; | |||
| // Write block to SD. | |||
| uint32_t usec = micros(); | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeData((uint8_t*)pBlock)) { | |||
| error("write data failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| usec = micros() - usec; | |||
| t1 = millis(); | |||
| if (usec > maxLatency) maxLatency = usec; | |||
| count += pBlock->count; | |||
| // Add overruns and possibly light LED. | |||
| if (pBlock->overrun) { | |||
| overruns += pBlock->overrun; | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, HIGH); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Move block to empty queue. | |||
| emptyQueue[emptyHead] = pBlock; | |||
| emptyHead = queueNext(emptyHead); | |||
| fullTail = queueNext(fullTail); | |||
| bn++; | |||
| if (bn == FILE_BLOCK_COUNT) { | |||
| // File full so stop ISR calls. | |||
| adcStop(); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (timerError) { | |||
| error("Missed timer event - rate too high"); | |||
| } | |||
| if (Serial.available()) { | |||
| // Stop ISR calls. | |||
| adcStop(); | |||
| if (isrBuf != 0 && isrBuf->count >= PIN_COUNT) { | |||
| // Truncate to last complete sample. | |||
| isrBuf->count = PIN_COUNT*(isrBuf->count/PIN_COUNT); | |||
| // Put buffer in full queue. | |||
| fullQueue[fullHead] = isrBuf; | |||
| fullHead = queueNext(fullHead); | |||
| isrBuf = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| if (fullHead == fullTail) break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeStop()) { | |||
| error("writeStop failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Truncate file if recording stopped early. | |||
| if (bn != FILE_BLOCK_COUNT) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Truncating file")); | |||
| if (!binFile.truncate(512L * bn)) { | |||
| error("Can't truncate file"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (!binFile.rename(sd.vwd(), binName)) { | |||
| error("Can't rename file"); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.print(F("File renamed: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(binName); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Max block write usec: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(maxLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Record time sec: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(0.001*(t1 - t0), 3); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Sample count: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(count/PIN_COUNT); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Samples/sec: ")); | |||
| Serial.println((1000.0/PIN_COUNT)*count/(t1-t0)); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Overruns: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(overruns); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| pinMode(ERROR_LED_PIN, OUTPUT); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| // Read the first sample pin to init the ADC. | |||
| analogRead(PIN_LIST[0]); | |||
| Serial.print(F("FreeRam: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(FreeRam()); | |||
| // initialize file system. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CS_PIN, SPI_FULL_SPEED)) { | |||
| sd.initErrorPrint(); | |||
| fatalBlink(); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop(void) { | |||
| // discard any input | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("type:")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("c - convert file to CSV")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("d - dump data to Serial")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("e - overrun error details")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("r - record ADC data")); | |||
| while(!Serial.available()) {} | |||
| char c = tolower(Serial.read()); | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, LOW); | |||
| } | |||
| // Read any extra Serial data. | |||
| do { | |||
| delay(10); | |||
| } while (Serial.read() >= 0); | |||
| if (c == 'c') { | |||
| binaryToCsv(); | |||
| } else if (c == 'd') { | |||
| dumpData(); | |||
| } else if (c == 'e') { | |||
| checkOverrun(); | |||
| } else if (c == 'r') { | |||
| logData(); | |||
| } else { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Invalid entry")); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 529
- 0
SdFat/examples/LowLatencyLogger/LowLatencyLogger.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,529 @@ | |||
| /** | |||
| * This program logs data to a binary file. Functions are included | |||
| * to convert the binary file to a CSV text file. | |||
| * | |||
| * Samples are logged at regular intervals. The maximum logging rate | |||
| * depends on the quality of your SD card and the time required to | |||
| * read sensor data. This example has been tested at 500 Hz with | |||
| * good SD card on an Uno. 4000 HZ is possible on a Due. | |||
| * | |||
| * If your SD card has a long write latency, it may be necessary to use | |||
| * slower sample rates. Using a Mega Arduino helps overcome latency | |||
| * problems since 13 512 byte buffers will be used. | |||
| * | |||
| * Data is written to the file using a SD multiple block write command. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // User data functions. Modify these functions for your data items. | |||
| #include "UserDataType.h" // Edit this include file to change data_t. | |||
| // Acquire a data record. | |||
| void acquireData(data_t* data) { | |||
| data->time = micros(); | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < ADC_DIM; i++) { | |||
| data->adc[i] = analogRead(i); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Print a data record. | |||
| void printData(Print* pr, data_t* data) { | |||
| pr->print(data->time); | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < ADC_DIM; i++) { | |||
| pr->write(','); | |||
| pr->print(data->adc[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| pr->println(); | |||
| } | |||
| // Print data header. | |||
| void printHeader(Print* pr) { | |||
| pr->print(F("time")); | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < ADC_DIM; i++) { | |||
| pr->print(F(",adc")); | |||
| pr->print(i); | |||
| } | |||
| pr->println(); | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Start of configuration constants. | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| //Interval between data records in microseconds. | |||
| const uint32_t LOG_INTERVAL_USEC = 2000; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Pin definitions. | |||
| // | |||
| // SD chip select pin. | |||
| const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = SS; | |||
| // | |||
| // Digital pin to indicate an error, set to -1 if not used. | |||
| // The led blinks for fatal errors. The led goes on solid for SD write | |||
| // overrun errors and logging continues. | |||
| const int8_t ERROR_LED_PIN = 3; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // File definitions. | |||
| // | |||
| // Maximum file size in blocks. | |||
| // The program creates a contiguous file with FILE_BLOCK_COUNT 512 byte blocks. | |||
| // This file is flash erased using special SD commands. The file will be | |||
| // truncated if logging is stopped early. | |||
| const uint32_t FILE_BLOCK_COUNT = 256000; | |||
| // log file base name. Must be six characters or less. | |||
| #define FILE_BASE_NAME "DATA" | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Buffer definitions. | |||
| // | |||
| // The logger will use SdFat's buffer plus BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT additional | |||
| // buffers. | |||
| // | |||
| #ifndef RAMEND | |||
| // Assume ARM. Use total of nine 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 8; | |||
| // | |||
| #elif RAMEND < 0X8FF | |||
| #error Too little SRAM | |||
| // | |||
| #elif RAMEND < 0X10FF | |||
| // Use total of two 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 1; | |||
| // | |||
| #elif RAMEND < 0X20FF | |||
| // Use total of five 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 4; | |||
| // | |||
| #else // RAMEND | |||
| // Use total of 13 512 byte buffers. | |||
| const uint8_t BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT = 12; | |||
| #endif // RAMEND | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // End of configuration constants. | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Temporary log file. Will be deleted if a reset or power failure occurs. | |||
| #define TMP_FILE_NAME "TMP_LOG.BIN" | |||
| // Size of file base name. Must not be larger than six. | |||
| const uint8_t BASE_NAME_SIZE = sizeof(FILE_BASE_NAME) - 1; | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdBaseFile binFile; | |||
| char binName[13] = FILE_BASE_NAME "00.BIN"; | |||
| // Number of data records in a block. | |||
| const uint16_t DATA_DIM = (512 - 4)/sizeof(data_t); | |||
| //Compute fill so block size is 512 bytes. FILL_DIM may be zero. | |||
| const uint16_t FILL_DIM = 512 - 4 - DATA_DIM*sizeof(data_t); | |||
| struct block_t { | |||
| uint16_t count; | |||
| uint16_t overrun; | |||
| data_t data[DATA_DIM]; | |||
| uint8_t fill[FILL_DIM]; | |||
| }; | |||
| const uint8_t QUEUE_DIM = BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT + 2; | |||
| block_t* emptyQueue[QUEUE_DIM]; | |||
| uint8_t emptyHead; | |||
| uint8_t emptyTail; | |||
| block_t* fullQueue[QUEUE_DIM]; | |||
| uint8_t fullHead; | |||
| uint8_t fullTail; | |||
| // Advance queue index. | |||
| inline uint8_t queueNext(uint8_t ht) {return ht < (QUEUE_DIM - 1) ? ht + 1 : 0;} | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Error messages stored in flash. | |||
| #define error(msg) error_P(PSTR(msg)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void error_P(const char* msg) { | |||
| sd.errorPrint_P(msg); | |||
| fatalBlink(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // | |||
| void fatalBlink() { | |||
| while (true) { | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, HIGH); | |||
| delay(200); | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, LOW); | |||
| delay(200); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Convert binary file to CSV file. | |||
| void binaryToCsv() { | |||
| uint8_t lastPct = 0; | |||
| block_t block; | |||
| uint32_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| uint32_t syncCluster = 0; | |||
| SdFile csvFile; | |||
| char csvName[13]; | |||
| if (!binFile.isOpen()) { | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("No current binary file")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| binFile.rewind(); | |||
| // Create a new csvFile. | |||
| strcpy(csvName, binName); | |||
| strcpy_P(&csvName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 3], PSTR("CSV")); | |||
| if (!csvFile.open(csvName, O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC)) { | |||
| error("open csvFile failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Writing: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(csvName); | |||
| Serial.println(F(" - type any character to stop")); | |||
| printHeader(&csvFile); | |||
| uint32_t tPct = millis(); | |||
| while (!Serial.available() && binFile.read(&block, 512) == 512) { | |||
| uint16_t i; | |||
| if (block.count == 0) break; | |||
| if (block.overrun) { | |||
| csvFile.print(F("OVERRUN,")); | |||
| csvFile.println(block.overrun); | |||
| } | |||
| for (i = 0; i < block.count; i++) { | |||
| printData(&csvFile, &block.data[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| if (csvFile.curCluster() != syncCluster) { | |||
| csvFile.sync(); | |||
| syncCluster = csvFile.curCluster(); | |||
| } | |||
| if ((millis() - tPct) > 1000) { | |||
| uint8_t pct = binFile.curPosition()/(binFile.fileSize()/100); | |||
| if (pct != lastPct) { | |||
| tPct = millis(); | |||
| lastPct = pct; | |||
| Serial.print(pct, DEC); | |||
| Serial.println('%'); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (Serial.available()) break; | |||
| } | |||
| csvFile.close(); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Done: ")); | |||
| Serial.print(0.001*(millis() - t0)); | |||
| Serial.println(F(" Seconds")); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // read data file and check for overruns | |||
| void checkOverrun() { | |||
| bool headerPrinted = false; | |||
| block_t block; | |||
| uint32_t bgnBlock, endBlock; | |||
| uint32_t bn = 0; | |||
| if (!binFile.isOpen()) { | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("No current binary file")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!binFile.contiguousRange(&bgnBlock, &endBlock)) { | |||
| error("contiguousRange failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| binFile.rewind(); | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Checking overrun errors - type any character to stop")); | |||
| while (binFile.read(&block, 512) == 512) { | |||
| if (block.count == 0) break; | |||
| if (block.overrun) { | |||
| if (!headerPrinted) { | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Overruns:")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("fileBlockNumber,sdBlockNumber,overrunCount")); | |||
| headerPrinted = true; | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.print(bn); | |||
| Serial.print(','); | |||
| Serial.print(bgnBlock + bn); | |||
| Serial.print(','); | |||
| Serial.println(block.overrun); | |||
| } | |||
| bn++; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!headerPrinted) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("No errors found")); | |||
| } else { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // dump data file to Serial | |||
| void dumpData() { | |||
| block_t block; | |||
| if (!binFile.isOpen()) { | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("No current binary file")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| binFile.rewind(); | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Type any character to stop")); | |||
| delay(1000); | |||
| printHeader(&Serial); | |||
| while (!Serial.available() && binFile.read(&block , 512) == 512) { | |||
| if (block.count == 0) break; | |||
| if (block.overrun) { | |||
| Serial.print(F("OVERRUN,")); | |||
| Serial.println(block.overrun); | |||
| } | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < block.count; i++) { | |||
| printData(&Serial, &block.data[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // log data | |||
| // max number of blocks to erase per erase call | |||
| uint32_t const ERASE_SIZE = 262144L; | |||
| void logData() { | |||
| uint32_t bgnBlock, endBlock; | |||
| // Allocate extra buffer space. | |||
| block_t block[BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT]; | |||
| block_t* curBlock = 0; | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| // Find unused file name. | |||
| if (BASE_NAME_SIZE > 6) { | |||
| error("FILE_BASE_NAME too long"); | |||
| } | |||
| while (sd.exists(binName)) { | |||
| if (binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1] != '9') { | |||
| binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1]++; | |||
| } else { | |||
| binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1] = '0'; | |||
| if (binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE] == '9') { | |||
| error("Can't create file name"); | |||
| } | |||
| binName[BASE_NAME_SIZE]++; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Delete old tmp file. | |||
| if (sd.exists(TMP_FILE_NAME)) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Deleting tmp file")); | |||
| if (!sd.remove(TMP_FILE_NAME)) { | |||
| error("Can't remove tmp file"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Create new file. | |||
| Serial.println(F("Creating new file")); | |||
| binFile.close(); | |||
| if (!binFile.createContiguous(sd.vwd(), | |||
| TMP_FILE_NAME, 512 * FILE_BLOCK_COUNT)) { | |||
| error("createContiguous failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Get the address of the file on the SD. | |||
| if (!binFile.contiguousRange(&bgnBlock, &endBlock)) { | |||
| error("contiguousRange failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Use SdFat's internal buffer. | |||
| uint8_t* cache = (uint8_t*)sd.vol()->cacheClear(); | |||
| if (cache == 0) error("cacheClear failed"); | |||
| // Flash erase all data in the file. | |||
| Serial.println(F("Erasing all data")); | |||
| uint32_t bgnErase = bgnBlock; | |||
| uint32_t endErase; | |||
| while (bgnErase < endBlock) { | |||
| endErase = bgnErase + ERASE_SIZE; | |||
| if (endErase > endBlock) endErase = endBlock; | |||
| if (!sd.card()->erase(bgnErase, endErase)) { | |||
| error("erase failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| bgnErase = endErase + 1; | |||
| } | |||
| // Start a multiple block write. | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeStart(bgnBlock, FILE_BLOCK_COUNT)) { | |||
| error("writeBegin failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Initialize queues. | |||
| emptyHead = emptyTail = 0; | |||
| fullHead = fullTail = 0; | |||
| // Use SdFat buffer for one block. | |||
| emptyQueue[emptyHead] = (block_t*)cache; | |||
| emptyHead = queueNext(emptyHead); | |||
| // Put rest of buffers in the empty queue. | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < BUFFER_BLOCK_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| emptyQueue[emptyHead] = &block[i]; | |||
| emptyHead = queueNext(emptyHead); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(F("Logging - type any character to stop")); | |||
| // Wait for Serial Idle. | |||
| Serial.flush(); | |||
| delay(10); | |||
| uint32_t bn = 0; | |||
| uint32_t t0 = millis(); | |||
| uint32_t t1 = t0; | |||
| uint32_t overrun = 0; | |||
| uint32_t overrunTotal = 0; | |||
| uint32_t count = 0; | |||
| uint32_t maxLatency = 0; | |||
| int32_t diff; | |||
| // Start at a multiple of interval. | |||
| uint32_t logTime = micros()/LOG_INTERVAL_USEC + 1; | |||
| logTime *= LOG_INTERVAL_USEC; | |||
| bool closeFile = false; | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| // Time for next data record. | |||
| logTime += LOG_INTERVAL_USEC; | |||
| if (Serial.available()) closeFile = true; | |||
| if (closeFile) { | |||
| if (curBlock != 0 && curBlock->count >= 0) { | |||
| // Put buffer in full queue. | |||
| fullQueue[fullHead] = curBlock; | |||
| fullHead = queueNext(fullHead); | |||
| curBlock = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } else { | |||
| if (curBlock == 0 && emptyTail != emptyHead) { | |||
| curBlock = emptyQueue[emptyTail]; | |||
| emptyTail = queueNext(emptyTail); | |||
| curBlock->count = 0; | |||
| curBlock->overrun = overrun; | |||
| overrun = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| do { | |||
| diff = logTime - micros(); | |||
| } while(diff > 0); | |||
| if (diff < -10) error("LOG_INTERVAL_USEC too small"); | |||
| if (curBlock == 0) { | |||
| overrun++; | |||
| } else { | |||
| acquireData(&curBlock->data[curBlock->count++]); | |||
| if (curBlock->count == DATA_DIM) { | |||
| fullQueue[fullHead] = curBlock; | |||
| fullHead = queueNext(fullHead); | |||
| curBlock = 0; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (fullHead == fullTail) { | |||
| // Exit loop if done. | |||
| if (closeFile) break; | |||
| } else if (!sd.card()->isBusy()) { | |||
| // Get address of block to write. | |||
| block_t* pBlock = fullQueue[fullTail]; | |||
| fullTail = queueNext(fullTail); | |||
| // Write block to SD. | |||
| uint32_t usec = micros(); | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeData((uint8_t*)pBlock)) { | |||
| error("write data failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| usec = micros() - usec; | |||
| t1 = millis(); | |||
| if (usec > maxLatency) maxLatency = usec; | |||
| count += pBlock->count; | |||
| // Add overruns and possibly light LED. | |||
| if (pBlock->overrun) { | |||
| overrunTotal += pBlock->overrun; | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, HIGH); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Move block to empty queue. | |||
| emptyQueue[emptyHead] = pBlock; | |||
| emptyHead = queueNext(emptyHead); | |||
| bn++; | |||
| if (bn == FILE_BLOCK_COUNT) { | |||
| // File full so stop | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeStop()) { | |||
| error("writeStop failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // Truncate file if recording stopped early. | |||
| if (bn != FILE_BLOCK_COUNT) { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Truncating file")); | |||
| if (!binFile.truncate(512L * bn)) { | |||
| error("Can't truncate file"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (!binFile.rename(sd.vwd(), binName)) { | |||
| error("Can't rename file"); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.print(F("File renamed: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(binName); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Max block write usec: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(maxLatency); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Record time sec: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(0.001*(t1 - t0), 3); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Sample count: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(count); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Samples/sec: ")); | |||
| Serial.println((1000.0)*count/(t1-t0)); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Overruns: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(overrunTotal); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| pinMode(ERROR_LED_PIN, OUTPUT); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| Serial.print(F("FreeRam: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(FreeRam()); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Records/block: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(DATA_DIM); | |||
| if (sizeof(block_t) != 512) error("Invalid block size"); | |||
| // initialize file system. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CS_PIN, SPI_FULL_SPEED)) { | |||
| sd.initErrorPrint(); | |||
| fatalBlink(); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop(void) { | |||
| // discard any input | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("type:")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("c - convert file to CSV")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("d - dump data to Serial")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("e - overrun error details")); | |||
| Serial.println(F("r - record data")); | |||
| while(!Serial.available()) {} | |||
| char c = tolower(Serial.read()); | |||
| // Discard extra Serial data. | |||
| do { | |||
| delay(10); | |||
| } while (Serial.read() >= 0); | |||
| if (ERROR_LED_PIN >= 0) { | |||
| digitalWrite(ERROR_LED_PIN, LOW); | |||
| } | |||
| if (c == 'c') { | |||
| binaryToCsv(); | |||
| } else if (c == 'd') { | |||
| dumpData(); | |||
| } else if (c == 'e') { | |||
| checkOverrun(); | |||
| } else if (c == 'r') { | |||
| logData(); | |||
| } else { | |||
| Serial.println(F("Invalid entry")); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 8
- 0
SdFat/examples/LowLatencyLogger/UserDataType.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,8 @@ | |||
| #ifndef UserDataType_h | |||
| #define UserDataType_h | |||
| const uint8_t ADC_DIM = 4; | |||
| struct data_t { | |||
| unsigned long time; | |||
| unsigned short adc[ADC_DIM]; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // UserDataType_h | |||
+ 40
- 0
SdFat/examples/OpenNext/OpenNext.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Print size, modify date/time, and name for all files in root. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system object | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| delay(1000); | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // open next file in root. The volume working directory, vwd, is root | |||
| while (file.openNext(sd.vwd(), O_READ)) { | |||
| file.printFileSize(&Serial); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| file.printModifyDateTime(&Serial); | |||
| Serial.write(' '); | |||
| file.printName(&Serial); | |||
| if (file.isDir()) { | |||
| // Indicate a directory. | |||
| Serial.write('/'); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println("Done!"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 119
- 0
SdFat/examples/PrintBenchmark/PrintBenchmark.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,119 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch is a simple Print benchmark. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // number of lines to print | |||
| const uint16_t N_PRINT = 20000; | |||
| // file system | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // test file | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| // Serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) { | |||
| // wait for Leonardo | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| uint32_t maxLatency; | |||
| uint32_t minLatency; | |||
| uint32_t totalLatency; | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) { | |||
| } | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) { | |||
| } | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| cout << pstr("Free RAM: ") << FreeRam() << endl; | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_FULL_SPEED for best performance. | |||
| // try SPI_HALF_SPEED if bus errors occur. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_FULL_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Type is FAT") << int(sd.vol()->fatType()) << endl; | |||
| // open or create file - truncate existing file. | |||
| if (!file.open("BENCH.TXT", O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_RDWR)) { | |||
| error("open failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("Starting print test. Please wait.\n\n"); | |||
| // do write test | |||
| for (int test = 0; test < 3; test++) { | |||
| switch(test) { | |||
| case 0: | |||
| cout << pstr("Test of println(uint16_t)\n"); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 1: | |||
| cout << pstr("Test of printField(uint16_t, char)\n"); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 2: | |||
| cout << pstr("Test of println(double)\n"); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| file.truncate(0); | |||
| maxLatency = 0; | |||
| minLatency = 999999; | |||
| totalLatency = 0; | |||
| uint32_t t = millis(); | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < N_PRINT; i++) { | |||
| uint32_t m = micros(); | |||
| switch(test) { | |||
| case 0: | |||
| file.println(i); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 1: | |||
| file.printField(i, '\n'); | |||
| break; | |||
| case 2: | |||
| file.println((double)0.01*i); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (file.writeError) { | |||
| error("write failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| m = micros() - m; | |||
| if (maxLatency < m) maxLatency = m; | |||
| if (minLatency > m) minLatency = m; | |||
| totalLatency += m; | |||
| } | |||
| file.sync(); | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| double s = file.fileSize(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Time ") << 0.001*t << pstr(" sec\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("File size ") << 0.001*s << pstr(" KB\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Write ") << s/t << pstr(" KB/sec\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Maximum latency: ") << maxLatency; | |||
| cout << pstr(" usec, Minimum Latency: ") << minLatency; | |||
| cout << pstr(" usec, Avg Latency: "); | |||
| cout << totalLatency/N_PRINT << pstr(" usec\n\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Done!\n\n"); | |||
| } | |||
+ 156
- 0
SdFat/examples/QuickStart/QuickStart.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,156 @@ | |||
| // Quick hardware test. | |||
| // | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // | |||
| // Set DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT to disable a second SPI device. | |||
| // For example, with the Ethernet shield, set DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT | |||
| // to 10 to disable the Ethernet controller. | |||
| const int8_t DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT = -1; | |||
| // | |||
| // Test with reduced SPI speed for breadboards. | |||
| // Change spiSpeed to SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance | |||
| // Use SPI_QUARTER_SPEED for even slower SPI bus speed | |||
| const uint8_t spiSpeed = SPI_HALF_SPEED; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Normally the SdFat class is used in applications in place | |||
| // of Sd2Card, SdVolume, and SdFile for root. | |||
| // These internal classes are used here to diagnose problems. | |||
| Sd2Card card; | |||
| SdVolume volume; | |||
| SdFile root; | |||
| // Serial streams | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| // input buffer for line | |||
| char cinBuf[40]; | |||
| ArduinoInStream cin(Serial, cinBuf, sizeof(cinBuf)); | |||
| // SD card chip select | |||
| int chipSelect; | |||
| void cardOrSpeed() { | |||
| cout << pstr("Try another SD card or reduce the SPI bus speed.\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Edit spiSpeed in this sketch to change it.\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| void reformatMsg() { | |||
| cout << pstr("Try reformatting the card. For best results use\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("the SdFormatter sketch in SdFat/examples or download\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("and use SDFormatter from www.sdcard.org/consumer.\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // Wait for Leonardo. | |||
| delay(1000); // Delay for Due. | |||
| cout << pstr("\nSPI pins:\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("MOSI: ") << int(MOSI) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("MISO: ") << int(MISO) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("SCK: ") << int(SCK) << endl; | |||
| if (DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT < 0) { | |||
| cout << pstr( | |||
| "\nBe sure to edit DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT if you have\n" | |||
| "a second SPI device. For example, with the Ethernet\n" | |||
| "shield, DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT should be set to 10\n" | |||
| "to disable the Ethernet controller.\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr( | |||
| "\nSD chip select is the key hardware option.\n" | |||
| "Common values are:\n" | |||
| "Arduino Ethernet shield, pin 4\n" | |||
| "Sparkfun SD shield, pin 8\n" | |||
| "Adafruit SD shields and modules, pin 10\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| bool firstTry = true; | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| // read any existing Serial data | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| if (!firstTry) cout << pstr("\nRestarting\n"); | |||
| firstTry = false; | |||
| cout << pstr("\nEnter the chip select pin number: "); | |||
| cin.readline(); | |||
| if (cin >> chipSelect) { | |||
| cout << chipSelect << endl; | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("\nInvalid pin number\n"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| if (DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT < 0) { | |||
| cout << pstr( | |||
| "\nAssuming the SD is the only SPI device.\n" | |||
| "Edit DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT to disable another device.\n"); | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("\nDisabling SPI device on pin "); | |||
| cout << int(DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT) << endl; | |||
| pinMode(DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT, OUTPUT); | |||
| digitalWrite(DISABLE_CHIP_SELECT, HIGH); | |||
| } | |||
| if (!card.init(spiSpeed, chipSelect)) { | |||
| cout << pstr( | |||
| "\nSD initialization failed.\n" | |||
| "Do not reformat the card!\n" | |||
| "Is the card correctly inserted?\n" | |||
| "Is chipSelect set to the correct value?\n" | |||
| "Does another SPI device need to be disabled?\n" | |||
| "Is there a wiring/soldering problem?\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("errorCode: ") << hex << showbase << int(card.errorCode()); | |||
| cout << pstr(", errorData: ") << int(card.errorData()); | |||
| cout << dec << noshowbase << endl; | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nCard successfully initialized.\n"); | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| uint32_t size = card.cardSize(); | |||
| if (size == 0) { | |||
| cout << pstr("Can't determine the card size.\n"); | |||
| cardOrSpeed(); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| uint32_t sizeMB = 0.000512 * size + 0.5; | |||
| cout << pstr("Card size: ") << sizeMB; | |||
| cout << pstr(" MB (MB = 1,000,000 bytes)\n"); | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| if (!volume.init(&card)) { | |||
| if (card.errorCode()) { | |||
| cout << pstr("Can't read the card.\n"); | |||
| cardOrSpeed(); | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("Can't find a valid FAT16/FAT32 partition.\n"); | |||
| reformatMsg(); | |||
| } | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("Volume is FAT") << int(volume.fatType()); | |||
| cout << pstr(", Cluster size (bytes): ") << 512L * volume.blocksPerCluster(); | |||
| cout << endl << endl; | |||
| root.close(); | |||
| if (!root.openRoot(&volume)) { | |||
| cout << pstr("Can't open root directory.\n"); | |||
| reformatMsg(); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("Files found (name date time size):\n"); | |||
| root.ls(LS_R | LS_DATE | LS_SIZE); | |||
| if ((sizeMB > 1100 && volume.blocksPerCluster() < 64) | |||
| || (sizeMB < 2200 && volume.fatType() == 32)) { | |||
| cout << pstr("\nThis card should be reformatted for best performance.\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Use a cluster size of 32 KB for cards larger than 1 GB.\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Only cards larger than 2 GB should be formatted FAT32.\n"); | |||
| reformatMsg(); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| // read any existing Serial data | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| cout << pstr("\nSuccess! Type any character to restart.\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() < 0) {} | |||
| } | |||
+ 174
- 0
SdFat/examples/RawWrite/RawWrite.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,174 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch illustrates raw write functions in SdFat that | |||
| * can be used for high speed data logging. These functions | |||
| * are used in the WaveRP library to record audio with the | |||
| * Adafruit Wave Shield using the built-in Arduino ADC. | |||
| * | |||
| * The WaveRP library captures data from the ADC in an ISR | |||
| * that is driven driven by timer one. Data is collected in | |||
| * two 512 byte buffers and written to the SD card. | |||
| * | |||
| * This sketch simulates logging from a source that produces | |||
| * data at a constant rate of one block every MICROS_PER_BLOCK. | |||
| * | |||
| * If a high quality SanDisk card is used with this sketch | |||
| * no overruns occur and the maximum block write time is | |||
| * under 2000 micros. | |||
| * | |||
| * Note: WaveRP creates a very large file then truncates it | |||
| * to the length that is used for a recording. It only takes | |||
| * a few seconds to erase a 500 MB file since the card only | |||
| * marks the blocks as erased; no data transfer is required. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // number of blocks in the contiguous file | |||
| const uint32_t BLOCK_COUNT = 10000UL; | |||
| // time to produce a block of data | |||
| const uint32_t MICROS_PER_BLOCK = 10000; | |||
| // file system | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // test file | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| // file extent | |||
| uint32_t bgnBlock, endBlock; | |||
| // Serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // log of first overruns | |||
| #define OVER_DIM 20 | |||
| struct { | |||
| uint32_t block; | |||
| uint32_t micros; | |||
| } over[OVER_DIM]; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop(void) { | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| cout << pstr("Free RAM: ") << FreeRam() << endl; | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_FULL_SPEED for best performance. | |||
| // try SPI_HALF_SPEED if bus errors occur. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_FULL_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // delete possible existing file | |||
| sd.remove("RAW.TXT"); | |||
| // create a contiguous file | |||
| if (!file.createContiguous(sd.vwd(), "RAW.TXT", 512UL*BLOCK_COUNT)) { | |||
| error("createContiguous failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // get the location of the file's blocks | |||
| if (!file.contiguousRange(&bgnBlock, &endBlock)) { | |||
| error("contiguousRange failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| //*********************NOTE************************************** | |||
| // NO SdFile calls are allowed while cache is used for raw writes | |||
| //*************************************************************** | |||
| // clear the cache and use it as a 512 byte buffer | |||
| uint8_t* pCache = (uint8_t*)sd.vol()->cacheClear(); | |||
| // fill cache with eight lines of 64 bytes each | |||
| memset(pCache, ' ', 512); | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 512; i += 64) { | |||
| // put line number at end of line then CR/LF | |||
| pCache[i + 61] = '0' + (i/64); | |||
| pCache[i + 62] = '\r'; | |||
| pCache[i + 63] = '\n'; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("Start raw write of ") << file.fileSize() << pstr(" bytes at\n"); | |||
| cout << 512000000UL/MICROS_PER_BLOCK << pstr(" bytes per second\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Please wait ") << (BLOCK_COUNT*MICROS_PER_BLOCK)/1000000UL; | |||
| cout << pstr(" seconds\n"); | |||
| // tell card to setup for multiple block write with pre-erase | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeStart(bgnBlock, BLOCK_COUNT)) { | |||
| error("writeStart failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // init stats | |||
| uint16_t overruns = 0; | |||
| uint32_t maxWriteTime = 0; | |||
| uint32_t t = micros(); | |||
| uint32_t tNext = t; | |||
| // write data | |||
| for (uint32_t b = 0; b < BLOCK_COUNT; b++) { | |||
| // write must be done by this time | |||
| tNext += MICROS_PER_BLOCK; | |||
| // put block number at start of first line in block | |||
| uint32_t n = b; | |||
| for (int8_t d = 5; d >= 0; d--){ | |||
| pCache[d] = n || d == 5 ? n % 10 + '0' : ' '; | |||
| n /= 10; | |||
| } | |||
| // write a 512 byte block | |||
| uint32_t tw = micros(); | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeData(pCache)) error("writeData failed"); | |||
| tw = micros() - tw; | |||
| // check for max write time | |||
| if (tw > maxWriteTime) { | |||
| maxWriteTime = tw; | |||
| } | |||
| // check for overrun | |||
| if (micros() > tNext) { | |||
| if (overruns < OVER_DIM) { | |||
| over[overruns].block = b; | |||
| over[overruns].micros = tw; | |||
| } | |||
| overruns++; | |||
| // advance time to reflect overrun | |||
| tNext = micros(); | |||
| } | |||
| else { | |||
| // wait for time to write next block | |||
| while(micros() < tNext); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // total write time | |||
| t = micros() - t; | |||
| // end multiple block write mode | |||
| if (!sd.card()->writeStop()) error("writeStop failed"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Done\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Elapsed time: ") << setprecision(3)<< 1.e-6*t; | |||
| cout << pstr(" seconds\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Max write time: ") << maxWriteTime << pstr(" micros\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Overruns: ") << overruns << endl; | |||
| if (overruns) { | |||
| uint8_t n = overruns > OVER_DIM ? OVER_DIM : overruns; | |||
| cout << pstr("fileBlock,micros") << endl; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| cout << over[i].block << ',' << over[i].micros << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // close file for next pass of loop | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| } | |||
+ 68
- 0
SdFat/examples/ReadWriteSdFat/ReadWriteSdFat.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,68 @@ | |||
| // Ported to SdFat from the native Arduino SD library example by Bill Greiman | |||
| // On the Ethernet Shield, CS is pin 4. SdFat handles setting SS | |||
| const int chipSelect = 4; | |||
| /* | |||
| SD card read/write | |||
| This example shows how to read and write data to and from an SD card file | |||
| The circuit: | |||
| * SD card attached to SPI bus as follows: | |||
| ** MOSI - pin 11 | |||
| ** MISO - pin 12 | |||
| ** CLK - pin 13 | |||
| ** CS - pin 4 | |||
| created Nov 2010 | |||
| by David A. Mellis | |||
| updated 2 Dec 2010 | |||
| by Tom Igoe | |||
| modified by Bill Greiman 11 Apr 2011 | |||
| This example code is in the public domain. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdFile myFile; | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| Serial.println("Type any character to start"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // Initialize SdFat or print a detailed error message and halt | |||
| // Use half speed like the native library. | |||
| // change to SPI_FULL_SPEED for more performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // open the file for write at end like the Native SD library | |||
| if (!myFile.open("test.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_AT_END)) { | |||
| sd.errorHalt("opening test.txt for write failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // if the file opened okay, write to it: | |||
| Serial.print("Writing to test.txt..."); | |||
| myFile.println("testing 1, 2, 3."); | |||
| // close the file: | |||
| myFile.close(); | |||
| Serial.println("done."); | |||
| // re-open the file for reading: | |||
| if (!myFile.open("test.txt", O_READ)) { | |||
| sd.errorHalt("opening test.txt for read failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println("test.txt:"); | |||
| // read from the file until there's nothing else in it: | |||
| int data; | |||
| while ((data = myFile.read()) >= 0) Serial.write(data); | |||
| // close the file: | |||
| myFile.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| // nothing happens after setup | |||
| } | |||
+ 486
- 0
SdFat/examples/SdFormatter/SdFormatter.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,486 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch will format an SD or SDHC card. | |||
| * Warning all data will be deleted! | |||
| * | |||
| * For SD/SDHC cards larger than 64 MB this | |||
| * sketch attempts to match the format | |||
| * generated by SDFormatter available here: | |||
| * | |||
| * http://www.sdcard.org/consumers/formatter/ | |||
| * | |||
| * For smaller cards this sketch uses FAT16 | |||
| * and SDFormatter uses FAT12. | |||
| */ | |||
| // Print extra info for debug if DEBUG_PRINT is nonzero | |||
| #define DEBUG_PRINT 0 | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #if DEBUG_PRINT | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| #endif // DEBUG_PRINT | |||
| // | |||
| // Change the value of chipSelect if your hardware does | |||
| // not use the default value, SS. Common values are: | |||
| // Arduino Ethernet shield: pin 4 | |||
| // Sparkfun SD shield: pin 8 | |||
| // Adafruit SD shields and modules: pin 10 | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // Change spiSpeed to SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance | |||
| // Use SPI_QUARTER_SPEED for even slower SPI bus speed | |||
| const uint8_t spiSpeed = SPI_HALF_SPEED; | |||
| // Serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| Sd2Card card; | |||
| uint32_t cardSizeBlocks; | |||
| uint16_t cardCapacityMB; | |||
| // cache for SD block | |||
| cache_t cache; | |||
| // MBR information | |||
| uint8_t partType; | |||
| uint32_t relSector; | |||
| uint32_t partSize; | |||
| // Fake disk geometry | |||
| uint8_t numberOfHeads; | |||
| uint8_t sectorsPerTrack; | |||
| // FAT parameters | |||
| uint16_t reservedSectors; | |||
| uint8_t sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| uint32_t fatStart; | |||
| uint32_t fatSize; | |||
| uint32_t dataStart; | |||
| // constants for file system structure | |||
| uint16_t const BU16 = 128; | |||
| uint16_t const BU32 = 8192; | |||
| // strings needed in file system structures | |||
| char noName[] = "NO NAME "; | |||
| char fat16str[] = "FAT16 "; | |||
| char fat32str[] = "FAT32 "; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #define sdError(msg) sdError_P(PSTR(msg)) | |||
| void sdError_P(const char* str) { | |||
| cout << pstr("error: "); | |||
| cout << pgm(str) << endl; | |||
| if (card.errorCode()) { | |||
| cout << pstr("SD error: ") << hex << int(card.errorCode()); | |||
| cout << ',' << int(card.errorData()) << dec << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| while (1); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #if DEBUG_PRINT | |||
| void debugPrint() { | |||
| cout << pstr("FreeRam: ") << FreeRam() << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("partStart: ") << relSector << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("partSize: ") << partSize << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("reserved: ") << reservedSectors << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("fatStart: ") << fatStart << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("fatSize: ") << fatSize << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("dataStart: ") << dataStart << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("clusterCount: "); | |||
| cout << ((relSector + partSize - dataStart)/sectorsPerCluster) << endl; | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Heads: ") << int(numberOfHeads) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Sectors: ") << int(sectorsPerTrack) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Cylinders: "); | |||
| cout << cardSizeBlocks/(numberOfHeads*sectorsPerTrack) << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // DEBUG_PRINT | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // write cached block to the card | |||
| uint8_t writeCache(uint32_t lbn) { | |||
| return card.writeBlock(lbn, cache.data); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // initialize appropriate sizes for SD capacity | |||
| void initSizes() { | |||
| if (cardCapacityMB <= 6) { | |||
| sdError("Card is too small."); | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 16) { | |||
| sectorsPerCluster = 2; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 32) { | |||
| sectorsPerCluster = 4; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 64) { | |||
| sectorsPerCluster = 8; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 128) { | |||
| sectorsPerCluster = 16; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 1024) { | |||
| sectorsPerCluster = 32; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 32768) { | |||
| sectorsPerCluster = 64; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // SDXC cards | |||
| sectorsPerCluster = 128; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("Blocks/Cluster: ") << int(sectorsPerCluster) << endl; | |||
| // set fake disk geometry | |||
| sectorsPerTrack = cardCapacityMB <= 256 ? 32 : 63; | |||
| if (cardCapacityMB <= 16) { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 2; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 32) { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 4; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 128) { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 8; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 504) { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 16; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 1008) { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 32; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 2016) { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 64; | |||
| } else if (cardCapacityMB <= 4032) { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 128; | |||
| } else { | |||
| numberOfHeads = 255; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // zero cache and optionally set the sector signature | |||
| void clearCache(uint8_t addSig) { | |||
| memset(&cache, 0, sizeof(cache)); | |||
| if (addSig) { | |||
| cache.mbr.mbrSig0 = BOOTSIG0; | |||
| cache.mbr.mbrSig1 = BOOTSIG1; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // zero FAT and root dir area on SD | |||
| void clearFatDir(uint32_t bgn, uint32_t count) { | |||
| clearCache(false); | |||
| if (!card.writeStart(bgn, count)) { | |||
| sdError("Clear FAT/DIR writeStart failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < count; i++) { | |||
| if ((i & 0XFF) == 0) cout << '.'; | |||
| if (!card.writeData(cache.data)) { | |||
| sdError("Clear FAT/DIR writeData failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (!card.writeStop()) { | |||
| sdError("Clear FAT/DIR writeStop failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // return cylinder number for a logical block number | |||
| uint16_t lbnToCylinder(uint32_t lbn) { | |||
| return lbn / (numberOfHeads * sectorsPerTrack); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // return head number for a logical block number | |||
| uint8_t lbnToHead(uint32_t lbn) { | |||
| return (lbn % (numberOfHeads * sectorsPerTrack)) / sectorsPerTrack; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // return sector number for a logical block number | |||
| uint8_t lbnToSector(uint32_t lbn) { | |||
| return (lbn % sectorsPerTrack) + 1; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // format and write the Master Boot Record | |||
| void writeMbr() { | |||
| clearCache(true); | |||
| part_t* p = cache.mbr.part; | |||
| p->boot = 0; | |||
| uint16_t c = lbnToCylinder(relSector); | |||
| if (c > 1023) sdError("MBR CHS"); | |||
| p->beginCylinderHigh = c >> 8; | |||
| p->beginCylinderLow = c & 0XFF; | |||
| p->beginHead = lbnToHead(relSector); | |||
| p->beginSector = lbnToSector(relSector); | |||
| p->type = partType; | |||
| uint32_t endLbn = relSector + partSize - 1; | |||
| c = lbnToCylinder(endLbn); | |||
| if (c <= 1023) { | |||
| p->endCylinderHigh = c >> 8; | |||
| p->endCylinderLow = c & 0XFF; | |||
| p->endHead = lbnToHead(endLbn); | |||
| p->endSector = lbnToSector(endLbn); | |||
| } else { | |||
| // Too big flag, c = 1023, h = 254, s = 63 | |||
| p->endCylinderHigh = 3; | |||
| p->endCylinderLow = 255; | |||
| p->endHead = 254; | |||
| p->endSector = 63; | |||
| } | |||
| p->firstSector = relSector; | |||
| p->totalSectors = partSize; | |||
| if (!writeCache(0)) sdError("write MBR"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // generate serial number from card size and micros since boot | |||
| uint32_t volSerialNumber() { | |||
| return (cardSizeBlocks << 8) + micros(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // format the SD as FAT16 | |||
| void makeFat16() { | |||
| uint32_t nc; | |||
| for (dataStart = 2 * BU16;; dataStart += BU16) { | |||
| nc = (cardSizeBlocks - dataStart)/sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| fatSize = (nc + 2 + 255)/256; | |||
| uint32_t r = BU16 + 1 + 2 * fatSize + 32; | |||
| if (dataStart < r) continue; | |||
| relSector = dataStart - r + BU16; | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| // check valid cluster count for FAT16 volume | |||
| if (nc < 4085 || nc >= 65525) sdError("Bad cluster count"); | |||
| reservedSectors = 1; | |||
| fatStart = relSector + reservedSectors; | |||
| partSize = nc * sectorsPerCluster + 2 * fatSize + reservedSectors + 32; | |||
| if (partSize < 32680) { | |||
| partType = 0X01; | |||
| } else if (partSize < 65536) { | |||
| partType = 0X04; | |||
| } else { | |||
| partType = 0X06; | |||
| } | |||
| // write MBR | |||
| writeMbr(); | |||
| clearCache(true); | |||
| fat_boot_t* pb = &cache.fbs; | |||
| pb->jump[0] = 0XEB; | |||
| pb->jump[1] = 0X00; | |||
| pb->jump[2] = 0X90; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < sizeof(pb->oemId); i++) { | |||
| pb->oemId[i] = ' '; | |||
| } | |||
| pb->bytesPerSector = 512; | |||
| pb->sectorsPerCluster = sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| pb->reservedSectorCount = reservedSectors; | |||
| pb->fatCount = 2; | |||
| pb->rootDirEntryCount = 512; | |||
| pb->mediaType = 0XF8; | |||
| pb->sectorsPerFat16 = fatSize; | |||
| pb->sectorsPerTrack = sectorsPerTrack; | |||
| pb->headCount = numberOfHeads; | |||
| pb->hidddenSectors = relSector; | |||
| pb->totalSectors32 = partSize; | |||
| pb->driveNumber = 0X80; | |||
| pb->bootSignature = EXTENDED_BOOT_SIG; | |||
| pb->volumeSerialNumber = volSerialNumber(); | |||
| memcpy(pb->volumeLabel, noName, sizeof(pb->volumeLabel)); | |||
| memcpy(pb->fileSystemType, fat16str, sizeof(pb->fileSystemType)); | |||
| // write partition boot sector | |||
| if (!writeCache(relSector)) { | |||
| sdError("FAT16 write PBS failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // clear FAT and root directory | |||
| clearFatDir(fatStart, dataStart - fatStart); | |||
| clearCache(false); | |||
| cache.fat16[0] = 0XFFF8; | |||
| cache.fat16[1] = 0XFFFF; | |||
| // write first block of FAT and backup for reserved clusters | |||
| if (!writeCache(fatStart) | |||
| || !writeCache(fatStart + fatSize)) { | |||
| sdError("FAT16 reserve failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // format the SD as FAT32 | |||
| void makeFat32() { | |||
| uint32_t nc; | |||
| relSector = BU32; | |||
| for (dataStart = 2 * BU32;; dataStart += BU32) { | |||
| nc = (cardSizeBlocks - dataStart)/sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| fatSize = (nc + 2 + 127)/128; | |||
| uint32_t r = relSector + 9 + 2 * fatSize; | |||
| if (dataStart >= r) break; | |||
| } | |||
| // error if too few clusters in FAT32 volume | |||
| if (nc < 65525) sdError("Bad cluster count"); | |||
| reservedSectors = dataStart - relSector - 2 * fatSize; | |||
| fatStart = relSector + reservedSectors; | |||
| partSize = nc * sectorsPerCluster + dataStart - relSector; | |||
| // type depends on address of end sector | |||
| // max CHS has lbn = 16450560 = 1024*255*63 | |||
| if ((relSector + partSize) <= 16450560) { | |||
| // FAT32 | |||
| partType = 0X0B; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // FAT32 with INT 13 | |||
| partType = 0X0C; | |||
| } | |||
| writeMbr(); | |||
| clearCache(true); | |||
| fat32_boot_t* pb = &cache.fbs32; | |||
| pb->jump[0] = 0XEB; | |||
| pb->jump[1] = 0X00; | |||
| pb->jump[2] = 0X90; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < sizeof(pb->oemId); i++) { | |||
| pb->oemId[i] = ' '; | |||
| } | |||
| pb->bytesPerSector = 512; | |||
| pb->sectorsPerCluster = sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| pb->reservedSectorCount = reservedSectors; | |||
| pb->fatCount = 2; | |||
| pb->mediaType = 0XF8; | |||
| pb->sectorsPerTrack = sectorsPerTrack; | |||
| pb->headCount = numberOfHeads; | |||
| pb->hidddenSectors = relSector; | |||
| pb->totalSectors32 = partSize; | |||
| pb->sectorsPerFat32 = fatSize; | |||
| pb->fat32RootCluster = 2; | |||
| pb->fat32FSInfo = 1; | |||
| pb->fat32BackBootBlock = 6; | |||
| pb->driveNumber = 0X80; | |||
| pb->bootSignature = EXTENDED_BOOT_SIG; | |||
| pb->volumeSerialNumber = volSerialNumber(); | |||
| memcpy(pb->volumeLabel, noName, sizeof(pb->volumeLabel)); | |||
| memcpy(pb->fileSystemType, fat32str, sizeof(pb->fileSystemType)); | |||
| // write partition boot sector and backup | |||
| if (!writeCache(relSector) | |||
| || !writeCache(relSector + 6)) { | |||
| sdError("FAT32 write PBS failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| clearCache(true); | |||
| // write extra boot area and backup | |||
| if (!writeCache(relSector + 2) | |||
| || !writeCache(relSector + 8)) { | |||
| sdError("FAT32 PBS ext failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| fat32_fsinfo_t* pf = &cache.fsinfo; | |||
| pf->leadSignature = FSINFO_LEAD_SIG; | |||
| pf->structSignature = FSINFO_STRUCT_SIG; | |||
| pf->freeCount = 0XFFFFFFFF; | |||
| pf->nextFree = 0XFFFFFFFF; | |||
| // write FSINFO sector and backup | |||
| if (!writeCache(relSector + 1) | |||
| || !writeCache(relSector + 7)) { | |||
| sdError("FAT32 FSINFO failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| clearFatDir(fatStart, 2 * fatSize + sectorsPerCluster); | |||
| clearCache(false); | |||
| cache.fat32[0] = 0x0FFFFFF8; | |||
| cache.fat32[1] = 0x0FFFFFFF; | |||
| cache.fat32[2] = 0x0FFFFFFF; | |||
| // write first block of FAT and backup for reserved clusters | |||
| if (!writeCache(fatStart) | |||
| || !writeCache(fatStart + fatSize)) { | |||
| sdError("FAT32 reserve failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // flash erase all data | |||
| uint32_t const ERASE_SIZE = 262144L; | |||
| void eraseCard() { | |||
| cout << endl << pstr("Erasing\n"); | |||
| uint32_t firstBlock = 0; | |||
| uint32_t lastBlock; | |||
| uint16_t n = 0; | |||
| do { | |||
| lastBlock = firstBlock + ERASE_SIZE - 1; | |||
| if (lastBlock >= cardSizeBlocks) lastBlock = cardSizeBlocks - 1; | |||
| if (!card.erase(firstBlock, lastBlock)) sdError("erase failed"); | |||
| cout << '.'; | |||
| if ((n++)%32 == 31) cout << endl; | |||
| firstBlock += ERASE_SIZE; | |||
| } while (firstBlock < cardSizeBlocks); | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| if (!card.readBlock(0, cache.data)) sdError("readBlock"); | |||
| cout << hex << showbase << setfill('0') << internal; | |||
| cout << pstr("All data set to ") << setw(4) << int(cache.data[0]) << endl; | |||
| cout << dec << noshowbase << setfill(' ') << right; | |||
| cout << pstr("Erase done\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void formatCard() { | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Formatting\n"); | |||
| initSizes(); | |||
| if (card.type() != SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC) { | |||
| cout << pstr("FAT16\n"); | |||
| makeFat16(); | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("FAT32\n"); | |||
| makeFat32(); | |||
| } | |||
| #if DEBUG_PRINT | |||
| debugPrint(); | |||
| #endif // DEBUG_PRINT | |||
| cout << pstr("Format done\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| char c; | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| cout << pstr( | |||
| "\n" | |||
| "This sketch can erase and/or format SD/SDHC cards.\n" | |||
| "\n" | |||
| "Erase uses the card's fast flash erase command.\n" | |||
| "Flash erase sets all data to 0X00 for most cards\n" | |||
| "and 0XFF for a few vendor's cards.\n" | |||
| "\n" | |||
| "Cards larger than 2 GB will be formatted FAT32 and\n" | |||
| "smaller cards will be formatted FAT16.\n" | |||
| "\n" | |||
| "Warning, all data on the card will be erased.\n" | |||
| "Enter 'Y' to continue: "); | |||
| while (!Serial.available()) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due restart problem | |||
| c = Serial.read(); | |||
| cout << c << endl; | |||
| if (c != 'Y') { | |||
| cout << pstr("Quiting, you did not enter 'Y'.\n"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| // read any existing Serial data | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| cout << pstr( | |||
| "\n" | |||
| "Options are:\n" | |||
| "E - erase the card and skip formatting.\n" | |||
| "F - erase and then format the card. (recommended)\n" | |||
| "Q - quick format the card without erase.\n" | |||
| "\n" | |||
| "Enter option: "); | |||
| while (!Serial.available()) {} | |||
| c = Serial.read(); | |||
| cout << c << endl; | |||
| if (!strchr("EFQ", c)) { | |||
| cout << pstr("Quiting, invalid option entered.") << endl; | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!card.init(spiSpeed, chipSelect)) { | |||
| cout << pstr( | |||
| "\nSD initialization failure!\n" | |||
| "Is the SD card inserted correctly?\n" | |||
| "Is chip select correct at the top of this sketch?\n"); | |||
| sdError("card.init failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| cardSizeBlocks = card.cardSize(); | |||
| if (cardSizeBlocks == 0) sdError("cardSize"); | |||
| cardCapacityMB = (cardSizeBlocks + 2047)/2048; | |||
| cout << pstr("Card Size: ") << cardCapacityMB; | |||
| cout << pstr(" MB, (MB = 1,048,576 bytes)") << endl; | |||
| if (c == 'E' || c == 'F') { | |||
| eraseCard(); | |||
| } | |||
| if (c == 'F' || c == 'Q') { | |||
| formatCard(); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 197
- 0
SdFat/examples/SdInfo/SdInfo.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,197 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch attempts to initialize an SD card and analyze its structure. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| /* | |||
| * SD chip select pin. Common values are: | |||
| * | |||
| * Arduino Ethernet shield, pin 4. | |||
| * SparkFun SD shield, pin 8. | |||
| * Adafruit SD shields and modules, pin 10. | |||
| * Default SD chip select is the SPI SS pin. | |||
| */ | |||
| const uint8_t SdChipSelect = SS; | |||
| Sd2Card card; | |||
| SdVolume vol; | |||
| // serial output steam | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| // global for card size | |||
| uint32_t cardSize; | |||
| // global for card erase size | |||
| uint32_t eraseSize; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash | |||
| #define sdErrorMsg(msg) sdErrorMsg_P(PSTR(msg)); | |||
| void sdErrorMsg_P(const char* str) { | |||
| cout << pgm(str) << endl; | |||
| if (card.errorCode()) { | |||
| cout << pstr("SD errorCode: "); | |||
| cout << hex << int(card.errorCode()) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("SD errorData: "); | |||
| cout << int(card.errorData()) << dec << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| uint8_t cidDmp() { | |||
| cid_t cid; | |||
| if (!card.readCID(&cid)) { | |||
| sdErrorMsg("readCID failed"); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nManufacturer ID: "); | |||
| cout << hex << int(cid.mid) << dec << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("OEM ID: ") << cid.oid[0] << cid.oid[1] << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Product: "); | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; i++) { | |||
| cout << cid.pnm[i]; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nVersion: "); | |||
| cout << int(cid.prv_n) << '.' << int(cid.prv_m) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Serial number: ") << hex << cid.psn << dec << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Manufacturing date: "); | |||
| cout << int(cid.mdt_month) << '/'; | |||
| cout << (2000 + cid.mdt_year_low + 10 * cid.mdt_year_high) << endl; | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| uint8_t csdDmp() { | |||
| csd_t csd; | |||
| uint8_t eraseSingleBlock; | |||
| if (!card.readCSD(&csd)) { | |||
| sdErrorMsg("readCSD failed"); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| if (csd.v1.csd_ver == 0) { | |||
| eraseSingleBlock = csd.v1.erase_blk_en; | |||
| eraseSize = (csd.v1.sector_size_high << 1) | csd.v1.sector_size_low; | |||
| } else if (csd.v2.csd_ver == 1) { | |||
| eraseSingleBlock = csd.v2.erase_blk_en; | |||
| eraseSize = (csd.v2.sector_size_high << 1) | csd.v2.sector_size_low; | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("csd version error\n"); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| eraseSize++; | |||
| cout << pstr("cardSize: ") << 0.000512*cardSize; | |||
| cout << pstr(" MB (MB = 1,000,000 bytes)\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("flashEraseSize: ") << int(eraseSize) << pstr(" blocks\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("eraseSingleBlock: "); | |||
| if (eraseSingleBlock) { | |||
| cout << pstr("true\n"); | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("false\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // print partition table | |||
| uint8_t partDmp() { | |||
| cache_t *p = vol.cacheClear(); | |||
| if (!p) { | |||
| sdErrorMsg("cacheClear failed"); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!card.readBlock(0, p->data)) { | |||
| sdErrorMsg("read MBR failed"); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nSD Partition Table\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("part,boot,type,start,length\n"); | |||
| for (uint8_t ip = 1; ip < 5; ip++) { | |||
| part_t *pt = &p->mbr.part[ip - 1]; | |||
| cout << int(ip) << ',' << hex << int(pt->boot) << ',' << int(pt->type); | |||
| cout << dec << ',' << pt->firstSector <<',' << pt->totalSectors << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void volDmp() { | |||
| cout << pstr("\nVolume is FAT") << int(vol.fatType()) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("blocksPerCluster: ") << int(vol.blocksPerCluster()) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("clusterCount: ") << vol.clusterCount() << endl; | |||
| uint32_t volFree = vol.freeClusterCount(); | |||
| cout << pstr("freeClusters: ") << volFree << endl; | |||
| float fs = 0.000512*volFree*vol.blocksPerCluster(); | |||
| cout << pstr("freeSpace: ") << fs << pstr(" MB (MB = 1,000,000 bytes)\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("fatStartBlock: ") << vol.fatStartBlock() << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("fatCount: ") << int(vol.fatCount()) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("blocksPerFat: ") << vol.blocksPerFat() << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("rootDirStart: ") << vol.rootDirStart() << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("dataStartBlock: ") << vol.dataStartBlock() << endl; | |||
| if (vol.dataStartBlock() % eraseSize) { | |||
| cout << pstr("Data area is not aligned on flash erase boundaries!\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Download and use formatter from www.sdcard.org/consumer!\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while(!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| // use uppercase in hex and use 0X base prefix | |||
| cout << uppercase << showbase << endl; | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("SdFat version: ") << SD_FAT_VERSION << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| // read any existing Serial data | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("\ntype any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| uint32_t t = millis(); | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!card.init(SPI_HALF_SPEED, SdChipSelect)) { | |||
| sdErrorMsg("\ncard.init failed"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| cardSize = card.cardSize(); | |||
| if (cardSize == 0) { | |||
| sdErrorMsg("cardSize failed"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\ninit time: ") << t << " ms" << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("\nCard type: "); | |||
| switch (card.type()) { | |||
| case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD1: | |||
| cout << pstr("SD1\n"); | |||
| break; | |||
| case SD_CARD_TYPE_SD2: | |||
| cout << pstr("SD2\n"); | |||
| break; | |||
| case SD_CARD_TYPE_SDHC: | |||
| if (cardSize < 70000000) { | |||
| cout << pstr("SDHC\n"); | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("SDXC\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| cout << pstr("Unknown\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| if (!cidDmp()) return; | |||
| if (!csdDmp()) return; | |||
| if (!partDmp()) return; | |||
| if (!vol.init(&card)) { | |||
| sdErrorMsg("\nvol.init failed"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| volDmp(); | |||
| } | |||
+ 201
- 0
SdFat/examples/StdioBench/StdioBench.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,201 @@ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <StdioStream.h> | |||
| // Define PRINT_FIELD nonzero to use printField. | |||
| #define PRINT_FIELD 0 | |||
| // Number of lines to list on Serial. | |||
| #define STDIO_LIST_COUNT 0 | |||
| #define VERIFY_CONTENT 0 | |||
| const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = SS; | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdFile printFile; | |||
| StdioStream stdioFile; | |||
| float f[100]; | |||
| char buf[20]; | |||
| char* label[] = | |||
| {"uint8_t 0 to 255, 100 times ", "uint16_t 0 to 20000", | |||
| "uint32_t 0 to 20000", "uint32_t 1000000000 to 1000010000", | |||
| "float nnn.ffff, 10000 times"}; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| uint32_t m; | |||
| uint32_t printSize; | |||
| uint32_t stdioSize; | |||
| uint32_t printTime; | |||
| uint32_t stdioTime; | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Type any character to start")); | |||
| while (!Serial.available()); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Starting test")); | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CS_PIN)) sd.errorHalt(); | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 100; i++) { | |||
| f[i] = 123.0 + 0.12345*i; | |||
| } | |||
| for (uint8_t dataType = 0; dataType < 5; dataType++) { | |||
| for (uint8_t fileType = 0; fileType < 2; fileType++) { | |||
| if (!fileType) { | |||
| if (!printFile.open("PRRINT.TXT", O_CREAT | O_RDWR | O_TRUNC)) { | |||
| Serial.println("open fail"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| printTime = millis(); | |||
| switch (dataType) { | |||
| case 0: | |||
| for (uint16_t i =0; i < 100; i++) { | |||
| for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 255; j++) { | |||
| printFile.println(j); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 1: | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { | |||
| printFile.println(i); | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 2: | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { | |||
| printFile.println(i); | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 3: | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { | |||
| printFile.println(i + 1000000000UL); | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 4: | |||
| for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) { | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 100; i++) { | |||
| printFile.println(f[i], 4); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| printFile.sync(); | |||
| printTime = millis() - printTime; | |||
| printFile.rewind(); | |||
| printSize = printFile.fileSize(); | |||
| } else { | |||
| if (!stdioFile.fopen("STREAM.TXT", "w+")) { | |||
| Serial.println("fopen fail"); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| stdioTime = millis(); | |||
| switch (dataType) { | |||
| case 0: | |||
| for (uint16_t i =0; i < 100; i++) { | |||
| for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 255; j++) { | |||
| #if PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.printField(j, '\n'); | |||
| #else // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.println(j); | |||
| #endif // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 1: | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { | |||
| #if PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.printField(i, '\n'); | |||
| #else // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.println(i); | |||
| #endif // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 2: | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < 20000; i++) { | |||
| #if PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.printField(i, '\n'); | |||
| #else // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.println(i); | |||
| #endif // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 3: | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { | |||
| #if PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.printField(i + 1000000000UL, '\n'); | |||
| #else // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.println(i + 1000000000UL); | |||
| #endif // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| case 4: | |||
| for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) { | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 100; i++) { | |||
| #if PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.printField(f[i], '\n', 4); | |||
| #else // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| stdioFile.println(f[i], 4); | |||
| #endif // PRINT_FIELD | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| break; | |||
| default: | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| stdioFile.fflush(); | |||
| stdioTime = millis() - stdioTime; | |||
| stdioSize = stdioFile.ftell(); | |||
| if (STDIO_LIST_COUNT) { | |||
| size_t len; | |||
| stdioFile.rewind(); | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < STDIO_LIST_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| stdioFile.fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), &len); | |||
| Serial.print(len);Serial.print(','); | |||
| Serial.print(buf); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(label[dataType]); | |||
| if (VERIFY_CONTENT && printSize == stdioSize) { | |||
| printFile.rewind(); | |||
| stdioFile.rewind(); | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < stdioSize; i++) { | |||
| if (printFile.read() != stdioFile.getc()) { | |||
| Serial.print(F("Files differ at pos: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(i); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.print("fileSize: "); | |||
| if (printSize != stdioSize) { | |||
| Serial.print(printSize); | |||
| Serial.print(" != "); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println(stdioSize); | |||
| Serial.print("print millis: "); | |||
| Serial.println(printTime); | |||
| Serial.print("stdio millis: "); | |||
| Serial.println(stdioTime); | |||
| Serial.print("ratio: "); | |||
| Serial.println((float)printTime/(float)stdioTime); | |||
| Serial.println(); | |||
| printFile.close(); | |||
| stdioFile.fclose(); | |||
| } | |||
| Serial.println("Done"); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 75
- 0
SdFat/examples/StressTest/StressTest.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,75 @@ | |||
| // This stress test will create and write files until the SD is full. | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin. | |||
| const uint8_t SD_CS_PIN = SS; | |||
| // Set write buffer size. | |||
| #ifdef __arm__ | |||
| #ifndef CORE_TEENSY | |||
| // Due | |||
| const size_t BUF_SIZE = 32768; | |||
| #else // CORE_TEENSY | |||
| // Teensy 3.0 | |||
| const size_t BUF_SIZE = 8192; | |||
| #endif // CORE_TEENSY | |||
| #elif defined(RAMEND) && RAMEND > 5000 | |||
| // AVR with more than 4 KB RAM | |||
| const size_t BUF_SIZE = 4096; | |||
| #else // __arm__ | |||
| // other | |||
| const size_t BUF_SIZE = 512; | |||
| #endif // __arm__ | |||
| const size_t FILE_SIZE_KB = 10240; | |||
| const uint16_t BUFS_PER_FILE = (1024L*FILE_SIZE_KB/BUF_SIZE); | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| uint8_t buf[BUF_SIZE]; | |||
| char name[13]; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| Serial.print("BUF_SIZE "); | |||
| Serial.println(BUF_SIZE); | |||
| Serial.println("Type any character to start"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() < 0) {} | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CS_PIN))sd.errorHalt("sd.begin"); | |||
| // Fill buf with known value. | |||
| for (size_t i = 0; i < BUF_SIZE; i++) buf[i] = i; | |||
| // Wait to begin. | |||
| do {delay(10);} while (Serial.read() >= 0); | |||
| Serial.println("Type any character to stop after next file"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| // Free KB on SD. | |||
| uint32_t freeKB = sd.vol()->freeClusterCount()*sd.vol()->blocksPerCluster()/2; | |||
| Serial.print("Free KB: "); | |||
| Serial.println(freeKB); | |||
| if (freeKB < 2*FILE_SIZE_KB) { | |||
| Serial.println(" Done!"); | |||
| while(1); | |||
| } | |||
| sprintf(name, "%lu.DAT", freeKB); | |||
| if (!file.open(name, O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC)) { | |||
| sd.errorHalt("Open error!"); | |||
| } | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < BUFS_PER_FILE; i++) { | |||
| if (file.write(buf, BUF_SIZE) != BUF_SIZE) { | |||
| sd.errorHalt("Write error!"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| if (Serial.available()) { | |||
| Serial.println("Stopped!"); | |||
| while(1); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 168
- 0
SdFat/examples/Timestamp/Timestamp.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,168 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch tests the dateTimeCallback() function | |||
| * and the timestamp() function. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| // Default SD chip select is SS pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // create Serial stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /* | |||
| * date/time values for debug | |||
| * normally supplied by a real-time clock or GPS | |||
| */ | |||
| // date 1-Oct-09 | |||
| uint16_t year = 2009; | |||
| uint8_t month = 10; | |||
| uint8_t day = 1; | |||
| // time 20:30:40 | |||
| uint8_t hour = 20; | |||
| uint8_t minute = 30; | |||
| uint8_t second = 40; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /* | |||
| * User provided date time callback function. | |||
| * See SdFile::dateTimeCallback() for usage. | |||
| */ | |||
| void dateTime(uint16_t* date, uint16_t* time) { | |||
| // User gets date and time from GPS or real-time | |||
| // clock in real callback function | |||
| // return date using FAT_DATE macro to format fields | |||
| *date = FAT_DATE(year, month, day); | |||
| // return time using FAT_TIME macro to format fields | |||
| *time = FAT_TIME(hour, minute, second); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Function to print all timestamps. | |||
| */ | |||
| void printTimestamps(SdFile& f) { | |||
| dir_t d; | |||
| if (!f.dirEntry(&d)) error("f.dirEntry failed"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Creation: "); | |||
| f.printFatDate(d.creationDate); | |||
| cout << ' '; | |||
| f.printFatTime(d.creationTime); | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Modify: "); | |||
| f.printFatDate(d.lastWriteDate); | |||
| cout <<' '; | |||
| f.printFatTime(d.lastWriteTime); | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Access: "); | |||
| f.printFatDate(d.lastAccessDate); | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (!Serial.available()); | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // remove files if they exist | |||
| sd.remove("CALLBACK.TXT"); | |||
| sd.remove("DEFAULT.TXT"); | |||
| sd.remove("STAMP.TXT"); | |||
| // create a new file with default timestamps | |||
| if (!file.open("DEFAULT.TXT", O_CREAT | O_WRITE)) { | |||
| error("open DEFAULT.TXT failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nOpen with default times\n"); | |||
| printTimestamps(file); | |||
| // close file | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| /* | |||
| * Test the date time callback function. | |||
| * | |||
| * dateTimeCallback() sets the function | |||
| * that is called when a file is created | |||
| * or when a file's directory entry is | |||
| * modified by sync(). | |||
| * | |||
| * The callback can be disabled by the call | |||
| * SdFile::dateTimeCallbackCancel() | |||
| */ | |||
| // set date time callback function | |||
| SdFile::dateTimeCallback(dateTime); | |||
| // create a new file with callback timestamps | |||
| if (!file.open("CALLBACK.TXT", O_CREAT | O_WRITE)) { | |||
| error("open CALLBACK.TXT failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| cout << ("\nOpen with callback times\n"); | |||
| printTimestamps(file); | |||
| // change call back date | |||
| day += 1; | |||
| // must add two to see change since FAT second field is 5-bits | |||
| second += 2; | |||
| // modify file by writing a byte | |||
| file.write('t'); | |||
| // force dir update | |||
| file.sync(); | |||
| cout << pstr("\nTimes after write\n"); | |||
| printTimestamps(file); | |||
| // close file | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| /* | |||
| * Test timestamp() function | |||
| * | |||
| * Cancel callback so sync will not | |||
| * change access/modify timestamp | |||
| */ | |||
| SdFile::dateTimeCallbackCancel(); | |||
| // create a new file with default timestamps | |||
| if (!file.open("STAMP.TXT", O_CREAT | O_WRITE)) { | |||
| error("open STAMP.TXT failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // set creation date time | |||
| if (!file.timestamp(T_CREATE, 2009, 11, 10, 1, 2, 3)) { | |||
| error("set create time failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // set write/modification date time | |||
| if (!file.timestamp(T_WRITE, 2009, 11, 11, 4, 5, 6)) { | |||
| error("set write time failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // set access date | |||
| if (!file.timestamp(T_ACCESS, 2009, 11, 12, 7, 8, 9)) { | |||
| error("set access time failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nTimes after timestamp() calls\n"); | |||
| printTimestamps(file); | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| cout << pstr("\nDone\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop(void){} | |||
+ 140
- 0
SdFat/examples/TwoCards/TwoCards.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,140 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Example use of two SD cards. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| #if !USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS | |||
| #error You must set USE_MULTIPLE_CARDS nonzero in SdFatConfig.h | |||
| #endif | |||
| SdFat sd1; | |||
| const uint8_t SD1_CS = 10; // chip select for sd1 | |||
| SdFat sd2; | |||
| const uint8_t SD2_CS = 9; // chip select for sd2 | |||
| const uint8_t BUF_DIM = 100; | |||
| uint8_t buf[BUF_DIM]; | |||
| const uint32_t FILE_SIZE = 1000000; | |||
| const uint16_t NWRITE = FILE_SIZE/BUF_DIM; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // print error msg, any SD error codes, and halt. | |||
| // store messages in flash | |||
| #define errorExit(msg) errorHalt_P(PSTR(msg)) | |||
| #define initError(msg) initErrorHalt_P(PSTR(msg)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| PgmPrint("FreeRam: "); | |||
| Serial.println(FreeRam()); | |||
| // fill buffer with known data | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(buf); i++) buf[i] = i; | |||
| PgmPrintln("type any character to start"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // disable sd2 while initializing sd1 | |||
| pinMode(SD2_CS, OUTPUT); | |||
| digitalWrite(SD2_CS, HIGH); | |||
| // initialize the first card | |||
| if (!sd1.begin(SD1_CS)) { | |||
| sd1.initError("sd1:"); | |||
| } | |||
| // create DIR1 on sd1 if it does not exist | |||
| if (!sd1.exists("/DIR1")) { | |||
| if (!sd1.mkdir("/DIR1")) sd1.errorExit("sd1.mkdir"); | |||
| } | |||
| // initialize the second card | |||
| if (!sd2.begin(SD2_CS)) { | |||
| sd2.initError("sd2:"); | |||
| } | |||
| // create DIR2 on sd2 if it does not exist | |||
| if (!sd2.exists("/DIR2")) { | |||
| if (!sd2.mkdir("/DIR2")) sd2.errorExit("sd2.mkdir"); | |||
| } | |||
| // list root directory on both cards | |||
| PgmPrintln("------sd1 root-------"); | |||
| sd1.ls(); | |||
| PgmPrintln("------sd2 root-------"); | |||
| sd2.ls(); | |||
| // make /DIR1 the default directory for sd1 | |||
| if (!sd1.chdir("/DIR1")) sd1.errorExit("sd1.chdir"); | |||
| // make /DIR2 the default directory for sd2 | |||
| if (!sd2.chdir("/DIR2")) sd2.errorExit("sd2.chdir"); | |||
| // list current directory on both cards | |||
| PgmPrintln("------sd1 DIR1-------"); | |||
| sd1.ls(); | |||
| PgmPrintln("------sd2 DIR2-------"); | |||
| sd2.ls(); | |||
| PgmPrintln("---------------------"); | |||
| // remove RENAME.BIN from /DIR2 directory of sd2 | |||
| if (sd2.exists("RENAME.BIN")) { | |||
| if (!sd2.remove("RENAME.BIN")) { | |||
| sd2.errorExit("remove RENAME.BIN"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // set the current working directory for open() to sd1 | |||
| sd1.chvol(); | |||
| // create or open /DIR1/TEST.BIN and truncate it to zero length | |||
| SdFile file1; | |||
| if (!file1.open("TEST.BIN", O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC)) { | |||
| sd1.errorExit("file1"); | |||
| } | |||
| PgmPrintln("Writing TEST.BIN to sd1"); | |||
| // write data to /DIR1/TEST.BIN on sd1 | |||
| for (int i = 0; i < NWRITE; i++) { | |||
| if (file1.write(buf, sizeof(buf)) != sizeof(buf)) { | |||
| sd1.errorExit("sd1.write"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // set the current working directory for open() to sd2 | |||
| sd2.chvol(); | |||
| // create or open /DIR2/COPY.BIN and truncate it to zero length | |||
| SdFile file2; | |||
| if (!file2.open("COPY.BIN", O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC)) { | |||
| sd2.errorExit("file2"); | |||
| } | |||
| PgmPrintln("Copying TEST.BIN to COPY.BIN"); | |||
| // copy file1 to file2 | |||
| file1.rewind(); | |||
| uint32_t t = millis(); | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| int n = file1.read(buf, sizeof(buf)); | |||
| if (n < 0) sd1.errorExit("read1"); | |||
| if (n == 0) break; | |||
| if (file2.write(buf, n) != n) sd2.errorExit("write2"); | |||
| } | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| PgmPrint("File size: "); | |||
| Serial.println(file2.fileSize()); | |||
| PgmPrint("Copy time: "); | |||
| Serial.print(t); | |||
| PgmPrintln(" millis"); | |||
| // close TEST.BIN | |||
| file1.close(); | |||
| // rename the copy | |||
| file2.close(); | |||
| if (!sd2.rename("COPY.BIN", "RENAME.BIN")) { | |||
| sd2.errorExit("sd2.rename"); | |||
| } | |||
| PgmPrintln("Done"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 173
- 0
SdFat/examples/bench/bench.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,173 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch is a simple binary write/read benchmark. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| #include <SdFatUtil.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // Size of read/write. | |||
| const size_t BUF_SIZE = 512; | |||
| // File size in MB where MB = 1,000,000 bytes. | |||
| const uint32_t FILE_SIZE_MB = 5; | |||
| // Write pass count. | |||
| const uint8_t WRITE_COUNT = 10; | |||
| // Read pass count. | |||
| const uint8_t READ_COUNT = 5; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // End of configuration constants. | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // File size in bytes. | |||
| const uint32_t FILE_SIZE = 1000000UL*FILE_SIZE_MB; | |||
| uint8_t buf[BUF_SIZE]; | |||
| // file system | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // test file | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| // Serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void cidDmp() { | |||
| cid_t cid; | |||
| if (!sd.card()->readCID(&cid)) { | |||
| error("readCID failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nManufacturer ID: "); | |||
| cout << hex << int(cid.mid) << dec << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("OEM ID: ") << cid.oid[0] << cid.oid[1] << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Product: "); | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; i++) { | |||
| cout << cid.pnm[i]; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << pstr("\nVersion: "); | |||
| cout << int(cid.prv_n) << '.' << int(cid.prv_m) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Serial number: ") << hex << cid.psn << dec << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Manufacturing date: "); | |||
| cout << int(cid.mdt_month) << '/'; | |||
| cout << (2000 + cid.mdt_year_low + 10 * cid.mdt_year_high) << endl; | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial){} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| cout << pstr("\nUse a freshly formatted SD for best performance.\n"); | |||
| // use uppercase in hex and use 0X base prefix | |||
| cout << uppercase << showbase << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| float s; | |||
| uint32_t t; | |||
| uint32_t maxLatency; | |||
| uint32_t minLatency; | |||
| uint32_t totalLatency; | |||
| // discard any input | |||
| while (Serial.read() >= 0) {} | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| cout << pstr("Free RAM: ") << FreeRam() << endl; | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_FULL_SPEED for best performance. | |||
| // try SPI_HALF_SPEED if bus errors occur. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_FULL_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Type is FAT") << int(sd.vol()->fatType()) << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("Card size: ") << sd.card()->cardSize()*512E-9; | |||
| cout << pstr(" GB (GB = 1E9 bytes)") << endl; | |||
| cidDmp(); | |||
| // open or create file - truncate existing file. | |||
| if (!file.open("BENCH.DAT", O_CREAT | O_TRUNC | O_RDWR)) { | |||
| error("open failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| // fill buf with known data | |||
| for (uint16_t i = 0; i < (BUF_SIZE-2); i++) { | |||
| buf[i] = 'A' + (i % 26); | |||
| } | |||
| buf[BUF_SIZE-2] = '\r'; | |||
| buf[BUF_SIZE-1] = '\n'; | |||
| cout << pstr("File size ") << FILE_SIZE_MB << pstr(" MB\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Buffer size ") << BUF_SIZE << pstr(" bytes\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Starting write test, please wait.") << endl << endl; | |||
| // do write test | |||
| uint32_t n = FILE_SIZE/sizeof(buf); | |||
| cout <<pstr("write speed and latency") << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("speed,max,min,avg") << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("KB/Sec,usec,usec,usec") << endl; | |||
| for (uint8_t nTest = 0; nTest < WRITE_COUNT; nTest++) { | |||
| file.truncate(0); | |||
| maxLatency = 0; | |||
| minLatency = 9999999; | |||
| totalLatency = 0; | |||
| t = millis(); | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| uint32_t m = micros(); | |||
| if (file.write(buf, sizeof(buf)) != sizeof(buf)) { | |||
| error("write failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| m = micros() - m; | |||
| if (maxLatency < m) maxLatency = m; | |||
| if (minLatency > m) minLatency = m; | |||
| totalLatency += m; | |||
| } | |||
| file.sync(); | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| s = file.fileSize(); | |||
| cout << s/t <<',' << maxLatency << ',' << minLatency; | |||
| cout << ',' << totalLatency/n << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << endl << pstr("Starting read test, please wait.") << endl; | |||
| cout << endl <<pstr("read speed and latency") << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("speed,max,min,avg") << endl; | |||
| cout << pstr("KB/Sec,usec,usec,usec") << endl; | |||
| // do read test | |||
| for (uint8_t nTest = 0; nTest < READ_COUNT; nTest++) { | |||
| file.rewind(); | |||
| maxLatency = 0; | |||
| minLatency = 9999999; | |||
| totalLatency = 0; | |||
| t = millis(); | |||
| for (uint32_t i = 0; i < n; i++) { | |||
| buf[BUF_SIZE-1] = 0; | |||
| uint32_t m = micros(); | |||
| if (file.read(buf, sizeof(buf)) != sizeof(buf)) { | |||
| error("read failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| m = micros() - m; | |||
| if (maxLatency < m) maxLatency = m; | |||
| if (minLatency > m) minLatency = m; | |||
| totalLatency += m; | |||
| if (buf[BUF_SIZE-1] != '\n') { | |||
| error("data check"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| t = millis() - t; | |||
| cout << s/t <<',' << maxLatency << ',' << minLatency; | |||
| cout << ',' << totalLatency/n << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << endl << pstr("Done") << endl; | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| } | |||
+ 34
- 0
SdFat/examples/cin_cout/cin_cout.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,34 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Demo of ArduinoInStream and ArduinoOutStream | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // create serial output stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| // input buffer for line | |||
| char cinBuf[40]; | |||
| // create serial input stream | |||
| ArduinoInStream cin(Serial, cinBuf, sizeof(cinBuf)); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| int32_t n; | |||
| cout << "\nenter an integer\n"; | |||
| cin.readline(); | |||
| if (cin >> n) { | |||
| cout << "The number is: " << n; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // will fail if no digits or not in range [-2147483648, 2147483647] | |||
| cout << "Invalid input: " << cinBuf; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| } | |||
+ 138
- 0
SdFat/examples/dataLogger/dataLogger.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,138 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Simple data logger. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin. Be sure to disable any other SPI devices such as Enet. | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // Interval between data records in milliseconds. | |||
| // The interval must be greater than the maximum SD write latency plus the | |||
| // time to acquire and write data to the SD to avoid overrun errors. | |||
| // Run the bench example to check the quality of your SD card. | |||
| const uint32_t SAMPLE_INTERVAL_MS = 200; | |||
| // Log file base name. Must be six characters or less. | |||
| #define FILE_BASE_NAME "DATA" | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // File system object. | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // Log file. | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| // Time in micros for next data record. | |||
| uint32_t logTime; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // User functions. Edit writeHeader() and logData() for your requirements. | |||
| const uint8_t ANALOG_COUNT = 4; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Write data header. | |||
| void writeHeader() { | |||
| file.print(F("micros")); | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < ANALOG_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| file.print(F(",adc")); | |||
| file.print(i, DEC); | |||
| } | |||
| file.println(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Log a data record. | |||
| void logData() { | |||
| uint16_t data[ANALOG_COUNT]; | |||
| // Read all channels to avoid SD write latency between readings. | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < ANALOG_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| data[i] = analogRead(i); | |||
| } | |||
| // Write data to file. Start with log time in micros. | |||
| file.print(logTime); | |||
| // Write ADC data to CSV record. | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < ANALOG_COUNT; i++) { | |||
| file.write(','); | |||
| file.print(data[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| file.println(); | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Error messages stored in flash. | |||
| #define error(msg) error_P(PSTR(msg)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void error_P(const char* msg) { | |||
| sd.errorHalt_P(msg); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| const uint8_t BASE_NAME_SIZE = sizeof(FILE_BASE_NAME) - 1; | |||
| char fileName[13] = FILE_BASE_NAME "00.CSV"; | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| delay(1000); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Type any character to start")); | |||
| while (!Serial.available()) {} | |||
| // Initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // Find an unused file name. | |||
| if (BASE_NAME_SIZE > 6) { | |||
| error("FILE_BASE_NAME too long"); | |||
| } | |||
| while (sd.exists(fileName)) { | |||
| if (fileName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1] != '9') { | |||
| fileName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1]++; | |||
| } else if (fileName[BASE_NAME_SIZE] != '9') { | |||
| fileName[BASE_NAME_SIZE + 1] = '0'; | |||
| fileName[BASE_NAME_SIZE]++; | |||
| } else { | |||
| error("Can't create file name"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| if (!file.open(fileName, O_CREAT | O_WRITE | O_EXCL)) error("file.open"); | |||
| do { | |||
| delay(10); | |||
| } while (Serial.read() >= 0); | |||
| Serial.print(F("Logging to: ")); | |||
| Serial.println(fileName); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Type any character to stop")); | |||
| // Write data header. | |||
| writeHeader(); | |||
| // Start on a multiple of the sample interval. | |||
| logTime = micros()/(1000UL*SAMPLE_INTERVAL_MS) + 1; | |||
| logTime *= 1000UL*SAMPLE_INTERVAL_MS; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop() { | |||
| // Time for next record. | |||
| logTime += 1000UL*SAMPLE_INTERVAL_MS; | |||
| // Wait for log time. | |||
| int32_t diff; | |||
| do { | |||
| diff = micros() - logTime; | |||
| } while (diff < 0); | |||
| // Check for data rate too high. | |||
| if (diff > 10) error("Missed data record"); | |||
| logData(); | |||
| // Force data to SD and update the directory entry to avoid data loss. | |||
| if (!file.sync() || file.getWriteError()) error("write error"); | |||
| if (Serial.available()) { | |||
| // Close file and stop. | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| Serial.println(F("Done")); | |||
| while(1) {} | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
+ 108
- 0
SdFat/examples/directoryFunctions/directoryFunctions.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,108 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Example use of chdir(), ls(), mkdir(), and rmdir(). | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD card chip select pin. | |||
| const uint8_t SD_CHIP_SELECT = SS; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Permit SD to be wiped if ALLOW_WIPE is true. | |||
| const bool ALLOW_WIPE = false; | |||
| // File system object. | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // Use for file creation in folders. | |||
| SdFile file; | |||
| // Create a Serial output stream. | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| // Buffer for Serial input. | |||
| char cinBuf[40]; | |||
| // Create a serial input stream. | |||
| ArduinoInStream cin(Serial, cinBuf, sizeof(cinBuf)); | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| // Error messages stored in flash. | |||
| #define error(msg) error_P(PSTR(msg)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void error_P(const char* msg) { | |||
| sd.errorHalt_P(msg); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| delay(1000); | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| // Wait for input line and discard. | |||
| cin.readline(); | |||
| // Initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(SD_CHIP_SELECT, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // Check for empty SD. | |||
| if (file.openNext(sd.vwd(), O_READ)) { | |||
| cout << pstr("Found files/folders in the root directory.\n"); | |||
| if (!ALLOW_WIPE) { | |||
| error("SD not empty, use a blank SD or set ALLOW_WIPE true."); | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << pstr("Type: 'WIPE' to delete all SD files.\n"); | |||
| char buf[10]; | |||
| cin.readline(); | |||
| cin.get(buf, sizeof(buf)); | |||
| if (cin.fail() || strncmp(buf, "WIPE", 4) || buf[4] >= ' ') { | |||
| error("Invalid WIPE input"); | |||
| } | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| sd.vwd()->rmRfStar(); | |||
| cout << pstr("***SD wiped clean.***\n\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // Create a new folder. | |||
| if (!sd.mkdir("FOLDER1")) error("Create FOLDER1 failed"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Created FOLDER1\n"); | |||
| // Create a file in FOLDER1 using a path. | |||
| if (!file.open("FOLDER1/FILE1.TXT", O_CREAT | O_WRITE)) { | |||
| error("create FOLDER1/FILE1.TXT failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Created FOLDER1/FILE1.TXT\n"); | |||
| // Change volume working directory to FOLDER1. | |||
| if (!sd.chdir("FOLDER1")) error("chdir failed for FOLDER1.\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("chdir to FOLDER1\n"); | |||
| // Create FILE2.TXT in current directory. | |||
| if (!file.open("FILE2.TXT", O_CREAT | O_WRITE)) { | |||
| error("create FILE2.TXT failed"); | |||
| } | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| cout << pstr("Created FILE2.TXT in current directory\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("List of files on the SD.\n"); | |||
| sd.ls("/", LS_R); | |||
| // Remove files from current directory. | |||
| if (!sd.remove("FILE1.TXT") || !sd.remove("FILE2.TXT")) error("remove failed"); | |||
| cout << pstr("\nFILE1.TXT and FILE2.TXT removed.\n"); | |||
| // Change current directory to root. | |||
| if (!sd.chdir()) error("chdir to root failed.\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("List of files on the SD.\n"); | |||
| sd.ls(LS_R); | |||
| // Remove FOLDER1. | |||
| if (!sd.rmdir("FOLDER1")) error("rmdir for FOLDER1 failed\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("\nFOLDER1 removed, SD empty.\n"); | |||
| cout << pstr("Done!\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Nothing happens in loop. | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 74
- 0
SdFat/examples/fgets/fgets.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,74 @@ | |||
| // Demo of fgets function to read lines from a file. | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // print stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash memory | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void demoFgets() { | |||
| char line[25]; | |||
| int n; | |||
| // open test file | |||
| SdFile rdfile("FGETS.TXT", O_READ); | |||
| // check for open error | |||
| if (!rdfile.isOpen()) error("demoFgets"); | |||
| cout << endl << pstr( | |||
| "Lines with '>' end with a '\\n' character\n" | |||
| "Lines with '#' do not end with a '\\n' character\n" | |||
| "\n"); | |||
| // read lines from the file | |||
| while ((n = rdfile.fgets(line, sizeof(line))) > 0) { | |||
| if (line[n - 1] == '\n') { | |||
| cout << '>' << line; | |||
| } else { | |||
| cout << '#' << line << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void makeTestFile() { | |||
| // create or open test file | |||
| SdFile wrfile("FGETS.TXT", O_WRITE | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC); | |||
| // check for open error | |||
| if (!wrfile.isOpen()) error("MakeTestFile"); | |||
| // write test file | |||
| wrfile.write_P(PSTR( | |||
| "Line with CRLF\r\n" | |||
| "Line with only LF\n" | |||
| "Long line that will require an extra read\n" | |||
| "\n" // empty line | |||
| "Line at EOF without NL" | |||
| )); | |||
| wrfile.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // Wait for Leonardo | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| makeTestFile(); | |||
| demoFgets(); | |||
| cout << pstr("\nDone\n"); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop(void) {} | |||
+ 66
- 0
SdFat/examples/formatting/formatting.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,66 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Print a table with various formatting options | |||
| * Format dates | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // create Serial stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // print a table to demonstrate format manipulators | |||
| void example(void) { | |||
| const int max = 10; | |||
| const int width = 4; | |||
| for (int row = 1; row <= max; row++) { | |||
| for (int col = 1; col <= max; col++) { | |||
| cout << setw(width) << row * col << (col == max ? '\n' : ' '); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // print a date as mm/dd/yyyy with zero fill in mm and dd | |||
| // shows how to set and restore the fill character | |||
| void showDate(int m, int d, int y) { | |||
| // convert two digit year | |||
| if (y < 100) y += 2000; | |||
| // set new fill to '0' save old fill character | |||
| char old = cout.fill('0'); | |||
| // print date | |||
| cout << setw(2) << m << '/' << setw(2) << d << '/' << y << endl; | |||
| // restore old fill character | |||
| cout.fill(old); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| delay(2000); | |||
| cout << endl << "default formatting" << endl; | |||
| example(); | |||
| cout << showpos << "showpos" << endl; | |||
| example(); | |||
| cout << hex << left << showbase << "hex left showbase" << endl; | |||
| example(); | |||
| cout << internal << setfill('0') << uppercase; | |||
| cout << "uppercase hex internal showbase fill('0')" <<endl; | |||
| example(); | |||
| // restore default format flags and fill character | |||
| cout.flags(ios::dec | ios::right | ios::skipws); | |||
| cout.fill(' '); | |||
| cout << "showDate example" <<endl; | |||
| showDate(7, 4, 11); | |||
| showDate(12, 25, 11); | |||
| } | |||
| void loop(void) {} | |||
+ 75
- 0
SdFat/examples/getline/getline.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,75 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * Example of getline from section 27.7.1.3 of the C++ standard | |||
| * Demonstrates the behavior of getline for various exceptions. | |||
| * See http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/iostream/istream/getline/ | |||
| * | |||
| * Note: This example is meant to demonstrate subtleties the standard and | |||
| * may not the best way to read a file. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system object | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // create a serial stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void makeTestFile() { | |||
| ofstream sdout("GETLINE.TXT"); | |||
| // use flash for text to save RAM | |||
| sdout << pstr( | |||
| "short line\n" | |||
| "\n" | |||
| "17 character line\n" | |||
| "too long for buffer\n" | |||
| "line with no nl"); | |||
| sdout.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void testGetline() { | |||
| const int line_buffer_size = 18; | |||
| char buffer[line_buffer_size]; | |||
| ifstream sdin("GETLINE.TXT"); | |||
| int line_number = 0; | |||
| while (sdin.getline(buffer, line_buffer_size, '\n') || sdin.gcount()) { | |||
| int count = sdin.gcount(); | |||
| if (sdin.fail()) { | |||
| cout << "Partial long line"; | |||
| sdin.clear(sdin.rdstate() & ~ios_base::failbit); | |||
| } else if (sdin.eof()) { | |||
| cout << "Partial final line"; // sdin.fail() is false | |||
| } else { | |||
| count--; // Don’t include newline in count | |||
| cout << "Line " << ++line_number; | |||
| } | |||
| cout << " (" << count << " chars): " << buffer << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup(void) { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| // pstr stores strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // make the test file | |||
| makeTestFile(); | |||
| // run the example | |||
| testGetline(); | |||
| cout << "\nDone!\n"; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void loop(void) {} | |||
+ 100
- 0
SdFat/examples/readCSV/readCSV.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,100 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This example reads a simple CSV, comma-separated values, file. | |||
| * Each line of the file has three values, a long and two floats. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system object | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // create Serial stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| char fileName[] = "TESTFILE.CSV"; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // read and print CSV test file | |||
| void readFile() { | |||
| long lg; | |||
| float f1, f2; | |||
| char text[10]; | |||
| char c1, c2, c3; // space for commas. | |||
| // open input file | |||
| ifstream sdin(fileName); | |||
| // check for open error | |||
| if (!sdin.is_open()) error("open"); | |||
| // read until input fails | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| // Get text field. | |||
| sdin.get(text, sizeof(text), ','); | |||
| // Assume EOF if fail. | |||
| if (sdin.fail()) break; | |||
| // Get commas and numbers. | |||
| sdin >> c1 >> lg >> c2 >> f1 >> c3 >> f2; | |||
| // Skip CR/LF. | |||
| sdin.skipWhite(); | |||
| if (sdin.fail()) error("bad input"); | |||
| // error in line if not commas | |||
| if (c1 != ',' || c2 != ',' || c3 != ',') error("comma"); | |||
| // print in six character wide columns | |||
| cout << text << setw(6) << lg << setw(6) << f1 << setw(6) << f2 << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| // Error in an input line if file is not at EOF. | |||
| if (!sdin.eof()) error("readFile"); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // write test file | |||
| void writeFile() { | |||
| // create or open and truncate output file | |||
| ofstream sdout(fileName); | |||
| // write file from string stored in flash | |||
| sdout << pstr( | |||
| "Line 1,1,2.3,4.5\n" | |||
| "Line 2,6,7.8,9.0\n" | |||
| "Line 3,9,8.7,6.5\n" | |||
| "Line 4,-4,-3.2,-1\n") << flush; | |||
| // check for any errors | |||
| if (!sdout) error("writeFile"); | |||
| sdout.close(); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| cout << pstr("Type any character to start\n"); | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // create test file | |||
| writeFile(); | |||
| cout << endl; | |||
| // read and print test | |||
| readFile(); | |||
| cout << "\nDone!" << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 77
- 0
SdFat/examples/rename/rename.ino
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,77 @@ | |||
| /* | |||
| * This sketch demonstrates use of SdFile::rename() | |||
| * and SdFat::rename(). | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <SdFat.h> | |||
| // SD chip select pin | |||
| const uint8_t chipSelect = SS; | |||
| // file system | |||
| SdFat sd; | |||
| // Serial print stream | |||
| ArduinoOutStream cout(Serial); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // store error strings in flash to save RAM | |||
| #define error(s) sd.errorHalt_P(PSTR(s)) | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void setup() { | |||
| Serial.begin(9600); | |||
| while (!Serial) {} // wait for Leonardo | |||
| cout << pstr("Insert an empty SD. Type any character to start.") << endl; | |||
| while (Serial.read() <= 0) {} | |||
| delay(400); // catch Due reset problem | |||
| // initialize the SD card at SPI_HALF_SPEED to avoid bus errors with | |||
| // breadboards. use SPI_FULL_SPEED for better performance. | |||
| if (!sd.begin(chipSelect, SPI_HALF_SPEED)) sd.initErrorHalt(); | |||
| // create a file and write one line to the file | |||
| SdFile file("NAME1.TXT", O_WRITE | O_CREAT); | |||
| if (!file.isOpen()) error("NAME1"); | |||
| file.println("A test line for NAME1.TXT"); | |||
| // rename the file NAME2.TXT and add a line. | |||
| // sd.vwd() is the volume working directory, root. | |||
| if (!file.rename(sd.vwd(), "NAME2.TXT")) error("NAME2"); | |||
| file.println("A test line for NAME2.TXT"); | |||
| // list files | |||
| cout << pstr("------") << endl; | |||
| sd.ls(LS_R); | |||
| // make a new directory - "DIR1" | |||
| if (!sd.mkdir("DIR1")) error("DIR1"); | |||
| // move file into DIR1, rename it NAME3.TXT and add a line | |||
| if (!file.rename(sd.vwd(), "DIR1/NAME3.TXT")) error("NAME3"); | |||
| file.println("A line for DIR1/NAME3.TXT"); | |||
| // list files | |||
| cout << pstr("------") << endl; | |||
| sd.ls(LS_R); | |||
| // make directory "DIR2" | |||
| if (!sd.mkdir("DIR2")) error("DIR2"); | |||
| // close file before rename(oldPath, newPath) | |||
| file.close(); | |||
| // move DIR1 into DIR2 and rename it DIR3 | |||
| if (!sd.rename("DIR1", "DIR2/DIR3")) error("DIR2/DIR3"); | |||
| // open file for append in new location and add a line | |||
| if (!file.open("DIR2/DIR3/NAME3.TXT", O_WRITE | O_APPEND)) { | |||
| error("DIR2/DIR3/NAME3.TXT"); | |||
| } | |||
| file.println("A line for DIR2/DIR3/NAME3.TXT"); | |||
| // list files | |||
| cout << pstr("------") << endl; | |||
| sd.ls(LS_R); | |||
| cout << pstr("Done") << endl; | |||
| } | |||
| void loop() {} | |||
+ 394
- 0
SdFat/ios.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,394 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef ios_h | |||
| #define ios_h | |||
| #include <SdBaseFile.h> | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief \ref ios_base and \ref ios classes | |||
| */ | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ios_base | |||
| * \brief Base class for all streams | |||
| */ | |||
| class ios_base { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** typedef for iostate bitmask */ | |||
| typedef unsigned char iostate; | |||
| // State flags. | |||
| /** iostate for no flags */ | |||
| static const iostate goodbit = 0x00; | |||
| /** iostate bad bit for a nonrecoverable error. */ | |||
| static const iostate badbit = 0X01; | |||
| /** iostate bit for end of file reached */ | |||
| static const iostate eofbit = 0x02; | |||
| /** iostate fail bit for nonfatal error */ | |||
| static const iostate failbit = 0X04; | |||
| /** | |||
| * unsigned size that can represent maximum file size. | |||
| * (violates spec - should be signed) | |||
| */ | |||
| typedef uint32_t streamsize; | |||
| /** type for absolute seek position */ | |||
| typedef uint32_t pos_type; | |||
| /** type for relative seek offset */ | |||
| typedef int32_t off_type; | |||
| /** enumerated type for the direction of relative seeks */ | |||
| enum seekdir { | |||
| /** seek relative to the beginning of the stream */ | |||
| beg, | |||
| /** seek relative to the current stream position */ | |||
| cur, | |||
| /** seek relative to the end of the stream */ | |||
| end | |||
| }; | |||
| /** type for format flags */ | |||
| typedef unsigned int fmtflags; | |||
| /** left adjust fields */ | |||
| static const fmtflags left = 0x0001; | |||
| /** right adjust fields */ | |||
| static const fmtflags right = 0x0002; | |||
| /** fill between sign/base prefix and number */ | |||
| static const fmtflags internal = 0x0004; | |||
| /** base 10 flag*/ | |||
| static const fmtflags dec = 0x0008; | |||
| /** base 16 flag */ | |||
| static const fmtflags hex = 0x0010; | |||
| /** base 8 flag */ | |||
| static const fmtflags oct = 0x0020; | |||
| // static const fmtflags fixed = 0x0040; | |||
| // static const fmtflags scientific = 0x0080; | |||
| /** use strings true/false for bool */ | |||
| static const fmtflags boolalpha = 0x0100; | |||
| /** use prefix 0X for hex and 0 for oct */ | |||
| static const fmtflags showbase = 0x0200; | |||
| /** always show '.' for floating numbers */ | |||
| static const fmtflags showpoint = 0x0400; | |||
| /** show + sign for nonnegative numbers */ | |||
| static const fmtflags showpos = 0x0800; | |||
| /** skip initial white space */ | |||
| static const fmtflags skipws = 0x1000; | |||
| // static const fmtflags unitbuf = 0x2000; | |||
| /** use uppercase letters in number representations */ | |||
| static const fmtflags uppercase = 0x4000; | |||
| /** mask for adjustfield */ | |||
| static const fmtflags adjustfield = left | right | internal; | |||
| /** mask for basefield */ | |||
| static const fmtflags basefield = dec | hex | oct; | |||
| // static const fmtflags floatfield = scientific | fixed; | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** typedef for iostream open mode */ | |||
| typedef uint8_t openmode; | |||
| // Openmode flags. | |||
| /** seek to end before each write */ | |||
| static const openmode app = 0X4; | |||
| /** open and seek to end immediately after opening */ | |||
| static const openmode ate = 0X8; | |||
| /** perform input and output in binary mode (as opposed to text mode) */ | |||
| static const openmode binary = 0X10; | |||
| /** open for input */ | |||
| static const openmode in = 0X20; | |||
| /** open for output */ | |||
| static const openmode out = 0X40; | |||
| /** truncate an existing stream when opening */ | |||
| static const openmode trunc = 0X80; | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| ios_base() : m_fill(' '), m_fmtflags(dec | right | skipws) | |||
| , m_precision(2), m_width(0) {} | |||
| /** \return fill character */ | |||
| char fill() {return m_fill;} | |||
| /** Set fill character | |||
| * \param[in] c new fill character | |||
| * \return old fill character | |||
| */ | |||
| char fill(char c) { | |||
| char r = m_fill; | |||
| m_fill = c; | |||
| return r; | |||
| } | |||
| /** \return format flags */ | |||
| fmtflags flags() const {return m_fmtflags;} | |||
| /** set format flags | |||
| * \param[in] fl new flag | |||
| * \return old flags | |||
| */ | |||
| fmtflags flags(fmtflags fl) { | |||
| fmtflags tmp = m_fmtflags; | |||
| m_fmtflags = fl; | |||
| return tmp; | |||
| } | |||
| /** \return precision */ | |||
| int precision() const {return m_precision;} | |||
| /** set precision | |||
| * \param[in] n new precision | |||
| * \return old precision | |||
| */ | |||
| int precision(unsigned int n) { | |||
| int r = m_precision; | |||
| m_precision = n; | |||
| return r; | |||
| } | |||
| /** set format flags | |||
| * \param[in] fl new flags to be or'ed in | |||
| * \return old flags | |||
| */ | |||
| fmtflags setf(fmtflags fl) { | |||
| fmtflags r = m_fmtflags; | |||
| m_fmtflags |= fl; | |||
| return r; | |||
| } | |||
| /** modify format flags | |||
| * \param[in] mask flags to be removed | |||
| * \param[in] fl flags to be set after mask bits have been cleared | |||
| * \return old flags | |||
| */ | |||
| fmtflags setf(fmtflags fl, fmtflags mask) { | |||
| fmtflags r = m_fmtflags; | |||
| m_fmtflags &= ~mask; | |||
| m_fmtflags |= fl; | |||
| return r; | |||
| } | |||
| /** clear format flags | |||
| * \param[in] fl flags to be cleared | |||
| * \return old flags | |||
| */ | |||
| void unsetf(fmtflags fl) { | |||
| m_fmtflags &= ~fl; | |||
| } | |||
| /** \return width */ | |||
| unsigned width() {return m_width;} | |||
| /** set width | |||
| * \param[in] n new width | |||
| * \return old width | |||
| */ | |||
| unsigned width(unsigned n) { | |||
| unsigned r = m_width; | |||
| m_width = n; | |||
| return r; | |||
| } | |||
| protected: | |||
| /** \return current number base */ | |||
| uint8_t flagsToBase() { | |||
| uint8_t f = flags() & basefield; | |||
| return f == oct ? 8 : f != hex ? 10 : 16; | |||
| } | |||
| private: | |||
| char m_fill; | |||
| fmtflags m_fmtflags; | |||
| unsigned char m_precision; | |||
| unsigned int m_width; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** function for boolalpha manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& boolalpha(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::boolalpha); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for dec manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& dec(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::dec, ios_base::basefield); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for hex manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& hex(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::hex, ios_base::basefield); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for internal manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& internal(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::internal, ios_base::adjustfield); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for left manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& left(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::left, ios_base::adjustfield); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for noboolalpha manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& noboolalpha(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.unsetf(ios_base::boolalpha); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for noshowbase manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& noshowbase(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.unsetf(ios_base::showbase); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for noshowpoint manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& noshowpoint(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.unsetf(ios_base::showpoint); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for noshowpos manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& noshowpos(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.unsetf(ios_base::showpos); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for noskipws manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& noskipws(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.unsetf(ios_base::skipws); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for nouppercase manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& nouppercase(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.unsetf(ios_base::uppercase); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for oct manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& oct(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::oct, ios_base::basefield); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for right manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& right(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::right, ios_base::adjustfield); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for showbase manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& showbase(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::showbase); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for showpos manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& showpos(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::showpos); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for showpoint manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& showpoint(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::showpoint); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for skipws manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& skipws(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::skipws); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| /** function for uppercase manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] str The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ios_base& uppercase(ios_base& str) { | |||
| str.setf(ios_base::uppercase); | |||
| return str; | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ios | |||
| * \brief Error and state information for all streams | |||
| */ | |||
| class ios : public ios_base { | |||
| public: | |||
| /** Create ios with no error flags set */ | |||
| ios() : m_iostate(0) {} | |||
| /** \return null pointer if fail() is true. */ | |||
| operator const void*() const { | |||
| return !fail() ? reinterpret_cast<const void*>(this) : 0; | |||
| } | |||
| /** \return true if fail() else false. */ | |||
| bool operator!() const {return fail();} | |||
| /** \return The iostate flags for this file. */ | |||
| iostate rdstate() const {return m_iostate;} | |||
| /** \return True if no iostate flags are set else false. */ | |||
| bool good() const {return m_iostate == goodbit;} | |||
| /** \return true if end of file has been reached else false. | |||
| * | |||
| * Warning: An empty file returns false before the first read. | |||
| * | |||
| * Moral: eof() is only useful in combination with fail(), to find out | |||
| * whether EOF was the cause for failure | |||
| */ | |||
| bool eof() const {return m_iostate & eofbit;} | |||
| /** \return true if any iostate bit other than eof are set else false. */ | |||
| bool fail() const {return m_iostate & (failbit | badbit);} | |||
| /** \return true if bad bit is set else false. */ | |||
| bool bad() const {return m_iostate & badbit;} | |||
| /** Clear iostate bits. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] state The flags you want to set after clearing all flags. | |||
| **/ | |||
| void clear(iostate state = goodbit) {m_iostate = state;} | |||
| /** Set iostate bits. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] state Bitts to set. | |||
| **/ | |||
| void setstate(iostate state) {m_iostate |= state;} | |||
| private: | |||
| iostate m_iostate; | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // ios_h | |||
+ 153
- 0
SdFat/iostream.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,153 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef iostream_h | |||
| #define iostream_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief \ref iostream class | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <istream.h> | |||
| #include <ostream.h> | |||
| /** Skip white space | |||
| * \param[in] is the Stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline istream& ws(istream& is) { | |||
| is.skipWhite(); | |||
| return is; | |||
| } | |||
| /** insert endline | |||
| * \param[in] os The Stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ostream& endl(ostream& os) { | |||
| os.put('\n'); | |||
| #if ENDL_CALLS_FLUSH | |||
| os.flush(); | |||
| #endif // ENDL_CALLS_FLUSH | |||
| return os; | |||
| } | |||
| /** flush manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] os The stream | |||
| * \return The stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ostream& flush(ostream& os) { | |||
| os.flush(); | |||
| return os; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct setfill | |||
| * \brief type for setfill manipulator | |||
| */ | |||
| struct setfill { | |||
| /** fill character */ | |||
| char c; | |||
| /** constructor | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] arg new fill character | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit setfill(char arg) : c(arg) {} | |||
| }; | |||
| /** setfill manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] os the stream | |||
| * \param[in] arg set setfill object | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ostream &operator<< (ostream &os, const setfill &arg) { | |||
| os.fill(arg.c); | |||
| return os; | |||
| } | |||
| /** setfill manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] obj the stream | |||
| * \param[in] arg set setfill object | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline istream &operator>>(istream &obj, const setfill &arg) { | |||
| obj.fill(arg.c); | |||
| return obj; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** \struct setprecision | |||
| * \brief type for setprecision manipulator | |||
| */ | |||
| struct setprecision { | |||
| /** precision */ | |||
| unsigned int p; | |||
| /** constructor | |||
| * \param[in] arg new precision | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit setprecision(unsigned int arg) : p(arg) {} | |||
| }; | |||
| /** setprecision manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] os the stream | |||
| * \param[in] arg set setprecision object | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ostream &operator<< (ostream &os, const setprecision &arg) { | |||
| os.precision(arg.p); | |||
| return os; | |||
| } | |||
| /** setprecision manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] is the stream | |||
| * \param[in] arg set setprecision object | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline istream &operator>>(istream &is, const setprecision &arg) { | |||
| is.precision(arg.p); | |||
| return is; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** \struct setw | |||
| * \brief type for setw manipulator | |||
| */ | |||
| struct setw { | |||
| /** width */ | |||
| unsigned w; | |||
| /** constructor | |||
| * \param[in] arg new width | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit setw(unsigned arg) : w(arg) {} | |||
| }; | |||
| /** setw manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] os the stream | |||
| * \param[in] arg set setw object | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline ostream &operator<< (ostream &os, const setw &arg) { | |||
| os.width(arg.w); | |||
| return os; | |||
| } | |||
| /** setw manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] is the stream | |||
| * \param[in] arg set setw object | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| inline istream &operator>>(istream &is, const setw &arg) { | |||
| is.width(arg.w); | |||
| return is; | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class iostream | |||
| * \brief Input/Output stream | |||
| */ | |||
| class iostream : public istream, public ostream { | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // iostream_h | |||
+ 411
- 0
SdFat/istream.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,411 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <float.h> | |||
| #include <istream.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character if one is available. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The character or -1 if a failure occurs. A failure is indicated | |||
| * by the stream state. | |||
| */ | |||
| int istream::get() { | |||
| int c; | |||
| m_gcount = 0; | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| if (c < 0) { | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| } else { | |||
| m_gcount = 1; | |||
| } | |||
| return c; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character if one is available. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] c location to receive the extracted character. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return always returns *this. A failure is indicated by the stream state. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& istream::get(char& c) { | |||
| int tmp = get(); | |||
| if (tmp >= 0) c = tmp; | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract characters. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] str Location to receive extracted characters. | |||
| * \param[in] n Size of str. | |||
| * \param[in] delim Delimiter | |||
| * | |||
| * Characters are extracted until extraction fails, n is less than 1, | |||
| * n-1 characters are extracted, or the next character equals | |||
| * \a delim (delim is not extracted). If no characters are extracted | |||
| * failbit is set. If end-of-file occurs the eofbit is set. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return always returns *this. A failure is indicated by the stream state. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& istream::get(char *str, streamsize n, char delim) { | |||
| int c; | |||
| FatPos_t pos; | |||
| m_gcount = 0; | |||
| while ((m_gcount + 1) < n) { | |||
| c = getch(&pos); | |||
| if (c < 0) { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (c == delim) { | |||
| setpos(&pos); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| str[m_gcount++] = c; | |||
| } | |||
| if (n > 0) str[m_gcount] = '\0'; | |||
| if (m_gcount == 0) setstate(failbit); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void istream::getBool(bool *b) { | |||
| if ((flags() & boolalpha) == 0) { | |||
| getNumber(b); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| PGM_P truePtr = PSTR("true"); | |||
| PGM_P falsePtr = PSTR("false"); | |||
| const uint8_t true_len = 4; | |||
| const uint8_t false_len = 5; | |||
| bool trueOk = true; | |||
| bool falseOk = true; | |||
| uint8_t i = 0; | |||
| int c = readSkip(); | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| falseOk = falseOk && c == pgm_read_byte(falsePtr + i); | |||
| trueOk = trueOk && c == pgm_read_byte(truePtr + i); | |||
| if (trueOk == false && falseOk == false) break; | |||
| i++; | |||
| if (trueOk && i == true_len) { | |||
| *b = true; | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| if (falseOk && i == false_len) { | |||
| *b = false; | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| } | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void istream::getChar(char* ch) { | |||
| int16_t c = readSkip(); | |||
| if (c < 0) { | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| } else { | |||
| *ch = c; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // | |||
| // http://www.exploringbinary.com/category/numbers-in-computers/ | |||
| // | |||
| int16_t const EXP_LIMIT = 100; | |||
| static const uint32_t uint32_max = (uint32_t)-1; | |||
| bool istream::getDouble(double* value) { | |||
| bool got_digit = false; | |||
| bool got_dot = false; | |||
| bool neg; | |||
| int16_t c; | |||
| bool expNeg = false; | |||
| int16_t exp = 0; | |||
| int16_t fracExp = 0; | |||
| uint32_t frac = 0; | |||
| FatPos_t endPos; | |||
| double pow10; | |||
| double v; | |||
| getpos(&endPos); | |||
| c = readSkip(); | |||
| neg = c == '-'; | |||
| if (c == '-' || c == '+') { | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| } | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| if (isdigit(c)) { | |||
| got_digit = true; | |||
| if (frac < uint32_max/10) { | |||
| frac = frac * 10 + (c - '0'); | |||
| if (got_dot) fracExp--; | |||
| } else { | |||
| if (!got_dot) fracExp++; | |||
| } | |||
| } else if (!got_dot && c == '.') { | |||
| got_dot = true; | |||
| } else { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (fracExp < -EXP_LIMIT || fracExp > EXP_LIMIT) goto fail; | |||
| c = getch(&endPos); | |||
| } | |||
| if (!got_digit) goto fail; | |||
| if (c == 'e' || c == 'E') { | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| expNeg = c == '-'; | |||
| if (c == '-' || c == '+') { | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| } | |||
| while (isdigit(c)) { | |||
| if (exp > EXP_LIMIT) goto fail; | |||
| exp = exp * 10 + (c - '0'); | |||
| c = getch(&endPos); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| v = static_cast<double>(frac); | |||
| exp = expNeg ? fracExp - exp : fracExp + exp; | |||
| expNeg = exp < 0; | |||
| if (expNeg) exp = -exp; | |||
| pow10 = 10.0; | |||
| while (exp) { | |||
| if (exp & 1) { | |||
| if (expNeg) { | |||
| // check for underflow | |||
| if (v < FLT_MIN * pow10 && frac != 0) goto fail; | |||
| v /= pow10; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // check for overflow | |||
| if (v > FLT_MAX / pow10) goto fail; | |||
| v *= pow10; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| pow10 *= pow10; | |||
| exp >>= 1; | |||
| } | |||
| setpos(&endPos); | |||
| *value = neg ? -v : v; | |||
| return true; | |||
| fail: | |||
| // error restore position to last good place | |||
| setpos(&endPos); | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract characters | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[out] str Location to receive extracted characters. | |||
| * \param[in] n Size of str. | |||
| * \param[in] delim Delimiter | |||
| * | |||
| * Characters are extracted until extraction fails, | |||
| * the next character equals \a delim (delim is extracted), or n-1 | |||
| * characters are extracted. | |||
| * | |||
| * The failbit is set if no characters are extracted or n-1 characters | |||
| * are extracted. If end-of-file occurs the eofbit is set. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return always returns *this. A failure is indicated by the stream state. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& istream::getline(char *str, streamsize n, char delim) { | |||
| FatPos_t pos; | |||
| int c; | |||
| m_gcount = 0; | |||
| if (n > 0) str[0] = '\0'; | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| c = getch(&pos); | |||
| if (c < 0) { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (c == delim) { | |||
| m_gcount++; | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if ((m_gcount + 1) >= n) { | |||
| setpos(&pos); | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| str[m_gcount++] = c; | |||
| str[m_gcount] = '\0'; | |||
| } | |||
| if (m_gcount == 0) setstate(failbit); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| bool istream::getNumber(uint32_t posMax, uint32_t negMax, uint32_t* num) { | |||
| int16_t c; | |||
| int8_t any = 0; | |||
| int8_t have_zero = 0; | |||
| uint8_t neg; | |||
| uint32_t val = 0; | |||
| uint32_t cutoff; | |||
| uint8_t cutlim; | |||
| FatPos_t endPos; | |||
| uint8_t f = flags() & basefield; | |||
| uint8_t base = f == oct ? 8 : f != hex ? 10 : 16; | |||
| getpos(&endPos); | |||
| c = readSkip(); | |||
| neg = c == '-' ? 1 : 0; | |||
| if (c == '-' || c == '+') { | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| } | |||
| if (base == 16 && c == '0') { // TESTSUITE | |||
| c = getch(&endPos); | |||
| if (c == 'X' || c == 'x') { | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| // remember zero in case no hex digits follow x/X | |||
| have_zero = 1; | |||
| } else { | |||
| any = 1; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| // set values for overflow test | |||
| cutoff = neg ? negMax : posMax; | |||
| cutlim = cutoff % base; | |||
| cutoff /= base; | |||
| while (1) { | |||
| if (isdigit(c)) { | |||
| c -= '0'; | |||
| } else if (isalpha(c)) { | |||
| c -= isupper(c) ? 'A' - 10 : 'a' - 10; | |||
| } else { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (c >= base) { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (val > cutoff || (val == cutoff && c > cutlim)) { | |||
| // indicate overflow error | |||
| any = -1; | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| val = val * base + c; | |||
| c = getch(&endPos); | |||
| any = 1; | |||
| } | |||
| setpos(&endPos); | |||
| if (any > 0 || (have_zero && any >= 0)) { | |||
| *num = neg ? -val : val; | |||
| return true; | |||
| } | |||
| setstate(failbit); | |||
| return false; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| void istream::getStr(char *str) { | |||
| FatPos_t pos; | |||
| uint16_t i = 0; | |||
| uint16_t m = width() ? width() - 1 : 0XFFFE; | |||
| if (m != 0) { | |||
| getpos(&pos); | |||
| int c = readSkip(); | |||
| while (i < m) { | |||
| if (c < 0) { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| if (isspace(c)) { | |||
| setpos(&pos); | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| str[i++] = c; | |||
| c = getch(&pos); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| str[i] = '\0'; | |||
| if (i == 0) setstate(failbit); | |||
| width(0); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract characters and discard them. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] n maximum number of characters to ignore. | |||
| * \param[in] delim Delimiter. | |||
| * | |||
| * Characters are extracted until extraction fails, \a n characters | |||
| * are extracted, or the next input character equals \a delim | |||
| * (the delimiter is extracted). If end-of-file occurs the eofbit is set. | |||
| * | |||
| * Failures are indicated by the state of the stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return *this | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& istream::ignore(streamsize n, int delim) { | |||
| int c; | |||
| m_gcount = 0; | |||
| while (m_gcount < n) { | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| if (c < 0) { | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| m_gcount++; | |||
| if (c == delim) break; | |||
| } | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * Return the next available character without consuming it. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return The character if the stream state is good else -1; | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| int istream::peek() { | |||
| int16_t c; | |||
| FatPos_t pos; | |||
| m_gcount = 0; | |||
| getpos(&pos); | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| if (c < 0) { | |||
| if (!bad()) setstate(eofbit); | |||
| } else { | |||
| setpos(&pos); | |||
| } | |||
| return c; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| int16_t istream::readSkip() { | |||
| int16_t c; | |||
| do { | |||
| c = getch(); | |||
| } while (isspace(c) && (flags() & skipws)); | |||
| return c; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** used to implement ws() */ | |||
| void istream::skipWhite() { | |||
| int c; | |||
| FatPos_t pos; | |||
| do { | |||
| c = getch(&pos); | |||
| } while (isspace(c)); | |||
| setpos(&pos); | |||
| } | |||
+ 307
- 0
SdFat/istream.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,307 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef istream_h | |||
| #define istream_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief \ref istream class | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <ios.h> | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class istream | |||
| * \brief Input Stream | |||
| */ | |||
| class istream : public virtual ios { | |||
| public: | |||
| istream() {} | |||
| /** call manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] pf function to call | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(istream& (*pf)(istream& str)) { | |||
| return pf(*this); | |||
| } | |||
| /** call manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] pf function to call | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(ios_base& (*pf)(ios_base& str)) { | |||
| pf(*this); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** call manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] pf function to call | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(ios& (*pf)(ios& str)) { | |||
| pf(*this); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character string | |||
| * \param[out] str location to store the string. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(char *str) { | |||
| getStr(str); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character | |||
| * \param[out] ch location to store the character. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(char& ch) { | |||
| getChar(&ch); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character string | |||
| * \param[out] str location to store the string. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(signed char *str) { | |||
| getStr(reinterpret_cast<char*>(str)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character | |||
| * \param[out] ch location to store the character. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(signed char& ch) { | |||
| getChar(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&ch)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character string | |||
| * \param[out] str location to store the string. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(unsigned char *str) { | |||
| getStr(reinterpret_cast<char*>(str)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a character | |||
| * \param[out] ch location to store the character. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(unsigned char& ch) { | |||
| getChar(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&ch)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type bool. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>>(bool& arg) { | |||
| getBool(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type short. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>>(short& arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| getNumber(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type unsigned short. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>>(unsigned short& arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| getNumber(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type int. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>>(int& arg) { | |||
| getNumber(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type unsigned int. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>>(unsigned int& arg) { | |||
| getNumber(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type long. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>>(long& arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| getNumber(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type unsigned long. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>>(unsigned long& arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| getNumber(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type double. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>> (double& arg) { | |||
| getDouble(&arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type float. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream &operator>> (float& arg) { | |||
| double v; | |||
| getDouble(&v); | |||
| arg = v; | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Extract a value of type void*. | |||
| * \param[out] arg location to store the value. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& operator>> (void*& arg) { | |||
| uint32_t val; | |||
| getNumber(&val); | |||
| arg = reinterpret_cast<void*>(val); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * \return The number of characters extracted by the last unformatted | |||
| * input function. | |||
| */ | |||
| streamsize gcount() const {return m_gcount;} | |||
| int get(); | |||
| istream& get(char& ch); | |||
| istream& get(char *str, streamsize n, char delim = '\n'); | |||
| istream& getline(char *str, streamsize count, char delim = '\n'); | |||
| istream& ignore(streamsize n = 1, int delim= -1); | |||
| int peek(); | |||
| // istream& read(char *str, streamsize count); | |||
| // streamsize readsome(char *str, streamsize count); | |||
| /** | |||
| * \return the stream position | |||
| */ | |||
| pos_type tellg() {return tellpos();} | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set the stream position | |||
| * \param[in] pos The absolute position in which to move the read pointer. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& seekg(pos_type pos) { | |||
| if (!seekpos(pos)) setstate(failbit); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set the stream position. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] off An offset to move the read pointer relative to way. | |||
| * \a off is a signed 32-bit int so the offset is limited to +- 2GB. | |||
| * \param[in] way One of ios::beg, ios::cur, or ios::end. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| istream& seekg(off_type off, seekdir way) { | |||
| if (!seekoff(off, way)) setstate(failbit); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| void skipWhite(); | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| /** | |||
| * Internal - do not use | |||
| * \return | |||
| */ | |||
| virtual int16_t getch() = 0; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[out] pos | |||
| * \return | |||
| */ | |||
| int16_t getch(FatPos_t* pos) { | |||
| getpos(pos); | |||
| return getch(); | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[out] pos | |||
| */ | |||
| virtual void getpos(FatPos_t* pos) = 0; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Internal - do not use | |||
| * \param[in] pos | |||
| */ | |||
| virtual bool seekoff(off_type off, seekdir way) = 0; | |||
| virtual bool seekpos(pos_type pos) = 0; | |||
| virtual void setpos(FatPos_t* pos) = 0; | |||
| virtual pos_type tellpos() = 0; | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| private: | |||
| void getBool(bool *b); | |||
| void getChar(char* ch); | |||
| bool getDouble(double* value); | |||
| template <typename T> void getNumber(T* value); | |||
| bool getNumber(uint32_t posMax, uint32_t negMax, uint32_t* num); | |||
| void getStr(char *str); | |||
| int16_t readSkip(); | |||
| size_t m_gcount; | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| template <typename T> | |||
| void istream::getNumber(T* value) { | |||
| uint32_t tmp; | |||
| if ((T)-1 < 0) { | |||
| // number is signed, max positive value | |||
| uint32_t const m = ((uint32_t)-1) >> (33 - sizeof(T) * 8); | |||
| // max absolute value of negative number is m + 1. | |||
| if (getNumber(m, m + 1, &tmp)) { | |||
| *value = (T)tmp; | |||
| } | |||
| } else { | |||
| // max unsigned value for T | |||
| uint32_t const m = (T)-1; | |||
| if (getNumber(m, m, &tmp)) { | |||
| *value = (T)tmp; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // istream_h | |||
+ 176
- 0
SdFat/ostream.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,176 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <ostream.h> | |||
| #ifndef PSTR | |||
| #define PSTR(x) x | |||
| #endif | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::do_fill(unsigned len) { | |||
| for (; len < width(); len++) putch(fill()); | |||
| width(0); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::fill_not_left(unsigned len) { | |||
| if ((flags() & adjustfield) != left) { | |||
| do_fill(len); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| char* ostream::fmtNum(uint32_t n, char *ptr, uint8_t base) { | |||
| char a = flags() & uppercase ? 'A' - 10 : 'a' - 10; | |||
| do { | |||
| uint32_t m = n; | |||
| n /= base; | |||
| char c = m - base * n; | |||
| *--ptr = c < 10 ? c + '0' : c + a; | |||
| } while (n); | |||
| return ptr; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::putBool(bool b) { | |||
| if (flags() & boolalpha) { | |||
| if (b) { | |||
| putPgm(PSTR("true")); | |||
| } else { | |||
| putPgm(PSTR("false")); | |||
| } | |||
| } else { | |||
| putChar(b ? '1' : '0'); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::putChar(char c) { | |||
| fill_not_left(1); | |||
| putch(c); | |||
| do_fill(1); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::putDouble(double n) { | |||
| uint8_t nd = precision(); | |||
| double round = 0.5; | |||
| char sign; | |||
| char buf[13]; // room for sign, 10 digits, '.', and zero byte | |||
| char *end = buf + sizeof(buf) - 1; | |||
| char *str = end; | |||
| // terminate string | |||
| *end = '\0'; | |||
| // get sign and make nonnegative | |||
| if (n < 0.0) { | |||
| sign = '-'; | |||
| n = -n; | |||
| } else { | |||
| sign = flags() & showpos ? '+' : '\0'; | |||
| } | |||
| // check for larger than uint32_t | |||
| if (n > 4.0E9) { | |||
| putPgm(PSTR("BIG FLT")); | |||
| return; | |||
| } | |||
| // round up and separate in and fraction parts | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; i < nd; ++i) round *= 0.1; | |||
| n += round; | |||
| uint32_t intPart = n; | |||
| double fractionPart = n - intPart; | |||
| // format intPart and decimal point | |||
| if (nd || (flags() & showpoint)) *--str = '.'; | |||
| str = fmtNum(intPart, str, 10); | |||
| // calculate length for fill | |||
| uint8_t len = sign ? 1 : 0; | |||
| len += nd + end - str; | |||
| // extract adjust field | |||
| fmtflags adj = flags() & adjustfield; | |||
| if (adj == internal) { | |||
| if (sign) putch(sign); | |||
| do_fill(len); | |||
| } else { | |||
| // do fill for internal or right | |||
| fill_not_left(len); | |||
| if (sign) *--str = sign; | |||
| } | |||
| putstr(str); | |||
| // output fraction | |||
| while (nd-- > 0) { | |||
| fractionPart *= 10.0; | |||
| int digit = static_cast<int>(fractionPart); | |||
| putch(digit + '0'); | |||
| fractionPart -= digit; | |||
| } | |||
| // do fill if not done above | |||
| do_fill(len); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::putNum(int32_t n) { | |||
| bool neg = n < 0 && flagsToBase() == 10; | |||
| if (neg) n = -n; | |||
| putNum(n, neg); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::putNum(uint32_t n, bool neg) { | |||
| char buf[13]; | |||
| char* end = buf + sizeof(buf) - 1; | |||
| char* num; | |||
| char* str; | |||
| uint8_t base = flagsToBase(); | |||
| *end = '\0'; | |||
| str = num = fmtNum(n, end, base); | |||
| if (base == 10) { | |||
| if (neg) { | |||
| *--str = '-'; | |||
| } else if (flags() & showpos) { | |||
| *--str = '+'; | |||
| } | |||
| } else if (flags() & showbase) { | |||
| if (flags() & hex) { | |||
| *--str = flags() & uppercase ? 'X' : 'x'; | |||
| } | |||
| *--str = '0'; | |||
| } | |||
| uint8_t len = end - str; | |||
| fmtflags adj = flags() & adjustfield; | |||
| if (adj == internal) { | |||
| while (str < num) putch(*str++); | |||
| } | |||
| if (adj != left) { | |||
| do_fill(len); | |||
| } | |||
| putstr(str); | |||
| do_fill(len); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::putPgm(const char* str) { | |||
| int n; | |||
| for (n = 0; pgm_read_byte(&str[n]); n++) {} | |||
| fill_not_left(n); | |||
| for (uint8_t c; (c = pgm_read_byte(str)); str++) { | |||
| putch(c); | |||
| } | |||
| do_fill(n); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| void ostream::putStr(const char *str) { | |||
| unsigned n = strlen(str); | |||
| fill_not_left(n); | |||
| putstr(str); | |||
| do_fill(n); | |||
| } | |||
+ 287
- 0
SdFat/ostream.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,287 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2012 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino SdFat Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino SdFat Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef ostream_h | |||
| #define ostream_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief \ref ostream class | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <ios.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** macro for flash inserter */ | |||
| #define pstr(str) pgm(PSTR(str)) | |||
| /** \struct pgm | |||
| * \brief type for string in flash | |||
| */ | |||
| struct pgm { | |||
| /** Pointer to flash string */ | |||
| char *ptr; | |||
| /** constructor | |||
| * \param[in] str initializer for pointer. | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit pgm(char* str) : ptr(str) {} | |||
| /** constructor | |||
| * \param[in] str initializer for pointer. | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit pgm(const char *str) : ptr(const_cast<char*>(str)) {} | |||
| }; | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * \class ostream | |||
| * \brief Output Stream | |||
| */ | |||
| class ostream : public virtual ios { | |||
| public: | |||
| ostream() {} | |||
| /** call manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] pf function to call | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream& operator<< (ostream& (*pf)(ostream& str)) { | |||
| return pf(*this); | |||
| } | |||
| /** call manipulator | |||
| * \param[in] pf function to call | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream& operator<< (ios_base& (*pf)(ios_base& str)) { | |||
| pf(*this); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output bool | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (bool arg) { | |||
| putBool(arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output string | |||
| * \param[in] arg string to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (const char *arg) { | |||
| putStr(arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output string | |||
| * \param[in] arg string to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (const signed char *arg) { | |||
| putStr((const char*)arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output string | |||
| * \param[in] arg string to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (const unsigned char *arg) { | |||
| putStr((const char*)arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output character | |||
| * \param[in] arg character to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (char arg) { | |||
| putChar(arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output character | |||
| * \param[in] arg character to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (signed char arg) { | |||
| putChar(static_cast<char>(arg)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output character | |||
| * \param[in] arg character to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (unsigned char arg) { | |||
| putChar(static_cast<char>(arg)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output double | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (double arg) { | |||
| putDouble(arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output float | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (float arg) { | |||
| putDouble(arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output signed short | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (short arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| putNum((int32_t)arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output unsigned short | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (unsigned short arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| putNum((uint32_t)arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output signed int | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (int arg) { | |||
| putNum((int32_t)arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output unsigned int | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (unsigned int arg) { | |||
| putNum((uint32_t)arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output signed long | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (long arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| putNum(arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output unsigned long | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (unsigned long arg) { // NOLINT | |||
| putNum(arg); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output pointer | |||
| * \param[in] arg value to output | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream& operator<< (const void* arg) { | |||
| putNum(reinterpret_cast<uint32_t>(arg)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output a string from flash using the pstr() macro | |||
| * \param[in] arg pgm struct pointing to string | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (pgm arg) { | |||
| putPgm(arg.ptr); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Output a string from flash using the Arduino F() macro. | |||
| * \param[in] arg pointing to flash string | |||
| * \return the stream | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream &operator<< (const __FlashStringHelper *arg) { | |||
| putPgm(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(arg)); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Puts a character in a stream. | |||
| * | |||
| * The unformatted output function inserts the element \a ch. | |||
| * It returns *this. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] ch The character | |||
| * \return A reference to the ostream object. | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream& put(char ch) { | |||
| putch(ch); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| // ostream& write(char *str, streamsize count); | |||
| /** | |||
| * Flushes the buffer associated with this stream. The flush function | |||
| * calls the sync function of the associated file. | |||
| * \return A reference to the ostream object. | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream& flush() { | |||
| if (!sync()) setstate(badbit); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * \return the stream position | |||
| */ | |||
| pos_type tellp() {return tellpos();} | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set the stream position | |||
| * \param[in] pos The absolute position in which to move the write pointer. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream& seekp(pos_type pos) { | |||
| if (!seekpos(pos)) setstate(failbit); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set the stream position. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] off An offset to move the write pointer relative to way. | |||
| * \a off is a signed 32-bit int so the offset is limited to +- 2GB. | |||
| * \param[in] way One of ios::beg, ios::cur, or ios::end. | |||
| * \return Is always *this. Failure is indicated by the state of *this. | |||
| */ | |||
| ostream& seekp(off_type off, seekdir way) { | |||
| if (!seekoff(off, way)) setstate(failbit); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| protected: | |||
| /// @cond SHOW_PROTECTED | |||
| /** Put character with binary/text conversion | |||
| * \param[in] ch character to write | |||
| */ | |||
| virtual void putch(char ch) = 0; | |||
| virtual void putstr(const char *str) = 0; | |||
| virtual bool seekoff(off_type pos, seekdir way) = 0; | |||
| virtual bool seekpos(pos_type pos) = 0; | |||
| virtual bool sync() = 0; | |||
| virtual pos_type tellpos() = 0; | |||
| /// @endcond | |||
| private: | |||
| void do_fill(unsigned len); | |||
| void fill_not_left(unsigned len); | |||
| char* fmtNum(uint32_t n, char *ptr, uint8_t base); | |||
| void putBool(bool b); | |||
| void putChar(char c); | |||
| void putDouble(double n); | |||
| void putNum(uint32_t n, bool neg = false); | |||
| void putNum(int32_t n); | |||
| void putPgm(const char* str); | |||
| void putStr(const char* str); | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // ostream_h | |||
+ 654
- 0
SdFat/utility/DigitalPin.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,654 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino DigitalIO Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino DigitalIO Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino DigitalIO Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| /** | |||
| * @file | |||
| * @brief Fast Digital Pin functions | |||
| * | |||
| * @defgroup digitalPin Fast Pin I/O | |||
| * @details Fast Digital I/O functions and template class. | |||
| * @{ | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef DigitalPin_h | |||
| #define DigitalPin_h | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| #ifdef __arm__ | |||
| #ifdef CORE_TEENSY | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** read pin value | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @return value read | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| bool fastDigitalRead(uint8_t pin) { | |||
| return *portInputRegister(pin); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Set pin value | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @param[in] level value to write | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void fastDigitalWrite(uint8_t pin, bool value) { | |||
| if (value) { | |||
| *portSetRegister(pin) = 1; | |||
| } else { | |||
| *portClearRegister(pin) = 1; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| #else // CORE_TEENSY | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** read pin value | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @return value read | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| bool fastDigitalRead(uint8_t pin){ | |||
| return g_APinDescription[pin].pPort->PIO_PDSR & g_APinDescription[pin].ulPin; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Set pin value | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @param[in] level value to write | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void fastDigitalWrite(uint8_t pin, bool value){ | |||
| if(value) { | |||
| g_APinDescription[pin].pPort->PIO_SODR = g_APinDescription[pin].ulPin; | |||
| } else { | |||
| g_APinDescription[pin].pPort->PIO_CODR = g_APinDescription[pin].ulPin; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // CORE_TEENSY | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| inline void fastDigitalToggle(uint8_t pin) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(pin, !fastDigitalRead(pin)); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| inline void fastPinMode(uint8_t pin, bool mode) {pinMode(pin, mode);} | |||
| #else // __arm__ | |||
| #include <avr/io.h> | |||
| #include <util/atomic.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * @class pin_map_t | |||
| * @brief struct for mapping digital pins | |||
| */ | |||
| struct pin_map_t { | |||
| volatile uint8_t* ddr; /**< address of DDR for this pin */ | |||
| volatile uint8_t* pin; /**< address of PIN for this pin */ | |||
| volatile uint8_t* port; /**< address of PORT for this pin */ | |||
| uint8_t bit; /**< bit number for this pin */ | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #if defined(__AVR_ATmega168__)\ | |||
| ||defined(__AVR_ATmega168P__)\ | |||
| ||defined(__AVR_ATmega328P__) | |||
| // 168 and 328 Arduinos | |||
| const static pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 0 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 1 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 2 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 3 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 4 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 5}, // D5 5 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6}, // D6 6 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 7 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 8 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 9 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 10 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 11 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 12 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 13 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 0}, // C0 14 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 1}, // C1 15 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 2}, // C2 16 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 3}, // C3 17 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 4}, // C4 18 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 5} // C5 19 | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #elif defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__) | |||
| // Mega | |||
| static const pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 0}, // E0 0 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 1}, // E1 1 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 4}, // E4 2 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 5}, // E5 3 | |||
| {&DDRG, &PING, &PORTG, 5}, // G5 4 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 3}, // E3 5 | |||
| {&DDRH, &PINH, &PORTH, 3}, // H3 6 | |||
| {&DDRH, &PINH, &PORTH, 4}, // H4 7 | |||
| {&DDRH, &PINH, &PORTH, 5}, // H5 8 | |||
| {&DDRH, &PINH, &PORTH, 6}, // H6 9 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 10 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 11 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 12 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 7}, // B7 13 | |||
| {&DDRJ, &PINJ, &PORTJ, 1}, // J1 14 | |||
| {&DDRJ, &PINJ, &PORTJ, 0}, // J0 15 | |||
| {&DDRH, &PINH, &PORTH, 1}, // H1 16 | |||
| {&DDRH, &PINH, &PORTH, 0}, // H0 17 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 18 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 19 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 20 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 21 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 0}, // A0 22 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 1}, // A1 23 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 2}, // A2 24 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 3}, // A3 25 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 4}, // A4 26 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 5}, // A5 27 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 6}, // A6 28 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 7}, // A7 29 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 7}, // C7 30 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 6}, // C6 31 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 5}, // C5 32 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 4}, // C4 33 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 3}, // C3 34 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 2}, // C2 35 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 1}, // C1 36 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 0}, // C0 37 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 38 | |||
| {&DDRG, &PING, &PORTG, 2}, // G2 39 | |||
| {&DDRG, &PING, &PORTG, 1}, // G1 40 | |||
| {&DDRG, &PING, &PORTG, 0}, // G0 41 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 7}, // L7 42 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 6}, // L6 43 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 5}, // L5 44 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 4}, // L4 45 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 3}, // L3 46 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 2}, // L2 47 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 1}, // L1 48 | |||
| {&DDRL, &PINL, &PORTL, 0}, // L0 49 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 50 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 51 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 52 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 53 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 0}, // F0 54 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 1}, // F1 55 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 2}, // F2 56 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 3}, // F3 57 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 4}, // F4 58 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 5}, // F5 59 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 6}, // F6 60 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 7}, // F7 61 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 0}, // K0 62 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 1}, // K1 63 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 2}, // K2 64 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 3}, // K3 65 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 4}, // K4 66 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 5}, // K5 67 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 6}, // K6 68 | |||
| {&DDRK, &PINK, &PORTK, 7} // K7 69 | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #elif defined(__AVR_ATmega1284P__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega1284__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega644P__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega644__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega64__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega32__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega324__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_ATmega16__) | |||
| #ifdef defined(VARIANT_MIGHTY) | |||
| // Mighty Layout | |||
| static const pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 0 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 1 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 2 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 3 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 4 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 5 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 6 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 7}, // B7 7 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 8 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 9 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 10 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 11 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 12 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 5}, // D5 13 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6}, // D6 14 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 15 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 0}, // C0 16 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 1}, // C1 17 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 2}, // C2 18 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 3}, // C3 19 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 4}, // C4 20 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 5}, // C5 21 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 6}, // C6 22 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 7}, // C7 23 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 0}, // A0 24 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 1}, // A1 25 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 2}, // A2 26 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 3}, // A3 27 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 4}, // A4 28 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 5}, // A5 29 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 6}, // A6 30 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 7} // A7 31 | |||
| }; | |||
| #elif defined(VARIANT_BOBUINO) | |||
| // Bobuino Layout | |||
| static const pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 0 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 1 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 2 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 3 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 4 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 5 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 6 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 7 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 5}, // D5 8 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6}, // D6 9 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 10 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 11 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 12 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 7}, // B7 13 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 7}, // A7 14 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 6}, // A6 15 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 5}, // A5 16 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 4}, // A4 17 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 3}, // A3 18 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 2}, // A2 19 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 1}, // A1 20 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 0}, // A0 21 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 0}, // C0 22 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 1}, // C1 23 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 2}, // C2 24 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 3}, // C3 25 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 4}, // C4 26 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 5}, // C5 27 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 6}, // C6 28 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 7}, // C7 29 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 30 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7} // D7 31 | |||
| }; | |||
| #elif defined(VARIANT_STANDARD) | |||
| // Standard Layout | |||
| static const pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 0 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 1 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 2 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 3 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 4 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 5 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 6 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 7}, // B7 7 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 8 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 9 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 10 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 11 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 12 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 5}, // D5 13 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6}, // D6 14 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 15 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 0}, // C0 16 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 1}, // C1 17 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 2}, // C2 18 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 3}, // C3 19 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 4}, // C4 20 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 5}, // C5 21 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 6}, // C6 22 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 7}, // C7 23 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 7}, // A7 24 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 6}, // A6 25 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 5}, // A5 26 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 4}, // A4 27 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 3}, // A3 28 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 2}, // A2 29 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 1}, // A1 30 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 0} // A0 31 | |||
| }; | |||
| #else // VARIANT_MIGHTY | |||
| #error Undefined variant 1284, 644, 324, 64, 32 | |||
| #endif // VARIANT_MIGHTY | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #elif defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) | |||
| #ifdef CORE_TEENSY | |||
| // Teensy 2.0 | |||
| static const pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 0 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 1 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 2 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 3 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 7}, // B7 4 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 5 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 6 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 7 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 8 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 6}, // C6 9 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 7}, // C7 10 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6}, // D6 11 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 12 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 13 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 14 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 15 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 7}, // F7 16 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 6}, // F6 17 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 5}, // F5 18 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 4}, // F4 19 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 1}, // F1 20 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 0}, // F0 21 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 22 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 5}, // D5 23 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 6} // E6 24 | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #else // CORE_TEENSY | |||
| // Leonardo | |||
| static const pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 0 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 1 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 2 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 3 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 4 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 6}, // C6 5 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 6 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 6}, // E6 7 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 8 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 9 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 10 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 7}, // B7 11 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6}, // D6 12 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 7}, // C7 13 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 14 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 15 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 16 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 17 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 7}, // F7 18 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 6}, // F6 19 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 5}, // F5 20 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 4}, // F4 21 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 1}, // F1 22 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 0}, // F0 23 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 24 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 25 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 26 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 27 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 28 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6} // D6 29 | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // CORE_TEENSY | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #elif defined(__AVR_AT90USB646__)\ | |||
| || defined(__AVR_AT90USB1286__) | |||
| // Teensy++ 1.0 & 2.0 | |||
| static const pin_map_t pinMap[] = { | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 0}, // D0 0 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 1}, // D1 1 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 2}, // D2 2 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 3}, // D3 3 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 4}, // D4 4 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 5}, // D5 5 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 6}, // D6 6 | |||
| {&DDRD, &PIND, &PORTD, 7}, // D7 7 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 0}, // E0 8 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 1}, // E1 9 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 0}, // C0 10 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 1}, // C1 11 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 2}, // C2 12 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 3}, // C3 13 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 4}, // C4 14 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 5}, // C5 15 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 6}, // C6 16 | |||
| {&DDRC, &PINC, &PORTC, 7}, // C7 17 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 6}, // E6 18 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 7}, // E7 19 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 0}, // B0 20 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 1}, // B1 21 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 2}, // B2 22 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 3}, // B3 23 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 4}, // B4 24 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 5}, // B5 25 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 6}, // B6 26 | |||
| {&DDRB, &PINB, &PORTB, 7}, // B7 27 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 0}, // A0 28 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 1}, // A1 29 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 2}, // A2 30 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 3}, // A3 31 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 4}, // A4 32 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 5}, // A5 33 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 6}, // A6 34 | |||
| {&DDRA, &PINA, &PORTA, 7}, // A7 35 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 4}, // E4 36 | |||
| {&DDRE, &PINE, &PORTE, 5}, // E5 37 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 0}, // F0 38 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 1}, // F1 39 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 2}, // F2 40 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 3}, // F3 41 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 4}, // F4 42 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 5}, // F5 43 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 6}, // F6 44 | |||
| {&DDRF, &PINF, &PORTF, 7} // F7 45 | |||
| }; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| #else // CPU type | |||
| #error unknown CPU type | |||
| #endif // CPU type | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** count of pins */ | |||
| static const uint8_t digitalPinCount = sizeof(pinMap)/sizeof(pin_map_t); | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** generate bad pin number error */ | |||
| void badPinNumber(void) | |||
| __attribute__((error("Pin number is too large or not a constant"))); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Check for valid pin number | |||
| * @param[in] pin Number of pin to be checked. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void badPinCheck(uint8_t pin) { | |||
| if (!__builtin_constant_p(pin) || pin >= digitalPinCount) { | |||
| badPinNumber(); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** fast write helper | |||
| * @param[in] address I/O register address | |||
| * @param[in] bit bit number to write | |||
| * @param[in] level value for bit | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void fastBitWriteSafe(volatile uint8_t* address, uint8_t bit, bool level) { | |||
| uint8_t oldSREG; | |||
| if (address > (uint8_t*)0X5F) { | |||
| oldSREG = SREG; | |||
| cli(); | |||
| } | |||
| if (level) { | |||
| *address |= 1 << bit; | |||
| } else { | |||
| *address &= ~(1 << bit); | |||
| } | |||
| if (address > (uint8_t*)0X5F) { | |||
| SREG = oldSREG; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** read pin value | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @return value read | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| bool fastDigitalRead(uint8_t pin) { | |||
| badPinCheck(pin); | |||
| return (*pinMap[pin].pin >> pinMap[pin].bit) & 1; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** toggle a pin | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * | |||
| * If the pin is in output mode toggle the pin level. | |||
| * If the pin is in input mode toggle the state of the 20K pullup. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void fastDigitalToggle(uint8_t pin) { | |||
| badPinCheck(pin); | |||
| if (pinMap[pin].pin > (uint8_t*)0X5F) { | |||
| // must write bit to high address port | |||
| *pinMap[pin].pin = 1 << pinMap[pin].bit; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // will compile to sbi and PIN register will not be read. | |||
| *pinMap[pin].pin |= 1 << pinMap[pin].bit; | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Set pin value | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @param[in] level value to write | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void fastDigitalWrite(uint8_t pin, bool level) { | |||
| badPinCheck(pin); | |||
| fastBitWriteSafe(pinMap[pin].port, pinMap[pin].bit, level); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** set pin mode | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @param[in] mode if true set output mode else input mode | |||
| * | |||
| * fastPinMode does not enable or disable the 20K pullup for input mode. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void fastPinMode(uint8_t pin, bool mode) { | |||
| badPinCheck(pin); | |||
| fastBitWriteSafe(pinMap[pin].ddr, pinMap[pin].bit, mode); | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // __arm__ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** set pin configuration | |||
| * @param[in] pin Arduino pin number | |||
| * @param[in] mode If true set output mode else input mode | |||
| * @param[in] level If mode is output, set level high/low. | |||
| * If mode is input, enable or disable the pin's 20K pullup. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void fastPinConfig(uint8_t pin, bool mode, bool level) { | |||
| fastPinMode(pin, mode); | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(pin, level); | |||
| } | |||
| //============================================================================== | |||
| /** | |||
| * @class DigitalPin | |||
| * @brief Fast digital port I/O | |||
| */ | |||
| template<uint8_t PinNumber> | |||
| class DigitalPin { | |||
| public: | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Constructor */ | |||
| DigitalPin() {} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Constructor | |||
| * @param[in] pinMode if true set output mode else input mode. | |||
| */ | |||
| explicit DigitalPin(bool pinMode) { | |||
| mode(pinMode); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Constructor | |||
| * @param[in] mode If true set output mode else input mode | |||
| * @param[in] level If mode is output, set level high/low. | |||
| * If mode is input, enable or disable the pin's 20K pullup. | |||
| */ | |||
| DigitalPin(bool mode, bool level) { | |||
| config(mode, level); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Asignment operator | |||
| * @param[in] value If true set the pin's level high else set the | |||
| * pin's level low. | |||
| * | |||
| * @return This DigitalPin instance. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline DigitalPin & operator = (bool value) __attribute__((always_inline)) { | |||
| write(value); | |||
| return *this; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Parenthesis operator | |||
| * @return Pin's level | |||
| */ | |||
| inline operator bool () const __attribute__((always_inline)) { | |||
| return read(); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** set pin configuration | |||
| * @param[in] mode If true set output mode else input mode | |||
| * @param[in] level If mode is output, set level high/low. | |||
| * If mode is input, enable or disable the pin's 20K pullup. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void config(bool mode, bool level) { | |||
| fastPinConfig(PinNumber, mode, level); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set pin level high if output mode or enable 20K pullup if input mode. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void high() {write(true);} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set pin level low if output mode or disable 20K pullup if input mode. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void low() {write(false);} | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** | |||
| * Set pin mode | |||
| * @param[in] pinMode if true set output mode else input mode. | |||
| * | |||
| * mode() does not enable or disable the 20K pullup for input mode. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void mode(bool pinMode) { | |||
| fastPinMode(PinNumber, pinMode); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** @return Pin's level */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| bool read() const { | |||
| return fastDigitalRead(PinNumber); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** toggle a pin | |||
| * | |||
| * If the pin is in output mode toggle the pin's level. | |||
| * If the pin is in input mode toggle the state of the 20K pullup. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void toggle() { | |||
| fastDigitalToggle(PinNumber); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Write the pin's level. | |||
| * @param[in] value If true set the pin's level high else set the | |||
| * pin's level low. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void write(bool value) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(PinNumber, value); | |||
| } | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // DigitalPin_h | |||
| /** @} */ | |||
+ 65
- 0
SdFat/utility/FatApiConstants.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ | |||
| /* FatLib Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the FatLib Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the FatLib Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef FatApiConstants_h | |||
| #define FatApiConstants_h | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // use the gnu style oflag in open() | |||
| /** open() oflag for reading */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_READ = 0X01; | |||
| /** open() oflag - same as O_IN */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_RDONLY = O_READ; | |||
| /** open() oflag for write */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_WRITE = 0X02; | |||
| /** open() oflag - same as O_WRITE */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_WRONLY = O_WRITE; | |||
| /** open() oflag for reading and writing */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_RDWR = (O_READ | O_WRITE); | |||
| /** open() oflag mask for access modes */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_ACCMODE = (O_READ | O_WRITE); | |||
| /** The file offset shall be set to the end of the file prior to each write. */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_APPEND = 0X04; | |||
| /** synchronous writes - call sync() after each write */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_SYNC = 0X08; | |||
| /** truncate the file to zero length */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_TRUNC = 0X10; | |||
| /** set the initial position at the end of the file */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_AT_END = 0X20; | |||
| /** create the file if nonexistent */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_CREAT = 0X40; | |||
| /** If O_CREAT and O_EXCL are set, open() shall fail if the file exists */ | |||
| uint8_t const O_EXCL = 0X80; | |||
| // SdBaseFile class static and const definitions | |||
| // flags for ls() | |||
| /** ls() flag to print modify date */ | |||
| uint8_t const LS_DATE = 1; | |||
| /** ls() flag to print file size */ | |||
| uint8_t const LS_SIZE = 2; | |||
| /** ls() flag for recursive list of subdirectories */ | |||
| uint8_t const LS_R = 4; | |||
| // flags for timestamp | |||
| /** set the file's last access date */ | |||
| uint8_t const T_ACCESS = 1; | |||
| /** set the file's creation date and time */ | |||
| uint8_t const T_CREATE = 2; | |||
| /** Set the file's write date and time */ | |||
| uint8_t const T_WRITE = 4; | |||
| #endif // FatApiConstants_h | |||
+ 678
- 0
SdFat/utility/FatStructs.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,678 @@ | |||
| /* FatLib Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the FatLib Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the FatLib Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef FatStructs_h | |||
| #define FatStructs_h | |||
| /** | |||
| * \file | |||
| * \brief FAT file structures | |||
| */ | |||
| /* | |||
| * mostly from Microsoft document fatgen103.doc | |||
| * http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/system/platform/firmware/fatgen.mspx | |||
| */ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Value for byte 510 of boot block or MBR */ | |||
| uint8_t const BOOTSIG0 = 0X55; | |||
| /** Value for byte 511 of boot block or MBR */ | |||
| uint8_t const BOOTSIG1 = 0XAA; | |||
| /** Value for bootSignature field int FAT/FAT32 boot sector */ | |||
| uint8_t const EXTENDED_BOOT_SIG = 0X29; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct partitionTable | |||
| * \brief MBR partition table entry | |||
| * | |||
| * A partition table entry for a MBR formatted storage device. | |||
| * The MBR partition table has four entries. | |||
| */ | |||
| struct partitionTable { | |||
| /** | |||
| * Boot Indicator . Indicates whether the volume is the active | |||
| * partition. Legal values include: 0X00. Do not use for booting. | |||
| * 0X80 Active partition. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t boot; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Head part of Cylinder-head-sector address of the first block in | |||
| * the partition. Legal values are 0-255. Only used in old PC BIOS. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t beginHead; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Sector part of Cylinder-head-sector address of the first block in | |||
| * the partition. Legal values are 1-63. Only used in old PC BIOS. | |||
| */ | |||
| unsigned beginSector : 6; | |||
| /** High bits cylinder for first block in partition. */ | |||
| unsigned beginCylinderHigh : 2; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Combine beginCylinderLow with beginCylinderHigh. Legal values | |||
| * are 0-1023. Only used in old PC BIOS. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t beginCylinderLow; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Partition type. See defines that begin with PART_TYPE_ for | |||
| * some Microsoft partition types. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t type; | |||
| /** | |||
| * head part of cylinder-head-sector address of the last sector in the | |||
| * partition. Legal values are 0-255. Only used in old PC BIOS. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t endHead; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Sector part of cylinder-head-sector address of the last sector in | |||
| * the partition. Legal values are 1-63. Only used in old PC BIOS. | |||
| */ | |||
| unsigned endSector : 6; | |||
| /** High bits of end cylinder */ | |||
| unsigned endCylinderHigh : 2; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Combine endCylinderLow with endCylinderHigh. Legal values | |||
| * are 0-1023. Only used in old PC BIOS. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t endCylinderLow; | |||
| /** Logical block address of the first block in the partition. */ | |||
| uint32_t firstSector; | |||
| /** Length of the partition, in blocks. */ | |||
| uint32_t totalSectors; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)); | |||
| /** Type name for partitionTable */ | |||
| typedef struct partitionTable part_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct masterBootRecord | |||
| * | |||
| * \brief Master Boot Record | |||
| * | |||
| * The first block of a storage device that is formatted with a MBR. | |||
| */ | |||
| struct masterBootRecord { | |||
| /** Code Area for master boot program. */ | |||
| uint8_t codeArea[440]; | |||
| /** Optional Windows NT disk signature. May contain boot code. */ | |||
| uint32_t diskSignature; | |||
| /** Usually zero but may be more boot code. */ | |||
| uint16_t usuallyZero; | |||
| /** Partition tables. */ | |||
| part_t part[4]; | |||
| /** First MBR signature byte. Must be 0X55 */ | |||
| uint8_t mbrSig0; | |||
| /** Second MBR signature byte. Must be 0XAA */ | |||
| uint8_t mbrSig1; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)); | |||
| /** Type name for masterBootRecord */ | |||
| typedef struct masterBootRecord mbr_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct fat_boot | |||
| * | |||
| * \brief Boot sector for a FAT12/FAT16 volume. | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| struct fat_boot { | |||
| /** | |||
| * The first three bytes of the boot sector must be valid, | |||
| * executable x 86-based CPU instructions. This includes a | |||
| * jump instruction that skips the next non-executable bytes. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t jump[3]; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This is typically a string of characters that identifies | |||
| * the operating system that formatted the volume. | |||
| */ | |||
| char oemId[8]; | |||
| /** | |||
| * The size of a hardware sector. Valid decimal values for this | |||
| * field are 512, 1024, 2048, and 4096. For most disks used in | |||
| * the United States, the value of this field is 512. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t bytesPerSector; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Number of sectors per allocation unit. This value must be a | |||
| * power of 2 that is greater than 0. The legal values are | |||
| * 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128. 128 should be avoided. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| /** | |||
| * The number of sectors preceding the start of the first FAT, | |||
| * including the boot sector. The value of this field is always 1. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t reservedSectorCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * The number of copies of the FAT on the volume. | |||
| * The value of this field is always 2. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t fatCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * For FAT12 and FAT16 volumes, this field contains the count of | |||
| * 32-byte directory entries in the root directory. For FAT32 volumes, | |||
| * this field must be set to 0. For FAT12 and FAT16 volumes, this | |||
| * value should always specify a count that when multiplied by 32 | |||
| * results in a multiple of bytesPerSector. FAT16 volumes should | |||
| * use the value 512. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t rootDirEntryCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This field is the old 16-bit total count of sectors on the volume. | |||
| * This count includes the count of all sectors in all four regions | |||
| * of the volume. This field can be 0; if it is 0, then totalSectors32 | |||
| * must be non-zero. For FAT32 volumes, this field must be 0. For | |||
| * FAT12 and FAT16 volumes, this field contains the sector count, and | |||
| * totalSectors32 is 0 if the total sector count fits | |||
| * (is less than 0x10000). | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t totalSectors16; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This dates back to the old MS-DOS 1.x media determination and is | |||
| * no longer usually used for anything. 0xF8 is the standard value | |||
| * for fixed (nonremovable) media. For removable media, 0xF0 is | |||
| * frequently used. Legal values are 0xF0 or 0xF8-0xFF. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t mediaType; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Count of sectors occupied by one FAT on FAT12/FAT16 volumes. | |||
| * On FAT32 volumes this field must be 0, and sectorsPerFat32 | |||
| * contains the FAT size count. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t sectorsPerFat16; | |||
| /** Sectors per track for interrupt 0x13. Not used otherwise. */ | |||
| uint16_t sectorsPerTrack; | |||
| /** Number of heads for interrupt 0x13. Not used otherwise. */ | |||
| uint16_t headCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Count of hidden sectors preceding the partition that contains this | |||
| * FAT volume. This field is generally only relevant for media | |||
| * visible on interrupt 0x13. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t hidddenSectors; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This field is the new 32-bit total count of sectors on the volume. | |||
| * This count includes the count of all sectors in all four regions | |||
| * of the volume. This field can be 0; if it is 0, then | |||
| * totalSectors16 must be non-zero. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t totalSectors32; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Related to the BIOS physical drive number. Floppy drives are | |||
| * identified as 0x00 and physical hard disks are identified as | |||
| * 0x80, regardless of the number of physical disk drives. | |||
| * Typically, this value is set prior to issuing an INT 13h BIOS | |||
| * call to specify the device to access. The value is only | |||
| * relevant if the device is a boot device. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t driveNumber; | |||
| /** used by Windows NT - should be zero for FAT */ | |||
| uint8_t reserved1; | |||
| /** 0X29 if next three fields are valid */ | |||
| uint8_t bootSignature; | |||
| /** | |||
| * A random serial number created when formatting a disk, | |||
| * which helps to distinguish between disks. | |||
| * Usually generated by combining date and time. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t volumeSerialNumber; | |||
| /** | |||
| * A field once used to store the volume label. The volume label | |||
| * is now stored as a special file in the root directory. | |||
| */ | |||
| char volumeLabel[11]; | |||
| /** | |||
| * A field with a value of either FAT, FAT12 or FAT16, | |||
| * depending on the disk format. | |||
| */ | |||
| char fileSystemType[8]; | |||
| /** X86 boot code */ | |||
| uint8_t bootCode[448]; | |||
| /** must be 0X55 */ | |||
| uint8_t bootSectorSig0; | |||
| /** must be 0XAA */ | |||
| uint8_t bootSectorSig1; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)); | |||
| /** Type name for FAT Boot Sector */ | |||
| typedef struct fat_boot fat_boot_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct fat32_boot | |||
| * | |||
| * \brief Boot sector for a FAT32 volume. | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| struct fat32_boot { | |||
| /** | |||
| * The first three bytes of the boot sector must be valid, | |||
| * executable x 86-based CPU instructions. This includes a | |||
| * jump instruction that skips the next non-executable bytes. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t jump[3]; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This is typically a string of characters that identifies | |||
| * the operating system that formatted the volume. | |||
| */ | |||
| char oemId[8]; | |||
| /** | |||
| * The size of a hardware sector. Valid decimal values for this | |||
| * field are 512, 1024, 2048, and 4096. For most disks used in | |||
| * the United States, the value of this field is 512. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t bytesPerSector; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Number of sectors per allocation unit. This value must be a | |||
| * power of 2 that is greater than 0. The legal values are | |||
| * 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128. 128 should be avoided. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t sectorsPerCluster; | |||
| /** | |||
| * The number of sectors preceding the start of the first FAT, | |||
| * including the boot sector. Must not be zero | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t reservedSectorCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * The number of copies of the FAT on the volume. | |||
| * The value of this field is always 2. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t fatCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * FAT12/FAT16 only. For FAT32 volumes, this field must be set to 0. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t rootDirEntryCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * For FAT32 volumes, this field must be 0. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t totalSectors16; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This dates back to the old MS-DOS 1.x media determination and is | |||
| * no longer usually used for anything. 0xF8 is the standard value | |||
| * for fixed (non-removable) media. For removable media, 0xF0 is | |||
| * frequently used. Legal values are 0xF0 or 0xF8-0xFF. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t mediaType; | |||
| /** | |||
| * On FAT32 volumes this field must be 0, and sectorsPerFat32 | |||
| * contains the FAT size count. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t sectorsPerFat16; | |||
| /** Sectors per track for interrupt 0x13. Not used otherwise. */ | |||
| uint16_t sectorsPerTrack; | |||
| /** Number of heads for interrupt 0x13. Not used otherwise. */ | |||
| uint16_t headCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Count of hidden sectors preceding the partition that contains this | |||
| * FAT volume. This field is generally only relevant for media | |||
| * visible on interrupt 0x13. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t hidddenSectors; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Contains the total number of sectors in the FAT32 volume. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t totalSectors32; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Count of sectors occupied by one FAT on FAT32 volumes. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t sectorsPerFat32; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This field is only defined for FAT32 media and does not exist on | |||
| * FAT12 and FAT16 media. | |||
| * Bits 0-3 -- Zero-based number of active FAT. | |||
| * Only valid if mirroring is disabled. | |||
| * Bits 4-6 -- Reserved. | |||
| * Bit 7 -- 0 means the FAT is mirrored at runtime into all FATs. | |||
| * -- 1 means only one FAT is active; it is the one referenced | |||
| * in bits 0-3. | |||
| * Bits 8-15 -- Reserved. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t fat32Flags; | |||
| /** | |||
| * FAT32 version. High byte is major revision number. | |||
| * Low byte is minor revision number. Only 0.0 define. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t fat32Version; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Cluster number of the first cluster of the root directory for FAT32. | |||
| * This usually 2 but not required to be 2. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t fat32RootCluster; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Sector number of FSINFO structure in the reserved area of the | |||
| * FAT32 volume. Usually 1. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t fat32FSInfo; | |||
| /** | |||
| * If non-zero, indicates the sector number in the reserved area | |||
| * of the volume of a copy of the boot record. Usually 6. | |||
| * No value other than 6 is recommended. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t fat32BackBootBlock; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Reserved for future expansion. Code that formats FAT32 volumes | |||
| * should always set all of the bytes of this field to 0. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t fat32Reserved[12]; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Related to the BIOS physical drive number. Floppy drives are | |||
| * identified as 0x00 and physical hard disks are identified as | |||
| * 0x80, regardless of the number of physical disk drives. | |||
| * Typically, this value is set prior to issuing an INT 13h BIOS | |||
| * call to specify the device to access. The value is only | |||
| * relevant if the device is a boot device. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t driveNumber; | |||
| /** used by Windows NT - should be zero for FAT */ | |||
| uint8_t reserved1; | |||
| /** 0X29 if next three fields are valid */ | |||
| uint8_t bootSignature; | |||
| /** | |||
| * A random serial number created when formatting a disk, | |||
| * which helps to distinguish between disks. | |||
| * Usually generated by combining date and time. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t volumeSerialNumber; | |||
| /** | |||
| * A field once used to store the volume label. The volume label | |||
| * is now stored as a special file in the root directory. | |||
| */ | |||
| char volumeLabel[11]; | |||
| /** | |||
| * A text field with a value of FAT32. | |||
| */ | |||
| char fileSystemType[8]; | |||
| /** X86 boot code */ | |||
| uint8_t bootCode[420]; | |||
| /** must be 0X55 */ | |||
| uint8_t bootSectorSig0; | |||
| /** must be 0XAA */ | |||
| uint8_t bootSectorSig1; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)); | |||
| /** Type name for FAT32 Boot Sector */ | |||
| typedef struct fat32_boot fat32_boot_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Lead signature for a FSINFO sector */ | |||
| uint32_t const FSINFO_LEAD_SIG = 0x41615252; | |||
| /** Struct signature for a FSINFO sector */ | |||
| uint32_t const FSINFO_STRUCT_SIG = 0x61417272; | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct fat32_fsinfo | |||
| * | |||
| * \brief FSINFO sector for a FAT32 volume. | |||
| * | |||
| */ | |||
| struct fat32_fsinfo { | |||
| /** must be 0X52, 0X52, 0X61, 0X41 */ | |||
| uint32_t leadSignature; | |||
| /** must be zero */ | |||
| uint8_t reserved1[480]; | |||
| /** must be 0X72, 0X72, 0X41, 0X61 */ | |||
| uint32_t structSignature; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Contains the last known free cluster count on the volume. | |||
| * If the value is 0xFFFFFFFF, then the free count is unknown | |||
| * and must be computed. Any other value can be used, but is | |||
| * not necessarily correct. It should be range checked at least | |||
| * to make sure it is <= volume cluster count. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t freeCount; | |||
| /** | |||
| * This is a hint for the FAT driver. It indicates the cluster | |||
| * number at which the driver should start looking for free clusters. | |||
| * If the value is 0xFFFFFFFF, then there is no hint and the driver | |||
| * should start looking at cluster 2. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint32_t nextFree; | |||
| /** must be zero */ | |||
| uint8_t reserved2[12]; | |||
| /** must be 0X00, 0X00, 0X55, 0XAA */ | |||
| uint8_t tailSignature[4]; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)); | |||
| /** Type name for FAT32 FSINFO Sector */ | |||
| typedef struct fat32_fsinfo fat32_fsinfo_t; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // End Of Chain values for FAT entries | |||
| /** FAT12 end of chain value used by Microsoft. */ | |||
| uint16_t const FAT12EOC = 0XFFF; | |||
| /** Minimum value for FAT12 EOC. Use to test for EOC. */ | |||
| uint16_t const FAT12EOC_MIN = 0XFF8; | |||
| /** FAT16 end of chain value used by Microsoft. */ | |||
| uint16_t const FAT16EOC = 0XFFFF; | |||
| /** Minimum value for FAT16 EOC. Use to test for EOC. */ | |||
| uint16_t const FAT16EOC_MIN = 0XFFF8; | |||
| /** FAT32 end of chain value used by Microsoft. */ | |||
| uint32_t const FAT32EOC = 0X0FFFFFFF; | |||
| /** Minimum value for FAT32 EOC. Use to test for EOC. */ | |||
| uint32_t const FAT32EOC_MIN = 0X0FFFFFF8; | |||
| /** Mask a for FAT32 entry. Entries are 28 bits. */ | |||
| uint32_t const FAT32MASK = 0X0FFFFFFF; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * \struct directoryEntry | |||
| * \brief FAT short directory entry | |||
| * | |||
| * Short means short 8.3 name, not the entry size. | |||
| * | |||
| * Date Format. A FAT directory entry date stamp is a 16-bit field that is | |||
| * basically a date relative to the MS-DOS epoch of 01/01/1980. Here is the | |||
| * format (bit 0 is the LSB of the 16-bit word, bit 15 is the MSB of the | |||
| * 16-bit word): | |||
| * | |||
| * Bits 9-15: Count of years from 1980, valid value range 0-127 | |||
| * inclusive (1980-2107). | |||
| * | |||
| * Bits 5-8: Month of year, 1 = January, valid value range 1-12 inclusive. | |||
| * | |||
| * Bits 0-4: Day of month, valid value range 1-31 inclusive. | |||
| * | |||
| * Time Format. A FAT directory entry time stamp is a 16-bit field that has | |||
| * a granularity of 2 seconds. Here is the format (bit 0 is the LSB of the | |||
| * 16-bit word, bit 15 is the MSB of the 16-bit word). | |||
| * | |||
| * Bits 11-15: Hours, valid value range 0-23 inclusive. | |||
| * | |||
| * Bits 5-10: Minutes, valid value range 0-59 inclusive. | |||
| * | |||
| * Bits 0-4: 2-second count, valid value range 0-29 inclusive (0 - 58 seconds). | |||
| * | |||
| * The valid time range is from Midnight 00:00:00 to 23:59:58. | |||
| */ | |||
| struct directoryEntry { | |||
| /** Short 8.3 name. | |||
| * | |||
| * The first eight bytes contain the file name with blank fill. | |||
| * The last three bytes contain the file extension with blank fill. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t name[11]; | |||
| /** Entry attributes. | |||
| * | |||
| * The upper two bits of the attribute byte are reserved and should | |||
| * always be set to 0 when a file is created and never modified or | |||
| * looked at after that. See defines that begin with DIR_ATT_. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t attributes; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Reserved for use by Windows NT. Set value to 0 when a file is | |||
| * created and never modify or look at it after that. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t reservedNT; | |||
| /** | |||
| * The granularity of the seconds part of creationTime is 2 seconds | |||
| * so this field is a count of tenths of a second and its valid | |||
| * value range is 0-199 inclusive. (WHG note - seems to be hundredths) | |||
| */ | |||
| uint8_t creationTimeTenths; | |||
| /** Time file was created. */ | |||
| uint16_t creationTime; | |||
| /** Date file was created. */ | |||
| uint16_t creationDate; | |||
| /** | |||
| * Last access date. Note that there is no last access time, only | |||
| * a date. This is the date of last read or write. In the case of | |||
| * a write, this should be set to the same date as lastWriteDate. | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t lastAccessDate; | |||
| /** | |||
| * High word of this entry's first cluster number (always 0 for a | |||
| * FAT12 or FAT16 volume). | |||
| */ | |||
| uint16_t firstClusterHigh; | |||
| /** Time of last write. File creation is considered a write. */ | |||
| uint16_t lastWriteTime; | |||
| /** Date of last write. File creation is considered a write. */ | |||
| uint16_t lastWriteDate; | |||
| /** Low word of this entry's first cluster number. */ | |||
| uint16_t firstClusterLow; | |||
| /** 32-bit unsigned holding this file's size in bytes. */ | |||
| uint32_t fileSize; | |||
| }__attribute__((packed)); | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Definitions for directory entries | |||
| // | |||
| /** Type name for directoryEntry */ | |||
| typedef struct directoryEntry dir_t; | |||
| /** escape for name[0] = 0XE5 */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_NAME_0XE5 = 0X05; | |||
| /** name[0] value for entry that is free after being "deleted" */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_NAME_DELETED = 0XE5; | |||
| /** name[0] value for entry that is free and no allocated entries follow */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_NAME_FREE = 0X00; | |||
| /** file is read-only */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_READ_ONLY = 0X01; | |||
| /** File should hidden in directory listings */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_HIDDEN = 0X02; | |||
| /** Entry is for a system file */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_SYSTEM = 0X04; | |||
| /** Directory entry contains the volume label */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_VOLUME_ID = 0X08; | |||
| /** Entry is for a directory */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_DIRECTORY = 0X10; | |||
| /** Old DOS archive bit for backup support */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_ARCHIVE = 0X20; | |||
| /** Test value for long name entry. Test is | |||
| (d->attributes & DIR_ATT_LONG_NAME_MASK) == DIR_ATT_LONG_NAME. */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_LONG_NAME = 0X0F; | |||
| /** Test mask for long name entry */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_LONG_NAME_MASK = 0X3F; | |||
| /** defined attribute bits */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_DEFINED_BITS = 0X3F; | |||
| /** Directory entry is part of a long name | |||
| * \param[in] dir Pointer to a directory entry. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true if the entry is for part of a long name else false. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t DIR_IS_LONG_NAME(const dir_t* dir) { | |||
| return (dir->attributes & DIR_ATT_LONG_NAME_MASK) == DIR_ATT_LONG_NAME; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Mask for file/subdirectory tests */ | |||
| uint8_t const DIR_ATT_FILE_TYPE_MASK = (DIR_ATT_VOLUME_ID | DIR_ATT_DIRECTORY); | |||
| /** Directory entry is for a file | |||
| * \param[in] dir Pointer to a directory entry. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true if the entry is for a normal file else false. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t DIR_IS_FILE(const dir_t* dir) { | |||
| return (dir->attributes & DIR_ATT_FILE_TYPE_MASK) == 0; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Directory entry is for a subdirectory | |||
| * \param[in] dir Pointer to a directory entry. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true if the entry is for a subdirectory else false. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t DIR_IS_SUBDIR(const dir_t* dir) { | |||
| return (dir->attributes & DIR_ATT_FILE_TYPE_MASK) == DIR_ATT_DIRECTORY; | |||
| } | |||
| /** Directory entry is for a file or subdirectory | |||
| * \param[in] dir Pointer to a directory entry. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return true if the entry is for a normal file or subdirectory else false. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t DIR_IS_FILE_OR_SUBDIR(const dir_t* dir) { | |||
| return (dir->attributes & DIR_ATT_VOLUME_ID) == 0; | |||
| } | |||
| /** date field for FAT directory entry | |||
| * \param[in] year [1980,2107] | |||
| * \param[in] month [1,12] | |||
| * \param[in] day [1,31] | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Packed date for dir_t entry. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint16_t FAT_DATE(uint16_t year, uint8_t month, uint8_t day) { | |||
| return (year - 1980) << 9 | month << 5 | day; | |||
| } | |||
| /** year part of FAT directory date field | |||
| * \param[in] fatDate Date in packed dir format. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Extracted year [1980,2107] | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint16_t FAT_YEAR(uint16_t fatDate) { | |||
| return 1980 + (fatDate >> 9); | |||
| } | |||
| /** month part of FAT directory date field | |||
| * \param[in] fatDate Date in packed dir format. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Extracted month [1,12] | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t FAT_MONTH(uint16_t fatDate) { | |||
| return (fatDate >> 5) & 0XF; | |||
| } | |||
| /** day part of FAT directory date field | |||
| * \param[in] fatDate Date in packed dir format. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Extracted day [1,31] | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t FAT_DAY(uint16_t fatDate) { | |||
| return fatDate & 0X1F; | |||
| } | |||
| /** time field for FAT directory entry | |||
| * \param[in] hour [0,23] | |||
| * \param[in] minute [0,59] | |||
| * \param[in] second [0,59] | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Packed time for dir_t entry. | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint16_t FAT_TIME(uint8_t hour, uint8_t minute, uint8_t second) { | |||
| return hour << 11 | minute << 5 | second >> 1; | |||
| } | |||
| /** hour part of FAT directory time field | |||
| * \param[in] fatTime Time in packed dir format. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Extracted hour [0,23] | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t FAT_HOUR(uint16_t fatTime) { | |||
| return fatTime >> 11; | |||
| } | |||
| /** minute part of FAT directory time field | |||
| * \param[in] fatTime Time in packed dir format. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Extracted minute [0,59] | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t FAT_MINUTE(uint16_t fatTime) { | |||
| return(fatTime >> 5) & 0X3F; | |||
| } | |||
| /** second part of FAT directory time field | |||
| * Note second/2 is stored in packed time. | |||
| * | |||
| * \param[in] fatTime Time in packed dir format. | |||
| * | |||
| * \return Extracted second [0,58] | |||
| */ | |||
| static inline uint8_t FAT_SECOND(uint16_t fatTime) { | |||
| return 2*(fatTime & 0X1F); | |||
| } | |||
| /** Default date for file timestamps is 1 Jan 2000 */ | |||
| uint16_t const FAT_DEFAULT_DATE = ((2000 - 1980) << 9) | (1 << 5) | 1; | |||
| /** Default time for file timestamp is 1 am */ | |||
| uint16_t const FAT_DEFAULT_TIME = (1 << 11); | |||
| #endif // FatStructs_h | |||
+ 405
- 0
SdFat/utility/FmtNumber.cpp
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,405 @@ | |||
| /* FatLib Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the FatLib Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the FatLib Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #include <avr/pgmspace.h> | |||
| #include <FmtNumber.h> | |||
| // Use Stimmer div/mod 10 on avr | |||
| #ifdef __AVR__ | |||
| #define USE_STIMMER | |||
| #endif // __AVR__ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Stimmer div/mod 10 for AVR | |||
| // this code fragment works out i/10 and i%10 by calculating | |||
| // i*(51/256)*(256/255)/2 == i*51/510 == i/10 | |||
| // by "j.k" I mean 32.8 fixed point, j is integer part, k is fractional part | |||
| // j.k = ((j+1.0)*51.0)/256.0 | |||
| // (we add 1 because we will be using the floor of the result later) | |||
| // divmod10_asm16 and divmod10_asm32 are public domain code by Stimmer. | |||
| // http://forum.arduino.cc/index.php?topic=167414.msg1293679#msg1293679 | |||
| #define divmod10_asm16(in32, mod8, tmp8) \ | |||
| asm volatile( \ | |||
| " ldi %2,51 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %A0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr %A0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add r0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %A0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mov %1,r0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %B0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr %B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %A0,r0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %B0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %1,%A0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %A0,%B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %B0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %1,%B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %A0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %B0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " lsr %B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ror %A0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ror %1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ldi %2,10 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %1,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mov %1,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| :"+r"(in32), "=d"(mod8), "=d"(tmp8) : : "r0") | |||
| #define divmod10_asm32(in32, mod8, tmp8) \ | |||
| asm volatile( \ | |||
| " ldi %2,51 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %A0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr %A0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add r0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %A0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mov %1,r0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %B0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr %B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %A0,r0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %B0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %C0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr %C0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %B0,r0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %C0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %D0,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr %D0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %C0,r0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %D0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %1,%A0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %A0,%B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %B0,%C0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %C0,%D0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %D0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %1,%B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %A0,%C0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %B0,%D0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %C0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %D0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " add %1,%D0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %A0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %B0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %C0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " adc %D0,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " lsr %D0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ror %C0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ror %B0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ror %A0 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ror %1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " ldi %2,10 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mul %1,%2 \n\t" \ | |||
| " mov %1,r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| " clr r1 \n\t" \ | |||
| :"+r"(in32), "=d"(mod8), "=d"(tmp8) : : "r0") | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /* | |||
| // C++ code is based on this version of divmod10 by robtillaart. | |||
| // http://forum.arduino.cc/index.php?topic=167414.msg1246851#msg1246851 | |||
| // from robtillaart post: | |||
| // The code is based upon the divu10() code from the book Hackers Delight1. | |||
| // My insight was that the error formula in divu10() was in fact modulo 10 | |||
| // but not always. Sometimes it was 10 more. | |||
| void divmod10(uint32_t in, uint32_t &div, uint32_t &mod) | |||
| { | |||
| // q = in * 0.8; | |||
| uint32_t q = (in >> 1) + (in >> 2); | |||
| q = q + (q >> 4); | |||
| q = q + (q >> 8); | |||
| q = q + (q >> 16); // not needed for 16 bit version | |||
| // q = q / 8; ==> q = in *0.1; | |||
| q = q >> 3; | |||
| // determine error | |||
| uint32_t r = in - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = in - q*10; | |||
| div = q + (r > 9); | |||
| if (r > 9) mod = r - 10; | |||
| else mod = r; | |||
| } | |||
| // Hackers delight function is here: | |||
| // http://www.hackersdelight.org/hdcodetxt/divuc.c.txt | |||
| // Code below uses 8/10 = 0.1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100 1100. | |||
| // 15 ops including the multiply, or 17 elementary ops. | |||
| unsigned divu10(unsigned n) { | |||
| unsigned q, r; | |||
| q = (n >> 1) + (n >> 2); | |||
| q = q + (q >> 4); | |||
| q = q + (q >> 8); | |||
| q = q + (q >> 16); | |||
| q = q >> 3; | |||
| r = n - q*10; | |||
| return q + ((r + 6) >> 4); | |||
| // return q + (r > 9); | |||
| } | |||
| */ | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| static const float m[] PROGMEM = {1e-1, 1e-2, 1e-4, 1e-8, 1e-16, 1e-32}; | |||
| static const float p[] PROGMEM = {1e+1, 1e+2, 1e+4, 1e+8, 1e+16, 1e+32}; | |||
| // scale float v by power of ten. return v*10^n | |||
| float scale10(float v, int8_t n) { | |||
| const float *s; | |||
| if (n < 0) { | |||
| n = -n; | |||
| s = m; | |||
| } else { | |||
| s = p; | |||
| } | |||
| n &= 63; | |||
| for (uint8_t i = 0; n; n >>= 1, i++) { | |||
| if (n & 1) v *= pgm_read_float(&s[i]); | |||
| } | |||
| return v; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // Format 16-bit unsigned | |||
| char* fmtDec(uint16_t n, char* p) { | |||
| while (n > 9) { | |||
| #ifdef USE_STIMMER | |||
| uint8_t tmp8, r; | |||
| divmod10_asm16(n, r, tmp8); | |||
| #else // USE_STIMMER | |||
| uint16_t t = n; | |||
| n = (n >> 1) + (n >> 2); | |||
| n = n + (n >> 4); | |||
| n = n + (n >> 8); | |||
| // n = n + (n >> 16); // no code for 16-bit n | |||
| n = n >> 3; | |||
| uint8_t r = t - (((n << 2) + n) << 1); | |||
| if (r > 9) { | |||
| n++; | |||
| r -= 10; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_STIMMER | |||
| *--p = r + '0'; | |||
| } | |||
| *--p = n + '0'; | |||
| return p; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| // format 32-bit unsigned | |||
| char* fmtDec(uint32_t n, char* p) { | |||
| while (n >> 16) { | |||
| #ifdef USE_STIMMER | |||
| uint8_t tmp8, r; | |||
| divmod10_asm32(n, r, tmp8); | |||
| #else // USE_STIMMER | |||
| uint32_t t = n; | |||
| n = (n >> 1) + (n >> 2); | |||
| n = n + (n >> 4); | |||
| n = n + (n >> 8); | |||
| n = n + (n >> 16); | |||
| n = n >> 3; | |||
| uint8_t r = t - (((n << 2) + n) << 1); | |||
| if (r > 9) { | |||
| n++; | |||
| r -= 10; | |||
| } | |||
| #endif // USE_STIMMER | |||
| *--p = r + '0'; | |||
| } | |||
| return fmtDec((uint16_t)n, p); | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| char* fmtFloat(float value, char* p, uint8_t prec) { | |||
| char sign = value < 0 ? '-' : 0; | |||
| if (sign) value = -value; | |||
| if (isnan(value)) { | |||
| *--p = 'n'; | |||
| *--p = 'a'; | |||
| *--p = 'n'; | |||
| return p; | |||
| } | |||
| if (isinf(value)) { | |||
| *--p = 'f'; | |||
| *--p = 'n'; | |||
| *--p = 'i'; | |||
| return p; | |||
| } | |||
| if (value > 4294967040.0) { | |||
| *--p = 'f'; | |||
| *--p = 'v'; | |||
| *--p = 'o'; | |||
| return p; | |||
| } | |||
| if (prec > 9) prec = 9; | |||
| value += scale10(0.5, -prec); | |||
| uint32_t whole = value; | |||
| if (prec) { | |||
| char* tmp = p - prec; | |||
| uint32_t fraction = scale10(value - whole, prec); | |||
| p = fmtDec(fraction, p); | |||
| while (p > tmp) *--p = '0'; | |||
| *--p = '.'; | |||
| } | |||
| p = fmtDec(whole, p); | |||
| if (sign) *--p = sign; | |||
| return p; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Print a number followed by a field terminator. | |||
| * \param[in] value The number to be printed. | |||
| * \param[in] ptr Pointer to last char in buffer. | |||
| * \param[in] prec Number of digits after decimal point. | |||
| * \param[in] expChar Use exp format if non zero. | |||
| * \return Pointer to first character of result. | |||
| */ | |||
| char* fmtFloat(float value, char* ptr, uint8_t prec, char expChar) { | |||
| bool neg = value < 0; | |||
| if (neg) value = -value; | |||
| // check for nan inf ovf | |||
| if (isnan(value)) { | |||
| *--ptr = 'n'; | |||
| *--ptr = 'a'; | |||
| *--ptr = 'n'; | |||
| return ptr; | |||
| } | |||
| if (isinf(value)) { | |||
| *--ptr = 'f'; | |||
| *--ptr = 'n'; | |||
| *--ptr = 'i'; | |||
| return ptr; | |||
| } | |||
| if (!expChar && value > 4294967040.0) { | |||
| *--ptr = 'f'; | |||
| *--ptr = 'v'; | |||
| *--ptr = 'o'; | |||
| return ptr; | |||
| } | |||
| if (prec > 9) prec = 9; | |||
| float round = scale10(0.5, -prec); | |||
| if (expChar) { | |||
| int8_t exp = 0; | |||
| bool expNeg = false; | |||
| if (value) { | |||
| while (value > 10.0) { | |||
| value *= 0.1; | |||
| exp++; | |||
| } | |||
| while (value < 1.0) { | |||
| value *= 10.0; | |||
| exp--; | |||
| } | |||
| value += round; | |||
| if (value > 10.0) { | |||
| value *= 0.1; | |||
| exp++; | |||
| } | |||
| expNeg = exp < 0; | |||
| if (expNeg) exp = -exp; | |||
| } | |||
| ptr = fmtDec((uint16_t)exp, ptr); | |||
| if (exp < 10) *--ptr = '0'; | |||
| *--ptr = expNeg ? '-' : '+'; | |||
| *--ptr = expChar; | |||
| } else { | |||
| // round value | |||
| value += round; | |||
| } | |||
| uint32_t whole = value; | |||
| if (prec) { | |||
| char* tmp = ptr - prec; | |||
| uint32_t fraction = scale10(value - whole, prec); | |||
| ptr = fmtDec(fraction, ptr); | |||
| while (ptr > tmp) *--ptr = '0'; | |||
| *--ptr = '.'; | |||
| } | |||
| ptr = fmtDec(whole, ptr); | |||
| if (neg) *--ptr = '-'; | |||
| return ptr; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| char* fmtHex(uint32_t n, char* p) { | |||
| do { | |||
| uint8_t h = n & 0XF; | |||
| *--p = h + (h < 10 ? '0' : 'A' - 10); | |||
| n >>= 4; | |||
| } while (n); | |||
| return p; | |||
| } | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| float scanFloat(const char* str, char** ptr) { | |||
| int16_t const EXP_LIMIT = 100; | |||
| bool digit = false; | |||
| bool dot = false; | |||
| uint32_t fract = 0; | |||
| int fracExp = 0; | |||
| uint8_t nd = 0; | |||
| bool neg; | |||
| int c; | |||
| float v; | |||
| const char* successPtr; | |||
| if (ptr) *ptr = const_cast<char*>(str); | |||
| while (isspace((c = *str++))) {} | |||
| neg = c == '-'; | |||
| if (c == '-' || c == '+') c = *str++; | |||
| // Skip leading zeros | |||
| while (c == '0') { | |||
| c = *str++; | |||
| digit = true; | |||
| } | |||
| for (;;) { | |||
| if (isdigit(c)) { | |||
| digit = true; | |||
| if (nd < 9) { | |||
| fract = 10*fract + c - '0'; | |||
| nd++; | |||
| if (dot) fracExp--; | |||
| } else { | |||
| if (!dot) fracExp++; | |||
| } | |||
| } else if (c == '.') { | |||
| if (dot) goto fail; | |||
| dot = true; | |||
| } else { | |||
| if (!digit) goto fail; | |||
| break; | |||
| } | |||
| successPtr = str; | |||
| c = *str++; | |||
| } | |||
| if (c == 'e' || c == 'E') { | |||
| int exp = 0; | |||
| c = *str++; | |||
| bool expNeg = c == '-'; | |||
| if (c == '-' || c == '+') { | |||
| c = *str++; | |||
| } | |||
| while (isdigit(c)) { | |||
| if (exp > EXP_LIMIT) goto fail; | |||
| exp = 10*exp + c - '0'; | |||
| successPtr = str; | |||
| c = *str++; | |||
| } | |||
| fracExp += expNeg ? -exp : exp; | |||
| } | |||
| if (ptr) *ptr = const_cast<char*>(successPtr); | |||
| v = scale10(static_cast<float>(fract), fracExp); | |||
| return neg ? -v: v; | |||
| fail: | |||
| return 0; | |||
| } | |||
+ 30
- 0
SdFat/utility/FmtNumber.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ | |||
| /* FatLib Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the FatLib Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the FatLib Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef FmtNumber_h | |||
| #define FmtNumber_h | |||
| #include <Arduino.h> | |||
| char* fmtDec(uint16_t n, char* p); | |||
| char* fmtDec(uint32_t n, char* p); | |||
| char* fmtFloat(float value, char* p, uint8_t prec); | |||
| char* fmtFloat(float value, char* ptr, uint8_t prec, char expChar); | |||
| char* fmtHex(uint32_t n, char* p); | |||
| float scale10(float v, int8_t n); | |||
| float scanFloat(const char* str, char** ptr); | |||
| #endif // FmtNumber_h | |||
+ 162
- 0
SdFat/utility/SoftSPI.h
Переглянути файл
| @@ -0,0 +1,162 @@ | |||
| /* Arduino DigitalIO Library | |||
| * Copyright (C) 2013 by William Greiman | |||
| * | |||
| * This file is part of the Arduino DigitalIO Library | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify | |||
| * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by | |||
| * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or | |||
| * (at your option) any later version. | |||
| * | |||
| * This Library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, | |||
| * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of | |||
| * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the | |||
| * GNU General Public License for more details. | |||
| * | |||
| * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License | |||
| * along with the Arduino DigitalIO Library. If not, see | |||
| * <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. | |||
| */ | |||
| /** | |||
| * @file | |||
| * @brief Software SPI. | |||
| * | |||
| * @defgroup softSPI Software SPI | |||
| * @details Software SPI Template Class. | |||
| * @{ | |||
| */ | |||
| #ifndef SoftSPI_h | |||
| #define SoftSPI_h | |||
| #include <DigitalPin.h> | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Nop for timing. */ | |||
| #define nop asm volatile ("nop\n\t") | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** Pin Mode for MISO is input.*/ | |||
| const bool MISO_MODE = false; | |||
| /** Pullups disabled for MISO are disabled. */ | |||
| const bool MISO_LEVEL = false; | |||
| /** Pin Mode for MOSI is output.*/ | |||
| const bool MOSI_MODE = true; | |||
| /** Pin Mode for SCK is output. */ | |||
| const bool SCK_MODE = true; | |||
| //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |||
| /** | |||
| * @class SoftSPI | |||
| * @brief Fast software SPI. | |||
| */ | |||
| template<uint8_t MisoPin, uint8_t MosiPin, uint8_t SckPin, uint8_t Mode = 0> | |||
| class SoftSPI { | |||
| public: | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Initialize SoftSPI pins. */ | |||
| void begin() { | |||
| fastPinConfig(MisoPin, MISO_MODE, MISO_LEVEL); | |||
| fastPinConfig(MosiPin, MOSI_MODE, !MODE_CPHA(Mode)); | |||
| fastPinConfig(SckPin, SCK_MODE, MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Soft SPI receive byte. | |||
| * @return Data byte received. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| uint8_t receive() { | |||
| uint8_t data = 0; | |||
| receiveBit(7, &data); | |||
| receiveBit(6, &data); | |||
| receiveBit(5, &data); | |||
| receiveBit(4, &data); | |||
| receiveBit(3, &data); | |||
| receiveBit(2, &data); | |||
| receiveBit(1, &data); | |||
| receiveBit(0, &data); | |||
| return data; | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Soft SPI send byte. | |||
| * @param[in] data Data byte to send. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void send(uint8_t data) { | |||
| sendBit(7, data); | |||
| sendBit(6, data); | |||
| sendBit(5, data); | |||
| sendBit(4, data); | |||
| sendBit(3, data); | |||
| sendBit(2, data); | |||
| sendBit(1, data); | |||
| sendBit(0, data); | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| /** Soft SPI transfer byte. | |||
| * @param[in] txData Data byte to send. | |||
| * @return Data byte received. | |||
| */ | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| uint8_t transfer(uint8_t txData) { | |||
| uint8_t rxData = 0; | |||
| transferBit(7, &rxData, txData); | |||
| transferBit(6, &rxData, txData); | |||
| transferBit(5, &rxData, txData); | |||
| transferBit(4, &rxData, txData); | |||
| transferBit(3, &rxData, txData); | |||
| transferBit(2, &rxData, txData); | |||
| transferBit(1, &rxData, txData); | |||
| transferBit(0, &rxData, txData); | |||
| return rxData; | |||
| } | |||
| private: | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| bool MODE_CPHA(uint8_t mode) {return (mode & 1) != 0;} | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| bool MODE_CPOL(uint8_t mode) {return (mode & 2) != 0;} | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void receiveBit(uint8_t bit, uint8_t* data) { | |||
| if (MODE_CPHA(Mode)) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, !MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| } | |||
| nop; | |||
| nop; | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, | |||
| MODE_CPHA(Mode) ? MODE_CPOL(Mode) : !MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| if (fastDigitalRead(MisoPin)) *data |= 1 << bit; | |||
| if (!MODE_CPHA(Mode)) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void sendBit(uint8_t bit, uint8_t data) { | |||
| if (MODE_CPHA(Mode)) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, !MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| } | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(MosiPin, data & (1 << bit)); | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, | |||
| MODE_CPHA(Mode) ? MODE_CPOL(Mode) : !MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| nop; | |||
| nop; | |||
| if (!MODE_CPHA(Mode)) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| inline __attribute__((always_inline)) | |||
| void transferBit(uint8_t bit, uint8_t* rxData, uint8_t txData) { | |||
| if (MODE_CPHA(Mode)) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, !MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| } | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(MosiPin, txData & (1 << bit)); | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, | |||
| MODE_CPHA(Mode) ? MODE_CPOL(Mode) : !MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| if (fastDigitalRead(MisoPin)) *rxData |= 1 << bit; | |||
| if (!MODE_CPHA(Mode)) { | |||
| fastDigitalWrite(SckPin, MODE_CPOL(Mode)); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
| }; | |||
| #endif // SoftSPI_h | |||
| /** @} */ | |||
+ 0
- 0
SdFatTestSuite/SdFatTestSuite.cpp
Переглянути файл
Деякі файли не було показано, через те що забагато файлів було змінено
Завантаження…